All scientific research requires observation, a problem posed, a hypothesis, an experimentation stage, a process of analysis and processing of information, a conclusion and the dissemination of the results.
Scientific research is carried out by specialists in various branches of science in order to make findings that clear up doubts or questions regarding a topic, solve a problem, predict a phenomenon or behavior, confirm or refute beliefs, add knowledge, understand certain issues and revolutionize everyday reality.
A good scientific researcher , in addition to theoretical resources that allow him to correctly apply the scientific method and a space adequately equipped to carry out his work, needs, among other skills and qualities, to have ethics, responsibility, credibility, commitment, discipline, curiosity, flexibility and perseverance.
Observation , data collection , the formation of a hypothesis , experimentation and analysis of the results obtained are key in any research project , throughout which there must also be a validation of processes and instruments and a conclusion . Reproducibility is also essential.
Types of scientific research
There is a huge variety of types of scientific research . The classifications that we will mention and describe below respond to different purposes or objectives, the style of data considered in each project, the prioritized field of research , the orientation and the way of carrying out each plan aimed at achieving some scientific advance .
This is applied research , for example, when efforts are aimed at discovering issues that can be used on a real level for, generally, the benefit of humanity. Basic or pure research , on the other hand, presents a more formal and theoretical essence and values the contribution to knowledge more than the practical application.
The modality known as qualitative research , for its part, uses surveys , testimonies , speeches , interviews , etc. in order to collect non-numerical data. It is common, especially, in the field of social sciences. Quantitative research differs from it because in its case it does work with numbers (arising from percentages, statistics, etc.) measuring and estimating magnitudes.
Interdisciplinary research , to add another variety, is characterized by bringing together referents, specialists, methodologies and researchers from multiple disciplines in the investigative process. And we should not overlook the features of participatory research , where research , collective participation and social action come together.
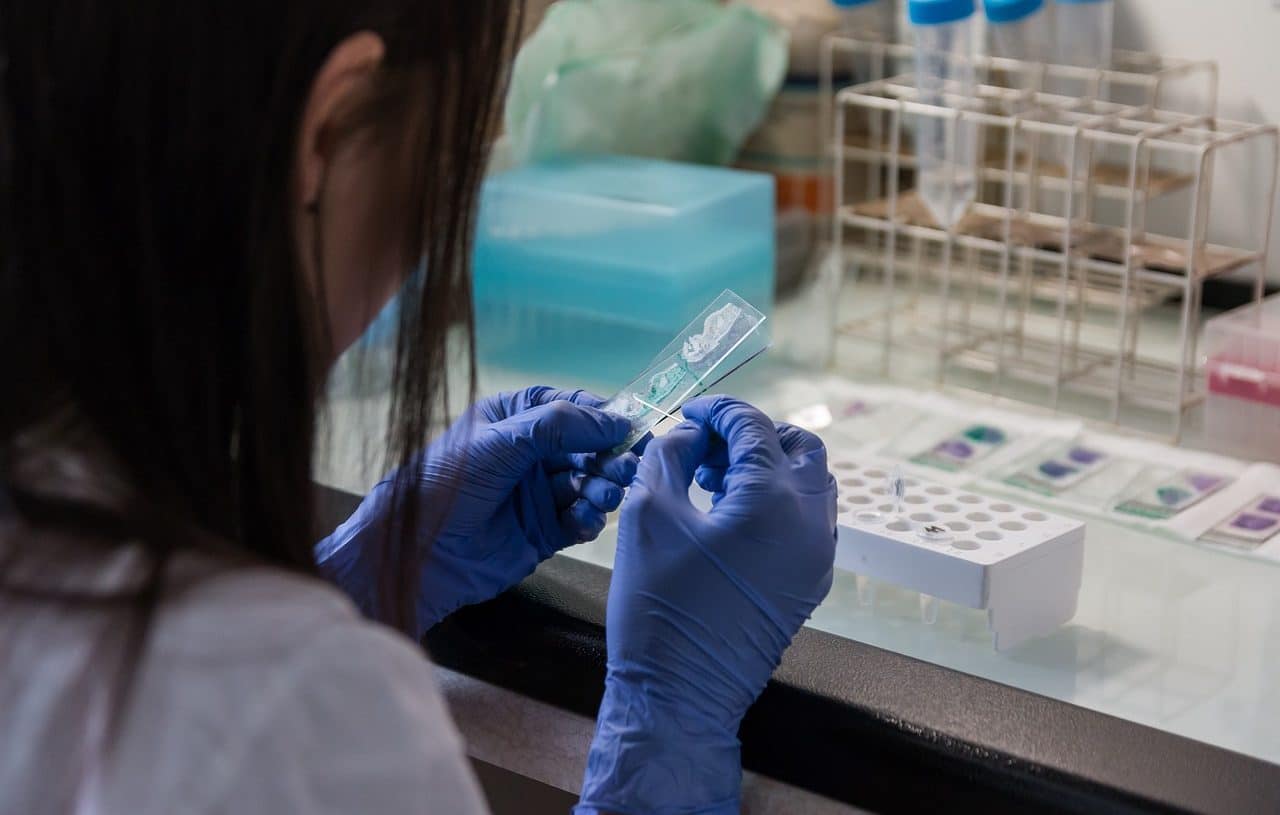

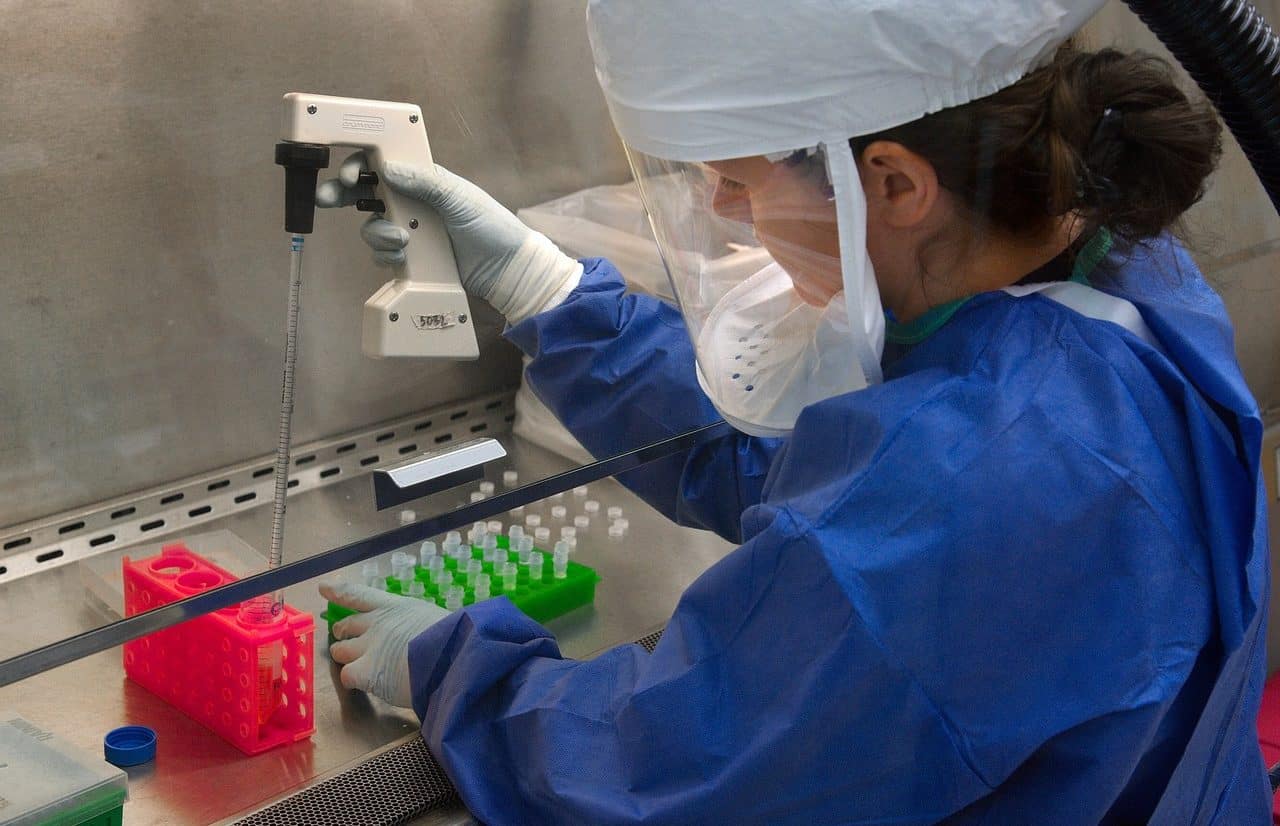
The laboratory is the ideal space to carry out tests, observations and other actions useful for scientific research.
