 The concept of fossil comes from the Latin term fossĭlis , which translates as “that which is obtained by digging.” Fossĭlis , meanwhile, comes from fodĕre (whose translation is “dig” ).
The concept of fossil comes from the Latin term fossĭlis , which translates as “that which is obtained by digging.” Fossĭlis , meanwhile, comes from fodĕre (whose translation is “dig” ).
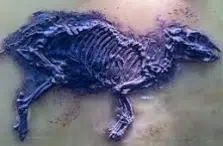
The remains of an organism and organic substances that present a certain degree of petrification are known as fossils. Fossils are naturally located in the various earth layers.
It can be said that fossils are vestiges of beings that lived in the past . These traces ( bones , eggs, etc.) are preserved converted into sedimentary rocks thanks to the action of minerals .
The formation of fossils is called fossilization , a process that involves alterations in the structure and composition of the remains. When an animal dies, its soft parts decompose or are eaten by other species. The skeleton, on the other hand, can end up covered by sediments (such as clay, mud or sand) that protect it. The minerals that were part of these sediments are then dissolved by the water from precipitation. As the water evaporates, the minerals settle in the gaps of the spongy tissue and finally harden, forming the fossil.
Those rocks that contain fossils can suffer the consequences of erosion and thus the remains are exposed. The science dedicated to the analysis of fossils is called paleontology .
A paleontologist , therefore, is dedicated to searching for fossils in sedimentary rocks. Once the fossils are found, they are dug up and cleaned for study. Thanks to paleontology, for example, we can know a lot about dinosaurs , animals that became extinct millions of years ago.
 We often associate the concept of fossil with dinosaurs, but it is important to understand that there are fossils of different species , both animals and plants. In Canada, for example, the oldest fish fossil on record, the Metaspriggina , was discovered, dating back approximately 505 million years. Fortunately for scientists, the remains are so well preserved that they have allowed them to estimate many of the species' facial features.
We often associate the concept of fossil with dinosaurs, but it is important to understand that there are fossils of different species , both animals and plants. In Canada, for example, the oldest fish fossil on record, the Metaspriggina , was discovered, dating back approximately 505 million years. Fortunately for scientists, the remains are so well preserved that they have allowed them to estimate many of the species' facial features.
Another of the most relevant fossils is that of Megalosaurus , a genus of dinosaurs that lived in the Jurassic period, about 166 million years ago in present-day Europe, and probably also in Africa, Asia and America. In 1676, a group of excavators found a partial femur in England and it was examined by an Oxford professor, who initially claimed that they were looking at the remains of a human giant. It was only two centuries later that this fossil was formally associated with a dinosaur and the species received its scientific name.
Beginning in the 18th century, many European paleontologists spent years unearthing peculiar-looking bones near rivers and lakes. When naturalist Georges Cuvier intervened, the puzzle was solved: they had discovered the fossil of Mosasaurus , a genus of sauropsids that inhabited parts of modern-day Western Europe and certain regions of the American continent until approximately 66 million years ago. It was named this way because it was found near the Meuse River.
In the Animal Crossing video game series, developed by the Japanese company Nintendo , the player must control a human avatar who arrives at a village inhabited by animals and stays to live with them. In your daily life you have several possible activities, almost all of them of your choice, to lead a kind of second life in the game: you can choose to relax by the sea, gather fruits to sell, plant various species of trees, fish or dig up fossils to donate them to the museum , among many other things.
