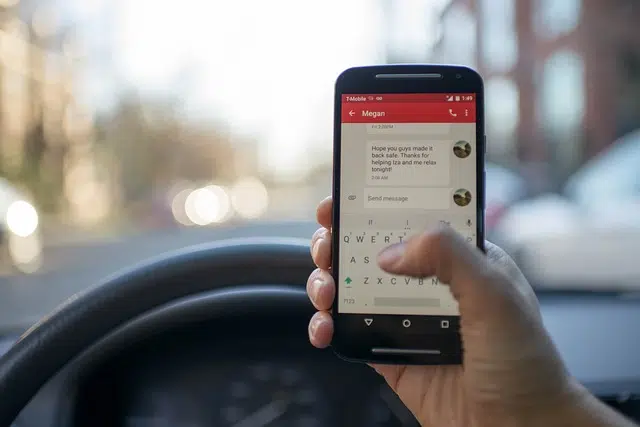
Using your phone while driving is an act of negligence.
Negligence , from the Latin negligentia , is lack of care or carelessness . Negligent conduct generally involves a risk to oneself or third parties and occurs due to failure to calculate the foreseeable and possible consequences of one's own action .
For example: a person who talks on the phone while driving a vehicle is committing negligence. It has been proven that talking and driving are two activities that cannot be carried out at the same time since the subject loses concentration and can cause a traffic accident.
Punishment for negligence
Negligence is punishable by Justice , whether civil or criminal depending on the case. Fault lies in the omission of conduct due to foresee and avoid the damage caused. In the case of the previous example, the person who drives while talking on the phone is acting inappropriately, given that the risk of causing an accident is known to everyone; Therefore, such conduct is punishable by law through infractions.
An individual who lights a bonfire in the middle of a forest is also acting negligently. In these cases, the subject's intention is not judged: that is, he is not accused of trying to start a fire. Beyond intentionality, their actions are negligent due to the carelessness they reflect and the potential damage they may cause to the environment and to their own person. If the fire gets out of control or is not put out as it should, the forest fire will occur even though this was not in their plans. Justice, therefore, will punish the subject.

Whoever lights a fire in a forest commits negligence.
Psychological damage
It is worth mentioning that negligence is not always as apparent as in the cases mentioned above; When it causes psychological damage to a third party, there is not always evidence to find those responsible and apply the full weight of the Law . This occurs with the various types of abuse to which a person can be subjected, especially with those that do not leave traces on the body.
When a person is psychologically abused, especially when the victim is a minor and is under the guardianship of one or more adults, the dynamics of the abuse usually have more components than what meets the eye: beyond the aggressor. and its prey , there may be one or more potential witnesses. Neglect occurs when they stay aside from the situation, either out of fear of intervening or as a result of denial , not wanting to accept that the abuse is real.
In a case like this, neglect, which may come from a parent or friend, causes damage almost as deep as the abuse itself. Not only must the victim carry the memory of the humiliations they have suffered over an often prolonged period of time, but their trust in others becomes their worst weakness ; the negligence of one or those loved ones who have not acted when they had time to interrupt or even avoid the abuse , they decided not to do so, becoming indirect participants, going from being friends to enemies . The wound increases when the abuser used to be part of the victim's inner circle.
Negligence and conduct
Something that negligence usually entails in most cases is serious consequences. This does not mean, on the other hand, that those who act without thinking are always aware of their mistakes and that they learn from them so as not to make them again.
However, when negligence is repeated systematically, given that it is impossible to ignore its impact, it is more accurate to speak of intentional acts; in other words, of conduct.
