
The World Health Organization is known by the acronym WHO.
WHO is the acronym for the World Health Organization , an entity of the United Nations ( UN ). The WHO is responsible for managing health policies on a global scale. It was created at the initiative of the UN Economic and Social Council and met for the first time in 1948 .
The WHO is governed by the World Health Assembly , made up of representatives of the one hundred and ninety-three member countries of the organization . This assembly meets every May .
Six regional offices that enjoy fairly extensive autonomy make up the WHO : the EMRO (Eastern Mediterranean Regional Office), the Pan American Health Organization (Regional Office for the Americas), the AFRO (Africa Regional Office), the WPRO (Regional Office for the Western Pacific), EURO (Regional Office for Europe) and SEARO (Regional Office for South East Asia).
WHO objectives
The main objective of the WHO , which was awarded the Prince of Asturias Award for International Cooperation , is that all people on the planet enjoy the highest level of health that can be achieved. For the WHO , health can be defined as the state of complete physical, mental and social well-being .
The classification of diseases , the preparation of a list of basic medications that the health systems of the States must have, the establishment of actions to combat epidemics , vaccination standards, the development of state programs to combat diseases such as HIV/AIDS. AIDS and the promotion of healthy lifestyles are part of WHO 's activities.
It can be indicated that WHO initiatives aim at the care and promotion of public health . The body is responsible for infectious diseases (such as Zika and malaria ), but also for non-communicable diseases ( cancer , obesity ). Her role leads her to analyze issues such as nutrition, sanitation, access to drinking water and hygiene promotion, working towards disease prevention.

The WHO is an entity of the UN.
Agency offices
As mentioned above, there are six offices of this organization throughout the world , which we will detail below:
- AFRO – Headquartered in the Republic of Congo , includes all nations in sub-Saharan Africa, except for some that belong to another region.
- EMRO : based in Cairo ( Egypt ), it serves all countries that are part of North Africa that are not within the territory served by AFRO .
- EURO : its headquarters are located in Copenhagen ( Denmark ). All countries on the European continent are part of it.
- SEARO : its facilities are located in New Delhi ( India ) and brings together all countries in Asia that are not in the jurisdiction of WPRO or EMPRO.
- WPRO : is based in Manila ( Philippines ) and covers all countries in Oceania , and those in Asia that are not served by SEARO or EMRO .
- AMPRO : also known as Pan American Health Organization ( PAHO ). Its base building is located in the city of Washington DC ( United States ). It is the oldest of all and serves all American nations .
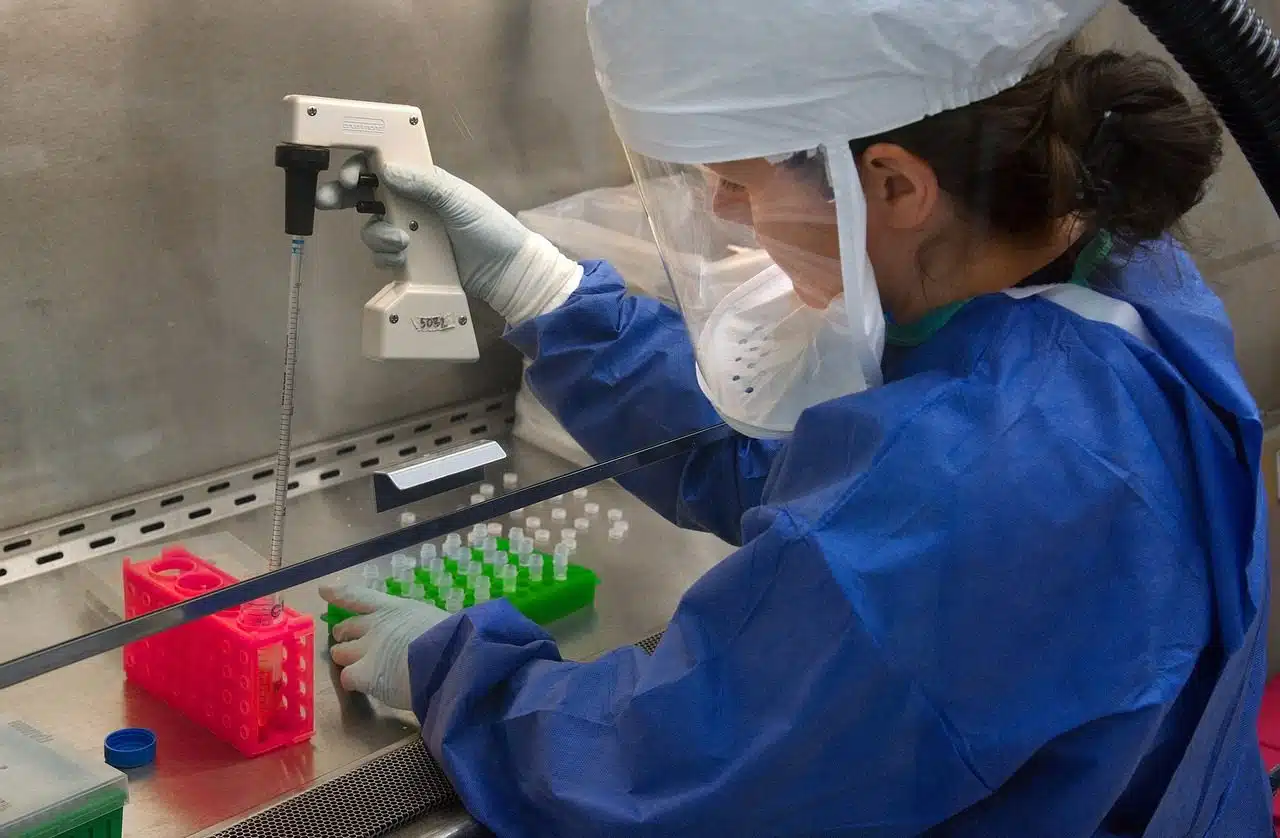
The WHO promotes health research.
WHO functions
It is worth mentioning that this body has a series of functions , the purpose of which is to contribute to international health in all its aspects:
- Offer a leading point of view on worrying health issues and seek agreements and alliances that ensure the quality of life of all societies.
- Maintain a line of research that is widely disseminated, so that valuable knowledge that can serve the inhabitants is available to everyone.
- Project a series of rules and procedures so that investigations can be carried out in the most effective way possible.
- Collaborate at the policy level to establish laws that are based on ethical principles and seek to improve health problems from a scientific perspective.
- Provide technical support to the different institutional departments of each country .
- Be aware of the various situations that exist on issues related to health and mark the recommended trends, also promoting their implementation in the various countries.
The COVID-19 pandemic
The WHO played a fundamental role during the COVID-19 pandemic , generated by the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus. The organization sought to guarantee health care and patient safety, promoting immunization to reduce infections and minimize the severity of the conditions.
In the face of health emergencies such as that caused by COVID-19 , the WHO must offer assistance to each health system . Likewise, the international community, through this entity, has to coordinate alert and response mechanisms to epidemics to try to mitigate the damage, which translates into the loss of life.
