Mitosis is the cell segmentation that occurs after the duplication of genetic material.
Mitosis is the segmentation of a cell that takes place after the genetic material has been duplicated, which allows each of the cells generated to have all of the chromosomes. The term derives from a Greek term meaning "to weave."
It is, therefore, the action that distributes the hereditary information found in DNA equitably. The process of mitosis generates cells that are genetically identical. Meiosis (another cell division process), on the other hand, produces cells that are genetically distinct.
Mitosis is, in short, a procedure in which cells multiply and which has a great impact on the growth , development and regeneration capacity of the organism. The formation of two new nuclei is known as karyokinesis , while the division of the cytoplasm is called cytokinesis .
Stages of mitosis
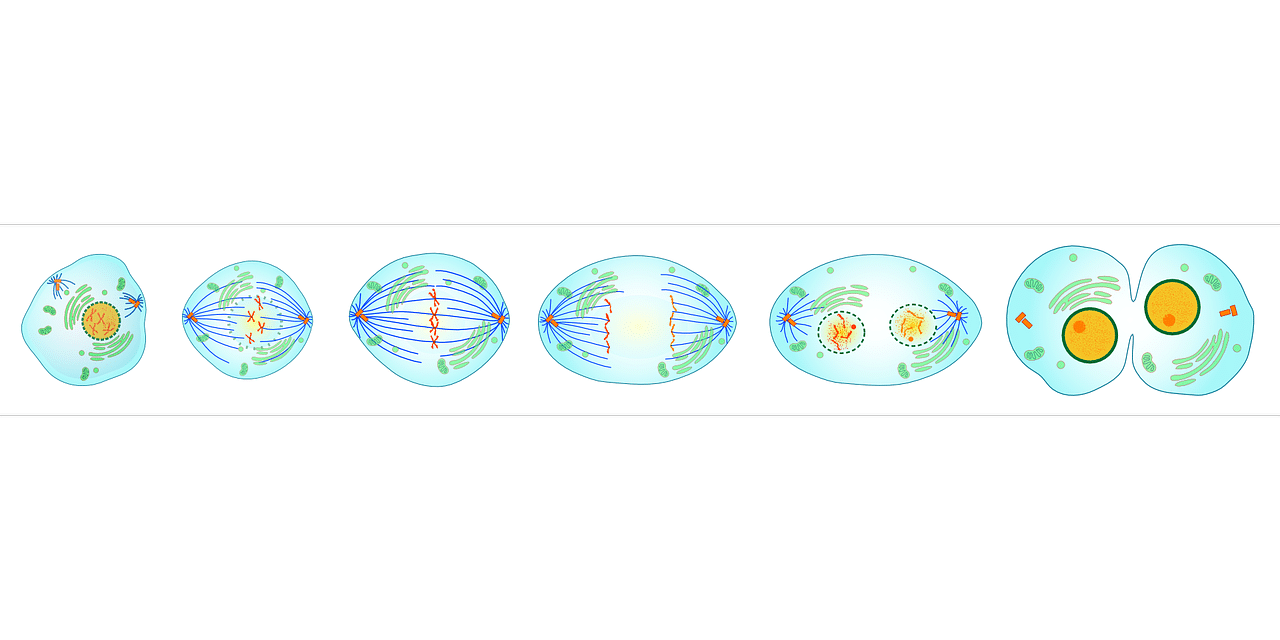
Mitosis is divided into four clearly differentiated stages or phases, the first of which is called prophase . In this the chromosomes can already be observed under the microscope and they stand out because they are made up of bars, called chromatids , that are held together.
The second stage is the so-called metaphase and what occurs in it is that the aforementioned pairs of chromatids move towards what is the center of the cell itself. Next, the third step takes place, which is called anaphase , which we can determine is the most important stage of mitosis because thanks to it, what is the division and subsequent transport and distribution of the two copies of what was the original genetic information.
Finally, the fourth and final phase is telophase . In this case we can establish that it is the moment in which the processes of previous stages are reversed, resulting in the obtaining of two daughter cells that are characterized by having the same amount of cytoplasm and also chromosomes.
It is also important to emphasize that when mitosis occurs in organisms that are multicellular, it not only gives rise to new individuals but also to the restitution of dead cells, the regeneration of what were damaged tissues and the healing of wounds.
Mitosis takes place in four phases.
Endoreduplication
Mitosis can also occur in a different way, not including cell division.
The process, called endomitosis or endoreduplication , produces cells with copies of the chromosome in question in the same nucleus. The cells generated by endomitosis are called endoploids .
Errors in mitosis
It should be noted that errors in mitosis can occur, although they are rare. They generally take place in the first cell segmentations in the zygote and affect the descendants of the mother cell that has the defects.
A chromosome that does not separate in the stage known as anaphase and chromosome damage that occurs from changes in the structure of the cell caused by the process are other problems that can arise during mitosis. There are times when the error can be detected and corrected in time.
