A messianic leader presents himself as a savior.
Messianic is an adjective that refers to that belonging to or relating to the messiah or messianism . The concept of messiah, for its part, is used in the field of religion to name the Anointed One (the Son of God or a man with the divine spirit) or in everyday language in reference to someone who is a creditor of excessive trust by part of people to achieve a goal or solve a problem.
The adjective messianic , therefore, can be applied to the person who declares himself or is considered to be a messiah or a savior. For example: “Sects usually have leaders with messianic pretensions who deceive people” , “The messianic movement does not stop growing” , “We believe that Master Brahmalogty is a messianic being who will lead us to a better world” , “ We must be careful with messianic groups: they are dangerous.”
Messianic Judaism
The religious group that maintains that Jesus of Nazareth is the Messiah is known as Messianic Judaism . Practitioners consider themselves part of the Jewish religion and follow the precepts of the Torah , although neither current of Judaism nor the State of Israel accepts messianics since they also follow the New Testament . For this reason, some Christian groups maintain that Messianic Judaism is a form of Christianity.
It is estimated that there are about 15,000 members of Messianic Judaism in Israel , a number that grows to 250,000 in the United States . It should be noted that this current is divided into several groups, such as Nazarene Messianic Judaism and Ebionite Messianic Judaism .
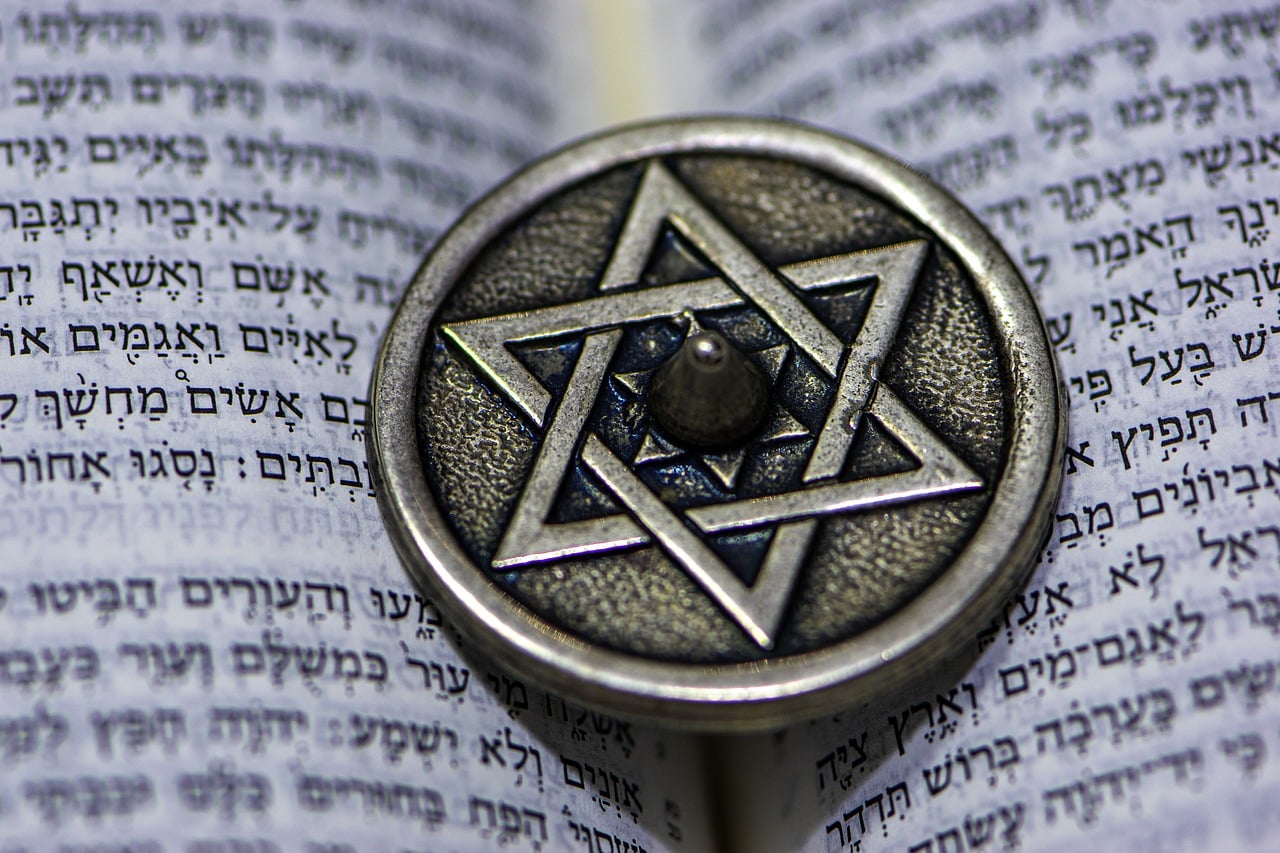

Messianic Judaism considers Jesus to be the Messiah.
Its emergence
Messianic Judaism emerged in England between the 19th and 20th centuries, during the Hebrew-Christian missions, with the aim of evangelizing the Jewish people. It is worth mentioning that its practitioners practice their faith by placing themselves in the position of authentic Torah observers , and their vision of themselves is that of Jews in religion .
The first congregation of Messianic Judaism was formed in the city of London and received the name "Ben Abraham" ; Its initial number of members was around forty. Also in the 19th century , one of the most important precursors of this religion appeared in Eastern Europe : Ignatz Lichtenstein , originally from Hungary . Throughout the 1890s , Lichtenstein produced a series of works in German that are considered classic messianic literature.
Beliefs of Messianic Judaism
Since Messianic Judaism is divided into several organizations, they are not all based on the same theology; The largest groups, however, share the following fundamental points:
- They believe that the Old Testament (the Tanakh ) and the New Testament ( Brit Hadashah ) arose by inspiration from God .
- They believe in Elohim , the God of the Bible, a being who brings together all the characteristics of the Christian version, such as omnipresence and his existence beyond creation. The different currents of messianic Judaism include trinitarian (which accepts the existence of one God in which three divine persons coexist), dualitarian (take the Father and the Son as a single entity ) and unicitarian (contemplate the presence of a single God with more than one demonstration).
- They affirm that Yeshua , called by Christians Jesus of Nazareth , is the Messiah who emerged from the people of Israel , which moves away from Christian and Muslim beliefs regarding his identity and nature. Yeshua is accepted as "God made flesh" and "word made flesh" and is believed to have fulfilled all the prophecies announced in the Tanakh .
- Regarding its festivities, the most important is Shabbat , which brings the faithful together on Friday afternoons ( Erev Shabbat ) and Saturday mornings and evenings ( Havdala ). Passover is called Passover and is celebrated on the 14th of Nisan (the first month of the biblical Hebrew calendar) and the Feast of Unleavened Bread takes place from the next day until the 22nd.
