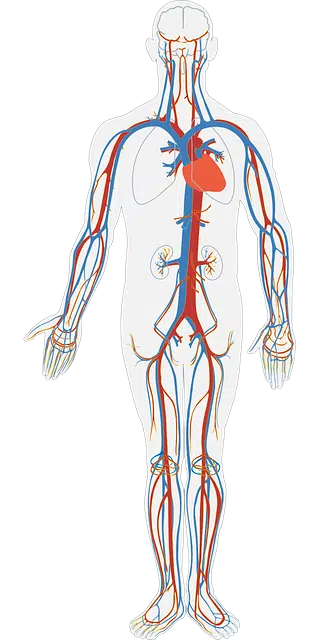
The circulatory system is made up of the structures and organs that make it possible for blood and lymph to travel through the body.
A system is a module whose components are interrelated with each other and maintain certain interactions. Circulatory , for its part, is an adjective that refers to what is linked to circulation (the act of circulating: flow, transit, move).
The idea of a circulatory system , therefore, is linked to the set of organs and structures that allow blood and lymph to travel through the body. Capillaries, veins, arteries and the heart are some of the main components of this system.
Through the circulatory system, cells access the nutrients they need to survive and develop. The circulatory system also contributes to the stabilization of pH and body temperature and helps collect waste that is then expelled through the exhalation of air and urine.
Functioning of the circulatory system
It is important to note that the circulatory system does not function the same in all species : there are different types of circulation and different compositions of the system. Blood circulation, for example, can be complete (oxygenated blood and deoxygenated blood do not mix) or incomplete (mixing of both types occurs). On the other hand, it is possible to differentiate between simple blood circulation (which passes, in each revolution, only once through the heart) and double blood circulation (in each revolution, the fluid passes twice through the organ).
The circulatory system can also be classified as open (the blood irrigates the cells directly and is not always inside the vessels) or closed (the blood, when circulating, never leaves the vessels).
If we focus on the human being , we can say that he has a closed circulatory system with complete and double blood circulation.
Thanks to the circulatory system, cells receive the nutrients they need to survive and develop.
Its importance for health
The circulatory system, especially the heart, is of great importance for our health , and that is why a minimal alteration in its function or shape is enough for disorders and tissue damage to appear. Statistics indicate that more than a quarter of the world's population suffers from some type of cardiovascular disease, and that this is one of the major causes of death.
From the moment of birth and until approximately 5 years of age, the health problems that human beings face are usually congenital in nature. Later, rheumatic types begin to appear. After the age of 35, coronary artery disorders, high blood pressure and arteriosclerosis arise, which can lead to a heart attack .
Diseases and disorders linked to the circulatory system
One of the most common diseases associated with the circulatory system is anemia , which is characterized by an abnormal decrease in the number of red blood cells in the blood. Since red blood cells are responsible for transporting oxygen to the body and collecting carbon dioxide from all the cells in the body, people who suffer from anemia also present an oxygen deficit in peripheral tissues.
On the other hand, there is angina , a symptom that usually manifests itself in the form of oppressive pain in the chest. Although it is not a disease, it does indicate that the heart muscle cannot obtain sufficient oxygen to meet its needs. From another point of view, if the body demands more oxygen than it has at its disposal, ischemia appears, and when this occurs in the heart, pain called angina arises.
Another disorder related to the circulatory system is varicose veins, which appear when the elasticity of the veins decreases, as a result of which blood begins to flow in two directions instead of going only towards the heart. It is worth mentioning that women are four times more likely to suffer from varicose veins than men .
