Space observatories provide valuable data about astronomical phenomena.
A space observatory is a scientific facility located in outer space designed to observe astronomical phenomena without the distortions caused by the Earth's atmosphere. These observatories can be in orbit around the Earth or other celestial bodies, and are often equipped with telescopes and other advanced instruments to capture data at different wavelengths, such as visible light, infrared, ultraviolet, X-rays, and more.
Best-known space observatories
- Copernicus Satellite : also known as OAO-3 (Orbiting Astronomical Observatory 3) or Copernicus Observatory , it was a space observatory launched in 1972;
- Arecibo Observatory (collapsed in 2020) : was a ground-based radio telescope located in Puerto Rico;
- Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) – NASA space observatory launched in 2010 to study the Sun;
- Compton Gamma Ray Observatory : operated between 1991 and 2000, specialized in observing gamma rays;
- Chandra X-ray Observatory – launched in 1999 to observe the universe in X-rays;
- Lynx X-ray Observatory (proposed) – would focus on X-ray observation;
- Herschel Space Observatory – was a European Space Agency (ESA) space observatory launched in 2009 to observe in the far infrared and submillimeter;
- Kepler Space Observatory – launched in 2009 to search for exoplanets;
- Solar Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO) – a joint ESA and NASA mission launched in 1995 to study the Sun;
- TESS (Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite) : launched in 2018 by NASA. It observes wide areas of the sky to detect small dips in the brightness of stars caused by planets passing in front of them, identifying new exoplanets.
Other observatories
The following are not space observatories , but often appear in the same context given their scientific contributions:
- Jodrell Bank Observatory – a ground-based observatory located in the United Kingdom;
- IceCube Neutrino Observatory – a neutrino detector located in Antarctica;
- Gemini Observatory – a ground-based observatory with two twin telescopes located in Hawaii and Chile;
- Simons Observatory – a series of ground-based telescopes located in the Atacama Desert, Chile.
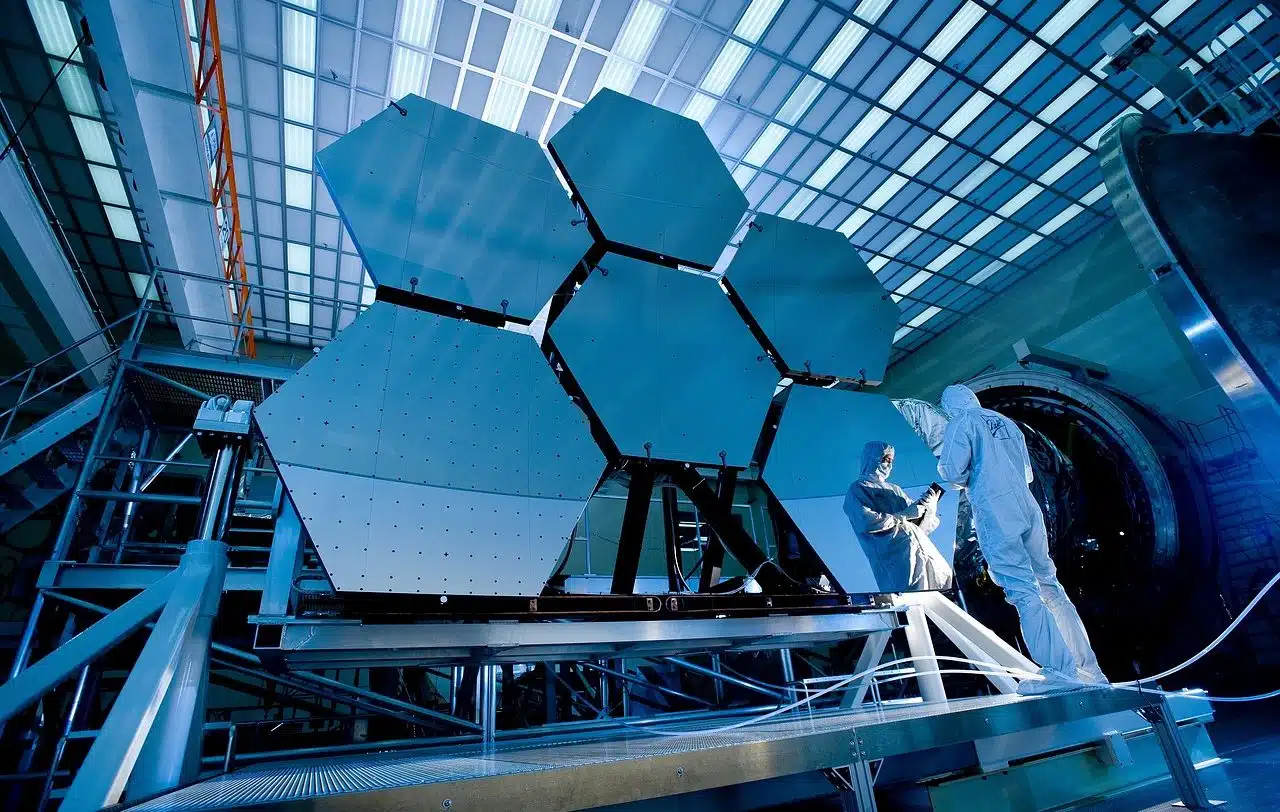

NASA and ESA launched the James Webb telescope in 2021 to study the formation of stars, galaxies and exoplanets.
