The energy transition requires innovation in energy.
The energy transition is the process carried out to modify the way of generation, distribution and consumption of energy with the aim of reducing the greenhouse effect . This change is promoted based on the acceptance of human interference in climate change .
In this sense, it should be mentioned that activities carried out using fossil fuels produce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions . That is why the energy transition aims to minimize the use of these fuels, replacing them with renewable energy or nuclear energy.
History of the energy transition
The history of the energy transition, in the broadest sense of the concept, is initially associated with the availability of resources .
In pre-industrial times, humans turned to water, wind, biomass , animals or their own power as a source of energy . These were elements that, in general, he had within his reach.
With the development of the industry, there was an energy transition towards resources that allowed mechanization of tasks. Wood, coal, peat, steam and whale oil were among the most used products before the massive transition to fossil fuels, especially oil and its derivatives.
Advantages and disadvantages of fossil fuels
Fossil fuels come from biomass that originated a long time ago and, after being buried, was transformed due to the increase in temperature and pressure, generating oil , natural gas or coal .
The main advantage that fossil fuels offer is that they are used to obtain concentrated energy. This characteristic led to the technological development associated with the Industrial Revolution that modified daily life through multiple machines powered by these fuels. It should be considered that most electricity is generated by transforming fossil fuels.
Although these fuels favored great progress, the environmental impact of their extraction and use is notorious. On the one hand, the extraction of natural resources is finite: oil, natural gas and coal will sooner or later run out since they cannot be regenerated to meet demand.
On the other hand, environmental claims are aimed at air pollution . Combustion produces carbon dioxide (CO2) when it is complete and carbon monoxide (CO) when it is incomplete. CO2 , methane (CH4) and other gases are identified as responsible for the greenhouse effect, since by accumulating in the atmosphere they prevent the sun's rays that bounce off the Earth's surface from returning to outer space.
The greenhouse effect , therefore, causes an increase in the earth's temperature. Because the emission of these gases is caused by human activity, global warming is understood to be anthropogenic .

Green electricity, obtained from renewable energy sources, is key to the energy transition.
The importance of the energy transition
Climate change related to global warming threatens biodiversity , increases ocean temperatures, melts glaciers and increases sea level. It also contributes to desertification , accentuates the intensity of meteorological phenomena and has social effects (causing migrations, for example).
Faced with these negative consequences, global society recognized the importance of reducing the use of fossil fuels and developing an energy transition. Instruments emerging from international climate negotiations such as the Paris Agreement and the Kyoto Protocol laid the foundations and established guidelines for the process.
In the case of the Paris Agreement , the governments of a large number of countries committed to working to keep global warming below a 2ºC increase in temperature compared to pre-industrial levels. Previously, the Kyoto Protocol had already established a commitment that the industrialized powers assumed to reduce their CO2 emissions and the rest of the greenhouse gases .
The energy transition requires divesting from fossil fuels and promoting the adoption of solar energy , wind energy and nuclear energy . With this change in energy policy, sustainable development can be achieved with a lower carbon footprint.
Decarbonization can be incentivized with environmental legislation , green energy subsidies, and taxes on carbon emissions, among other measures. It must be taken into account that, to achieve the energy transition, work must be done on numerous aspects. These include energy efficiency and energy conservation.
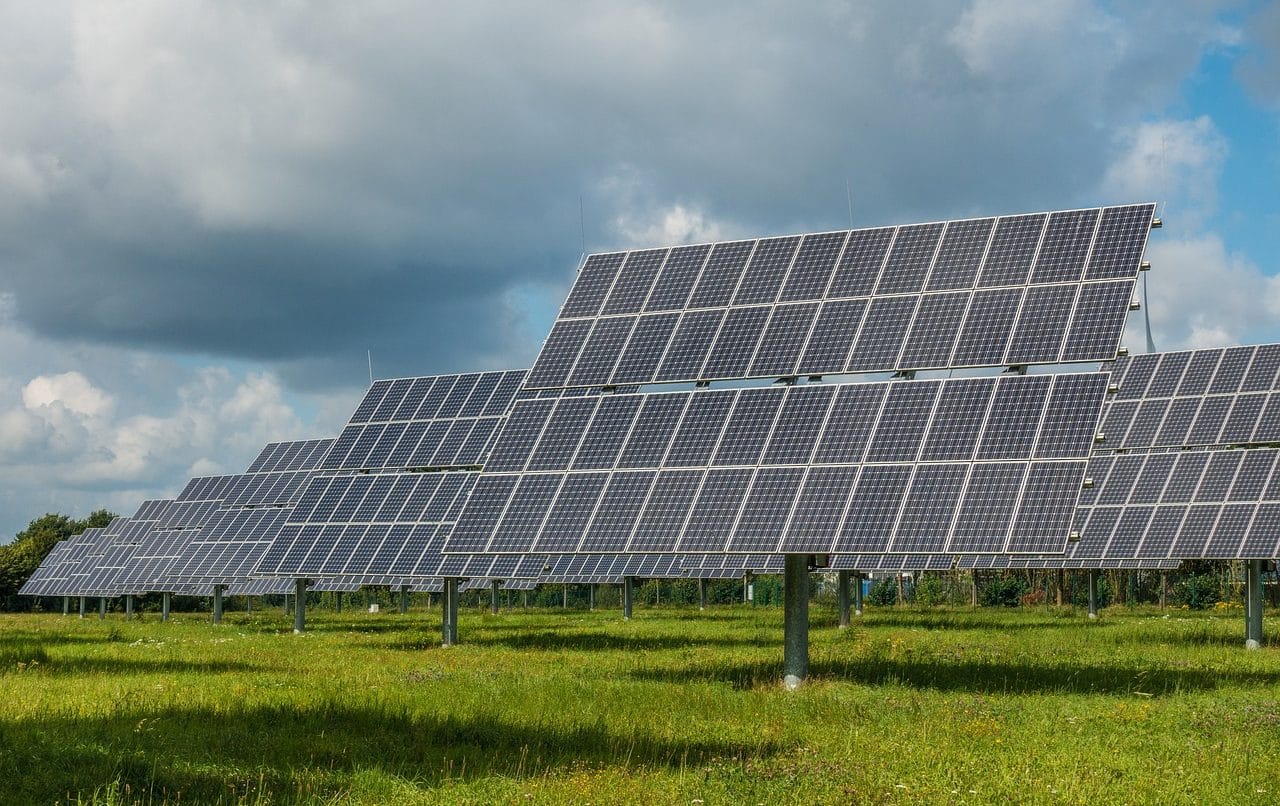

The energy transition is necessary to achieve many of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) established by the UN.
electrification
Specialists agree that, on the path to decarbonization, it is essential to advance with electrification . This notion refers to using electricity obtained from renewable sources as an energy vector of the transition process.
Promoting the use of electric vehicles, in this context, is essential in the fight against global warming. To promote the adoption of cars that run on electricity instead of fossil fuels, appropriate charging infrastructure must be developed to aid sustainable mobility .