Before concluding this list, it is enriching to note that, sometimes, it is chosen to develop a longitudinal study (a type of observational work that investigates several subjects over a certain period of time that looks back or looks into the future), while that in other circumstances it is decided to carry out a cross-sectional study evaluating measurements in the present time.
Key stages
All scientific research goes through key stages. Initially, the principal investigator establishes a project and forms a research team .
In this context, it is time to specify the field of study in which one intends to work and what question or search will be pursued. A specific objective and a hypothesis are also needed.
The idea is to contemplate previous content from reports , theories , bibliography and already completed studies but direct explorations, deductions and results to obtain new material of interest and useful findings. It is also important to specify what instruments, methodologies, strategies, resources or techniques will be used in the research .
Already in the final section, it is essential to write a report in which the results and conclusions are expressed in writing. Finally, scientific dissemination is carried out in order to transmit said information to a specific group or to the scientific community as a whole. It is convenient to know that those who lead research have the possibility of managing and obtaining patents that protect intellectual property , that is, they recognize and protect the work, effort and discoveries of scientists .

Technological developments and innovations in procedures, techniques and materials enrich scientific research.
Technology, financing and innovation at the service of scientific research
To promote scientific research , be able to deepen those that are already underway and stimulate the emergence of new research projects , investment is required ( financing with both public and private funds), infrastructure , innovation in materials and methods , new technologies and training .
Although researchers have always faced restrictions , limitations and many obstacles to overcome, fortunately scientific progress is undeniable and frequent.
Drones and artificial intelligence , for example, are modern inventions that are revolutionizing the field of scientific research .
Findings ? Hundreds of thousands and based on a wide range of topics: from issues that feed our knowledge about the origin and formation of the universe to achievements linked to the prevention or cure of diseases through vaccines , medications , therapies , etc. In the middle, discoveries appear that provide details to improve human nutrition or that add interesting or curious data about the behavior, needs or life expectancy of different species of animals , to detail some possibilities for reference.
