
Medical professionals have extensive knowledge of human anatomy.
Medicine is a term that comes from the Latin medicīna and refers to the science that allows us to prevent and cure diseases of the human body . The concept is also used as a synonym for medicine (from the Latin medicamentum ), which is the substance used for the prevention, relief and cure of conditions or their consequences.
Medicine, together with pharmacy , nursing and other disciplines, form the group of health sciences, dedicated to the diagnosis, prevention and treatment of disorders that affect the body.
Medicine practice
To practice medicine, it is necessary to complete studies that allow you to obtain the necessary degree and the corresponding qualification. In this way, the doctor or doctor received is in a position to become a health agent in the health process, establishing a relationship with the passive agent (the patient , who is the sick person or who seeks to take care of his or her health).
There are numerous specialties within medicine, according to the part of the body they are dedicated to, the types of diseases or other factors that make classification possible. Cardiology , for example, deals with conditions of the heart and circulatory system.
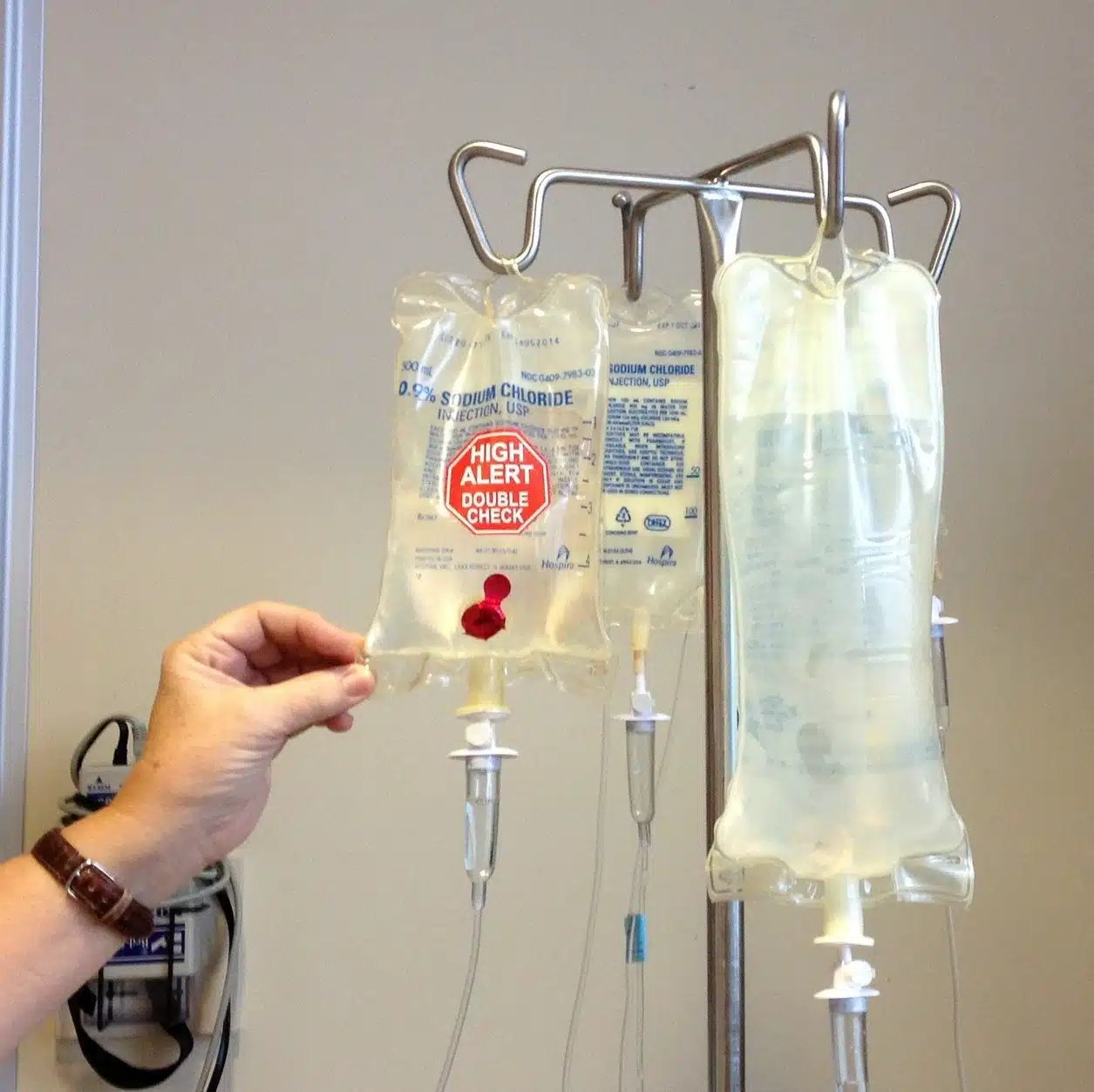
Oncology is the specialty of medicine that treats cancer.
Various specialties
In the same way, we must not forget other equally significant branches or specialties, such as, for example, neurosurgery . It is the one whose object of study and work is the nervous system, both central, vegetative and peripheral.
Equally important is also ophthalmology , which is the specialty within medicine that is responsible for carrying out the study of diseases and pathologies that affect the eyeball. It also focuses on the tear duct and the muscle system of the eyes.
Rheumatology , for its part, is the branch that basically focuses on the connective tissue and the musculoskeletal system . In this way, it works treating the different diseases that affect both areas such as osteoarthritis, arthritis, sclerosis, vasculitis, low back pain and osteoporosis , among others.
