An atomic model is a graphic representation of the atomic dimension of a matter.
Among the multiple uses of the term model , there is one that associates the concept with a representation or a scheme. Atomic , on the other hand, is what is linked to the atom (the smallest amount of a chemical element that is indivisible and has its own existence).
An atomic model , therefore, consists of graphically representing matter in its atomic dimension . The objective of these models is to make the study of this material level easier by abstracting the logic of the atom and transferring it to a scheme .
Types of atomic model
There are different types of atomic models. The Bohr or Bohr-Rutherford atomic model, for example, is a quantized model of the atom that was developed to explain the way in which electrons manage to trace stable orbits around the nucleus. This functional model is not based on the physical representation of the atom: it is oriented, instead, to using equations to explain its operation.
The Schrödinger atomic model , for its part, is a non-relativistic quantum model based on the resolution of the so-called Schrödinger equation for an electrostatic potential with spherical symmetry.
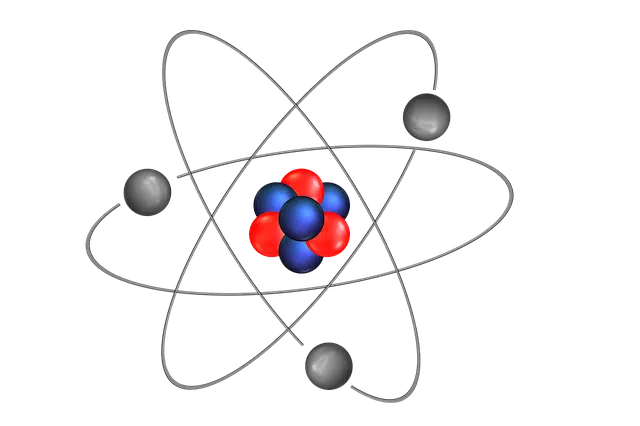
There are multiple types of atomic model.
Schrödinger's work
This character, the aforementioned Erwin Schrödinger, an Austrian physicist who was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1933 for having carried out the development of the aforementioned Schrödinger equation, which is considered the founder of the current atomic method. . Through it what is achieved is the description of the temporal evolution of what is a massive but non-relativistic particle.
Specifically, as we said before, this scientist is considered the father of the current atomic model, which is also known as the "Wave Equation." A name under which a mathematical formula is located that has as its principles values such as the duality of matter, the so-called probability in a place of certainty, energy levels or stationary states as well as the presence of an atomic nucleus with respect to the known particles.
Atomic models of Thomson, Rutherford and Dalton
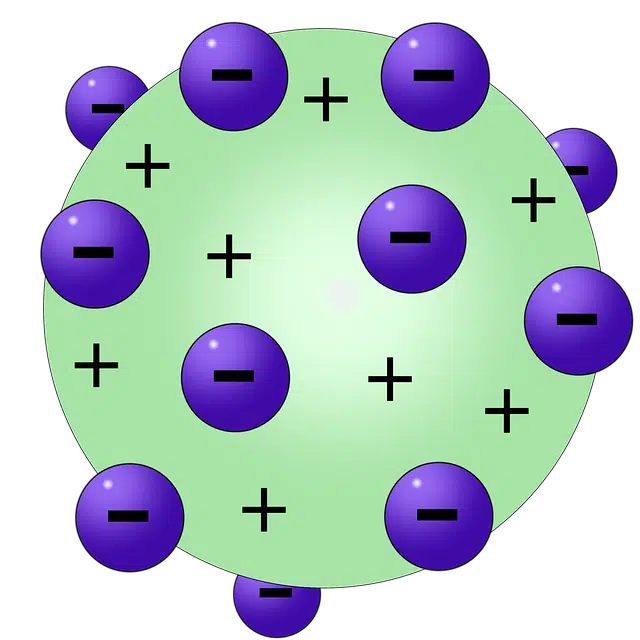
Another atomic model is the Thomson model, also known as the pudding model . This is a theory proposed by Joseph John Thomson (who discovered the electron) about atomic structure.
We can also mention the Rutherford atomic model , devised by Ernest Rutherford to provide an explanation for the result of his experiments with gold sheets. This physicist and chemist indicated that atoms have electrons and that they are rotating around a central nucleus. Such a nucleus, for Rutherford , would concentrate almost all of the mass and all the positive charge of an atom.
In the same way we cannot ignore Dalton's atomic model . It was at the beginning of the 19th century that this approach came to light. Although it had certain errors, it was a very important milestone at that time and it offered important advances regarding the structure of matter.
Among the main pillars of this theory are ideas such as that matter is made up of particles called atoms, that atoms that belong to the same element are identical or that these aforementioned atoms cannot be divided.
