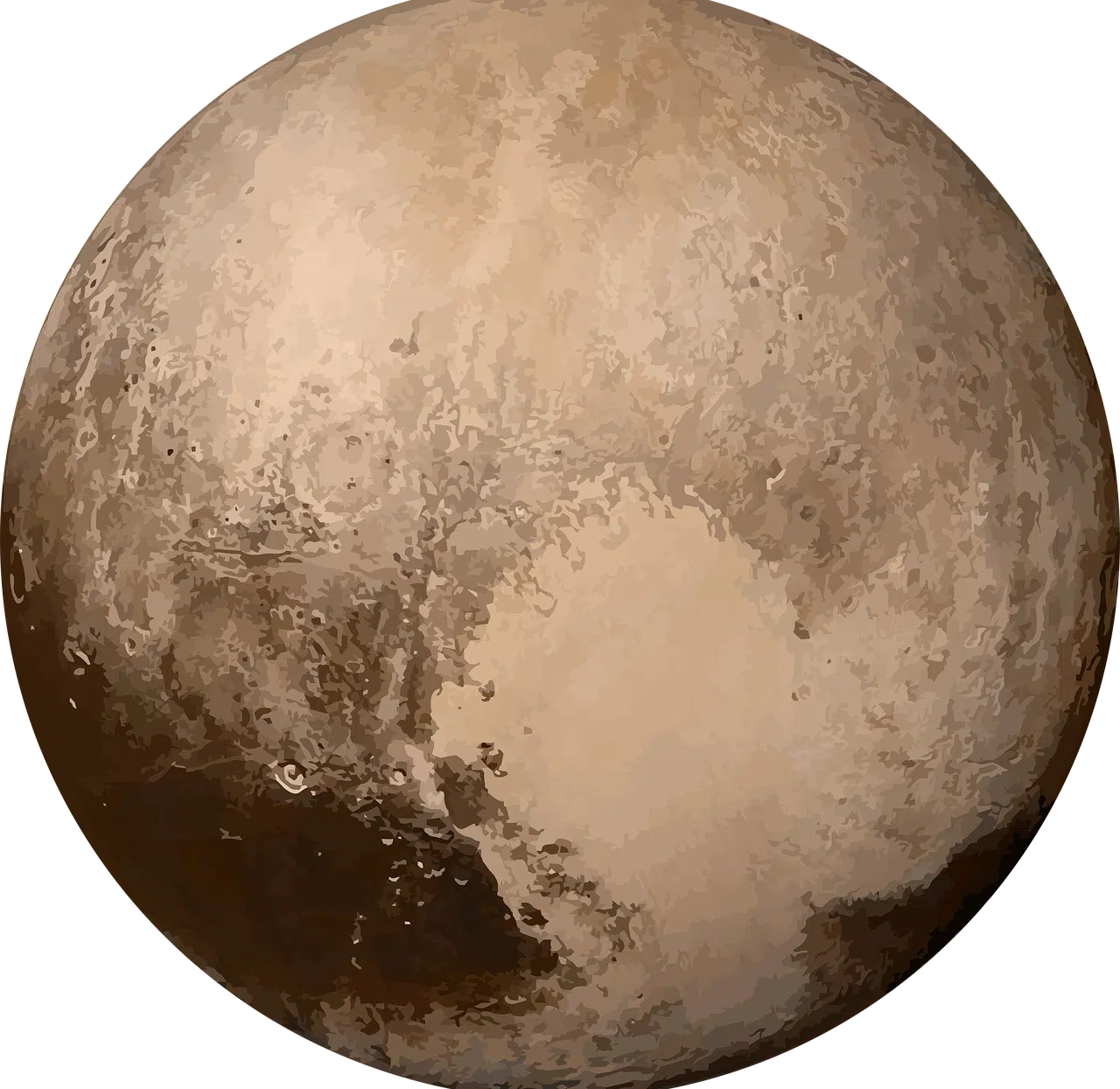
Pluto is the best-known dwarf planet in the solar system.
Pluto , the most famous dwarf planet in the solar system, has fascinated scientists and space enthusiasts since its mention in 1930 by Clyde Tombaugh (discoverer).
Pluto's atmosphere is tenuous. Located in the distant Kuiper Belt , this planet is one of the so-called icy bodies (objects composed mainly of ice). It has a diameter of approximately 2,377 kilometers , less than half the width of the United States. Its elliptical and eccentric orbit sometimes takes it closer to the Sun than Neptune. Charon (Pluto's largest satellite) is one of its five known moons.
History
The story of Pluto begins with its discovery on February 18, 1930 by Clyde Tombaugh, a young astronomer working at the Lowell Observatory in Flagstaff, Arizona. The observatory was founded by Percival Lowell, who had postulated the existence of a ninth planet, provisionally named Planet X , due to disturbances observed in the orbits of Neptune and Uranus . Although Lowell died before his theory could be confirmed, his legacy led Tombaugh to meticulously scrutinize the night sky, ultimately leading to the discovery of Pluto.