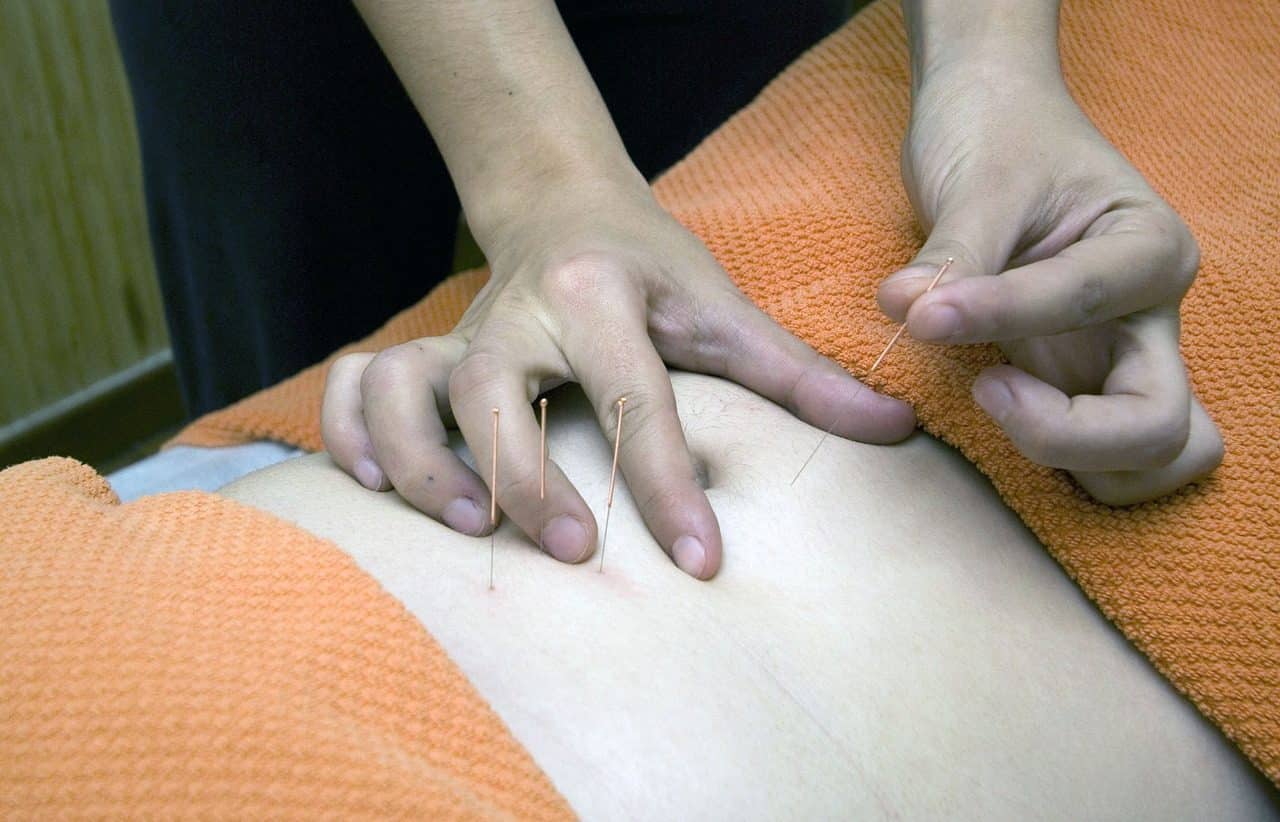
Homeopathy and acupuncture are part of what is known as alternative medicine.
Other branches of medicine
Likewise, we cannot ignore the existence of other specialties within medicine such as psychiatry , toxicology , urology , sports medicine or forensic medicine . The latter branch is responsible for examining a corpse to determine the causes of death, although its professionals also carry out the study of a person to establish the origin and severity of their injuries.
Dermatology is the medical specialty that focuses on skin care and diseases. Traumatology , for its part, is dedicated to traumatic injuries of the spine and extremities that affect bones, ligaments, joints, muscles and tendons.
There are other specialties that arise according to the age of the patient, such as pediatrics (dedicated to children) and geriatrics (focused on the elderly).
Gynecology , obstetrics , endocrinology , and neurology are other specializations of medicine.
health centers
Doctors , along with nurses and more professionals in this field, work in health centers. Hospitals , clinics , sanatoriums and other establishments are the places where medicine is practiced and where patients go.
Depending on the characteristics of the health center, various therapies can be carried out ( radiotherapy , chemotherapy , etc.), diagnoses , apply vaccines, develop rehabilitation and even advance clinical research. The patient can go directly to a guard or go to a consultation with a specialist.
Many times these facilities are prepared to carry out a laboratory test to detect viruses or bacteria that affect people. If they have an operating room , they have surgeons and specialists who can apply the anesthesia necessary to perform surgical interventions.
Sometimes, the person arrives at the hospital by ambulance . Emergency care is very important because it saves lives.
Medicine in the COVID-19 pandemic
In March 2020 , the World Health Organization ( WHO ) declared the existence of a COVID-19 pandemic . The disease, caused by the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus, caused nearly 7 million deaths worldwide.
Thanks to medicine and epidemiology experts, the COVID-19 pandemic was not even more serious and could be controlled: in May 2023 , the WHO considered that the global health emergency had come to an end.
In this process, the public health effort in prevention (with campaigns on the importance of hygiene), treatment and vaccination, as well as political management when implementing mandatory quarantines and isolations, was key. The scientific community worked at great speed to find a vaccine against the disease and the pharmaceutical industry produced the necessary doses urgently.
It cannot be ignored, however, that there are those who believe that the vaccine in question can cause a serious side effect , which in some cases could lead to death. However, the consensus of international medicine continues to maintain that vaccines are safe and were essential to save millions of lives.
