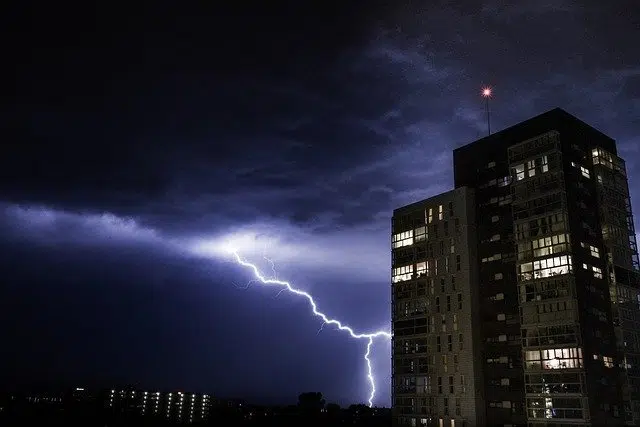

Meteorological weather refers to atmospheric phenomena that develop in a certain place and in a particular period.
The idea of time refers to the physical magnitude that makes it possible to measure and establish sequences of events. The concept also refers to how long the events last. Meteorological , for its part, is that linked to meteorology (the science that studies the atmosphere).
It is known as meteorological weather or atmospheric weather , therefore, to the series of phenomena that take place in the atmosphere in a specific period and in a certain space . These phenomena are measured in values that reflect temperature, relative humidity, pressure, visibility and other data, such as the presence of storms.
Differences between weather and climate
Meteorological weather, which is often referred to simply as weather , reveals the activity of phenomena over a period of one or more days . When an average of the measured values is made over a longer period, it is called climate . It can be said, therefore, that time indicates the atmospheric activity of the day or in the short term and that climate refers to the average values of said activity sustained over time.
Knowing the weather is essential for many activities and is even very important in everyday life. If a person, before going to work, turns on the television and sees that the temperature is 2° C , they will leave their house very warm so as not to get cold. This weather indicator is therefore very useful for you.
Weather forecasting is very important for planning multiple activities.
The importance of forecasting
It should be noted that weather can be forecast from the analysis of various data. To achieve greater precision, weather stations must be located at strategic points and maintain a good level of communication. Thus, for example, a meteorologist may announce that rain is expected for a city within two or three days.
Weather forecasting is one of the most important activities worldwide. Much of the functioning of a city, especially that of its vehicular transport systems (whether by land, air or sea), depends on this analysis at the regional level, since it allows a significant number of accidents to be avoided , and this translates not only in the protection of living beings but also of the economy.
If human beings could not anticipate the phenomena associated with meteorological weather, it would be almost impossible for them to sustain the complexity of their current organization, which includes, in addition to transportation, commercial activities, agriculture and construction, without leaving aside the provision of services that may be affected by inclement weather.
Factors that affect weather
Temperature, humidity differences between two given locations, and air pressure are the factors that drive weather. The latitude from the tropics causes the angle of the sun to vary from one point to another on the planet, and this explains the differences that can be seen when these phenomena are studied.
The marked contrast that can be seen between the temperature of tropical air and that of the polar air results in an increase in the jet stream , a narrow and strong current of air that concentrates and runs along an axis in the stratosphere or upper troposphere, with a pronounced wind shear, both vertical and horizontal. Wind shear (also known as wind shear ) is understood as the difference that is perceived in the direction of the wind, or in its speed, taking as reference two places within the Earth's atmosphere.
The instability of the flow of such jet streams sometimes brings with it meteorological weather systems such as mid-latitude cyclones (also called extratropical cyclones ), a set that is characterized by its low pressure and is related to horizontal thermal gradients and with the fronts.