At this point Greek mythology (related to the name of Pluto) comes into play. An eleven-year-old English girl named Venetia Burney thought of Pluto as the god of the underworld and decided that it was the perfect name for the planet, since it resides in the darkest and coldest regions of the solar system , far from the heat of the Sun. The community astronomical did not take long to accept his proposal. It is worth mentioning that the name Charon has a similar origin: he was the ferryman of the underworld.
As technology advanced and more Pluto-like objects were discovered in the Kuiper Belt , astronomers began to question its classification as the ninth planet . The situation culminated in 2006 when the International Astronomical Union (IAU) officially redefined the term planet , noting that it must meet three criteria:
- orbit the Sun;
- be massive enough that its gravity molds it into a roughly spherical shape;
- having cleared its orbit of other bodies.
Pluto meets the first two criteria, but not the third, since it shares its orbit with other Kuiper Belt objects. As a result, the IAU reclassified it as a dwarf planet . This decision was controversial and sparked widespread debate. Despite its new status, interest in Pluto did not wane, and NASA 's New Horizons mission, which flew by it in 2015, provided detailed images and data that revealed a surprisingly active and geologically diverse world, rekindling the fascination with this distant and enigmatic celestial body.

Pluto's largest moon is called Charon, after the ferryman of the underworld.
Physical characteristics
Pluto presents a number of unique and fascinating physical characteristics that notably distinguish it within our solar system.
Chemical composition
Pluto is primarily composed of a mixture of rock and more than one layer of ice. Its surface includes layers of frozen nitrogen and methane ice, with traces of carbon monoxide, which reflect sunlight and give it its shiny appearance.
Geology
Pluto's geology is surprisingly diverse and active. The New Horizons mission revealed a varied surface including mountains of water ice up to 3,500 meters high, plains, and Pluto's well-known glaciers . Sputnik Planitia's vast nitrogen ice plains show cellular patterns and evidence of ice convection, indicating recent geological activity.
Geological activity and cryo-volcanism
Pluto shows signs of continued geological activity, an unexpected feature for a body so small and distant from the Sun. Features have been identified that could be cryo-volcanoes, which expel a mixture of liquid or semi-liquid water, ammonia and methane. This activity, called cryo-volcanism, suggests that Pluto has an internal source of heat, possibly generated by radioactive decay in its rocky core.
Mass
Pluto's mass is around 1.31 × 10²² kilograms , which represents less than 0.24% of the Earth's mass. Despite its small size, Pluto has five known moons . Charon is so large compared to Pluto that both bodies orbit a common point outside it, which is known as a binary system.
Thanks to missions like New Horizons, our knowledge of outer space is renewed.
Natural satellites
Pluto, in addition to its largest satellite Charon, has four smaller natural satellites: Nix, Hydra, Kerberos and Styx. Discovered in the last decade and a half, they present interesting characteristics that shed light on the dynamics and formation of the system.
These smaller satellites exhibit orbital resonance : their orbital periods are in a simple ratio of whole numbers, a relationship in which the bodies exert regular and repetitive gravitational influences on each other, which can stabilize their orbits or, in some cases, make them more chaotic. . They are believed to have formed from debris resulting from a collision between Pluto and another Kuiper Belt object, similar to the history of Earth's moon.
Nix (satellite)
Discovered in 2005 along with Hydra, Nix is Pluto's third largest satellite. It has an irregular shape and an estimated diameter of about 49 kilometers . Like the other minor satellites, it has a surface covered mainly with water ice, which gives it high reflectivity. Its name comes from Greek mythology , in which Nyx is the goddess of the night.
Hydra (satellite)
Also discovered in 2005, Hydra is slightly larger than Nix, with a diameter of approximately 58 kilometers . It is the furthest satellite from Pluto compared to the other minors. It has a highly reflective surface, suggesting a composition rich in water ice. Its name is inspired by the multi-headed serpent from Greek mythology that was defeated by Hercules.
Kerberos (satellite)
It was discovered in 2011. It is considerably smaller than Nix and Hydra, with an estimated diameter between 12 and 34 kilometers . Kerberos has an irregular shape and its surface appears to be less reflective, suggesting differences in its composition or surface structure. Its name comes from Cerberus, the three-headed dog who guards the gates of the underworld in Greek mythology.
Styx (satellite)
It is the smallest of Pluto's satellites and was discovered in 2012. It has an estimated diameter between 10 and 25 kilometers . Like the others, Styx has an irregular shape and an icy surface. Its name is due to the River Styx , which in Greek mythology separates the world of the living from the underworld.