Most famous telescopes
- Green Bank Telescope – A radio telescope located in West Virginia, USA, operated by the Green Bank Observatory. It is the largest steerable radio telescope in the world. It is used for radio astronomy, studying everything from objects in the Solar System to distant galaxies;
- Chinese Space Station Telescope (CSST) – Also known as Xuntian , it is a space telescope planned by China to be launched around 2024. They intend it to be comparable to Hubble in terms of observation capabilities. It will observe in visible and ultraviolet light to study the universe, including the formation and evolution of galaxies;
- MeerKAT radio telescope – a large radio telescope array in South Africa, part of the SKA (Square Kilometer Array) project. It is used to explore the universe at radio wavelengths, investigating the formation of galaxies , pulsars and black holes;
- EHT (Event Horizon Telescope) – A network of globally distributed radio telescopes working together to form an Earth-sized telescope . It was instrumental in capturing the first image of a black hole in 2019;
- Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope – a NASA space observatory launched in 2008, designed to study phenomena in the gamma-ray range. Observe highly energetic events such as gamma ray bursts and blazars;
- Hubble Space Telescope - Launched in 1990 by NASA and ESA, it is one of the most famous and productive space telescopes. It has provided detailed images and data on galaxies, nebulae, exoplanets and other astronomical objects;
- James Webb Space Telescope – Launched in December 2021, it is a space telescope of NASA, ESA and the Canadian Space Agency. It observes in the infrared, allowing studies on the formation of stars, galaxies and exoplanets;
- Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope (planned) – Formerly known as WFIRST , it is a space telescope planned by NASA to be launched in the second half of the 2020s. It will study dark energy, exoplanets, and galaxies;
- Spitzer Space Telescope – was a NASA infrared space telescope, operated from 2003 to 2020. It studied cold, distant objects such as planets, forming stars, and infrared galaxies;
- Giant Magellan Telescope – Under construction in Chile, it will be one of the largest optical telescopes in the world with an array of seven primary mirrors. It will allow extremely detailed observations of stars, exoplanets and galaxies;
- James Clerk Maxwell Telescope – is a submillimeter-wave telescope in Hawaii. Observe dust and gas in space , contributing to the understanding of star and galaxy formation;
- Very Large Telescope (VLT) – array of four optical telescopes located at the Paranal Observatory in Chile, operated by ESO. Make detailed observations of astronomical objects at multiple wavelengths;
- Daniel K. Inouye Solar Telescope – The largest solar telescope in the world, located in Hawaii. Study the surface of the Sun and its activity with unprecedented resolution;
- Subaru Telescope – optical and infrared telescope at the Mauna Kea Observatory in Hawaii, operated by the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan . It is used for a wide range of astronomical observations, including galaxy studies and searches for exoplanets.

Terrestrial observatories carry out complementary work to space observatories.
Space probes
Ulysses Solar Probe
It was a joint NASA and European Space Agency (ESA) space probe, launched in 1990. It studied the Sun and interplanetary space, focusing on the polar regions of the Sun. Ulysses was the first probe to explore this area, providing data on the solar wind, the heliosphere and the solar magnetic fields. The mission ended in 2009.
WMAP (Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe)
It was a NASA space probe launched in 2001 to measure temperature differences in the cosmic microwave background (CMB). It provided a detailed map of the CMB, allowing scientists to study the conditions of the early universe and support the Big Bang model. WMAP completed its mission in 2010, and its data has been crucial to modern cosmology .
Parker Solar Probe
Launched by NASA in 2018, the Parker Solar Probe is a mission designed to get closer to the Sun than any previous probe . It investigates the solar corona and the solar wind , providing data on the behavior of the Sun and the mechanisms that drive its activity. The Parker probe has revolutionized our understanding of solar processes by approaching just a few million kilometers from the surface of the Sun.
Voyager Probes
The Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 probes were launched by NASA in 1977 with the mission of exploring the outer planets of the solar system and then continuing into interstellar space. They made close flights of Jupiter and Saturn; Voyager 2 also visited Uranus and Neptune. Both probes have provided detailed images and data about these planets and their moons. They are now in interstellar space, sending information about this unknown region. Voyager 1 is the most distant man-made object from Earth.
