
An individual's behavior in an organization may be governed by a code of ethics.
Ethics is linked to morality and establishes what is good , bad, permitted or desired regarding an action or decision. The concept comes from the Greek ethikos , which means "character."
Ethics can be defined as the science of moral behavior, since it studies and determines how the members of a society should act.
A code , for its part, is a combination of signs that has a certain value within an established system . In law , the set of rules that regulate a specific matter is known as a code.
What is a code of ethics
A code of ethics , therefore, sets standards that regulate the behaviors of people within a company or organization . Although ethics is not coercive (it does not impose legal punishments), the code of ethics is an internal regulation that must be complied with.
Not disclosing confidential information, not discriminating against clients or co-workers based on race, nationality or religion and not accepting bribes, for example, are some of the postulates that are usually included in codes of ethics.
The standards mentioned in codes of ethics may be linked to legal standards (for example, discrimination is a crime punishable by law). The main objective of these codes is to maintain a uniform line of behavior among all members of a company. By including written instructions, it is not necessary for a manager to explain at every moment what obligations an employee has.
On the other hand, those people who write the code of ethics are in a hierarchical position over the rest, since they are in a position to stipulate what are the correct behaviors from a moral point of view.
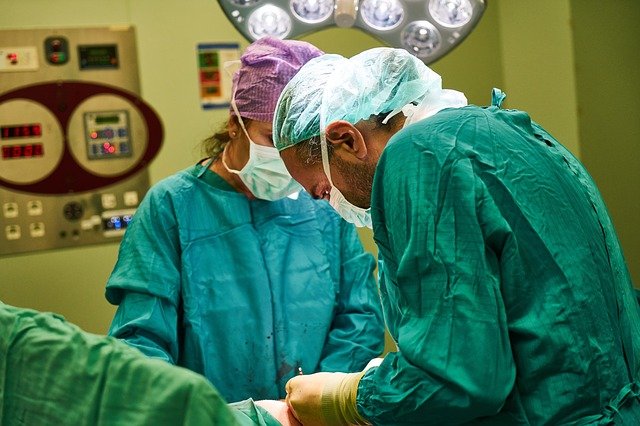
The code of ethics is very important in medicine.
The concept in medicine
As we have already expressed, the obligation of every professional is to demonstrate impeccable conduct where ethics is their main objective. As it is a social service, it must be based on wanting good for the community in which it operates.
The first to express a series of rules that should be followed when carrying out any social task was Hippocrates , when medicine did not yet exist as such. It was he who set the ethical guidelines that would later become fundamental for the practice of medicine anywhere on the planet. In any case, it was not until 1979 that the ethical and moral principles that every professional should manifest were described within the medical circle. This treatise was called Ballantine's and was published in 1979.
In the medical career there are a series of subjects whose importance is to instill in future doctors ideas of the common good and, above all, a critical and balanced spirit, to always know how to act in pursuit of the common good and the quality of life of their patients. . In this training, the criteria they need to make the best decisions are instilled in the individual, within the scope of their profession.
A doctor without ethics will be a professional who will put money and fame before the good of the patients and this will represent a moral disorder in the actions of the individual and a serious risk for the community he assists.
Unfortunately, throughout history, medicine has derailed from its primary purpose: helping people improve their quality of life and has become an instrument of manipulation for various ideologies; This has led many people to disbelieve in medicine and it has become a legal business. Despite this, it is important to point out the importance of recovering the true meaning that this science had in its origins .
