Before entering fully into the meaning of the term phylogeny, we are going to proceed to know its etymological origin. In this case, we can state that it is a word that is a neologism and that derives from Greek, since it is the result of the sum of several lexical components of said language:
-The noun “phylon”, which can be translated as “tribe” or “race”.
-The root “gene”, which is synonymous with “produce”.
-The suffix “-ia”, which is used to indicate “quality”.
The idea of phylogeny is used in the context of biology to refer to the origin and evolution of species . The concept can also refer to the branch of this science that focuses on the kinship ties that exist between the various groups of living beings.
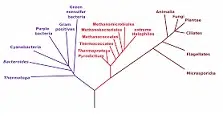 Based on the theory of evolution promoted by the English scientist Charles Darwin , it became necessary to know the evolutionary history of each species. Phylogeny arose with the objective of studying evolutionary relationships, analyzing how the characters of the various taxa are distributed.
Based on the theory of evolution promoted by the English scientist Charles Darwin , it became necessary to know the evolutionary history of each species. Phylogeny arose with the objective of studying evolutionary relationships, analyzing how the characters of the various taxa are distributed.
These data allow the creation of phylogenetic trees , which detail the evolutionary relationships between those species that have a common ancestor. Phylogenetic trees, in turn, allow the development of the phylogenetic classification that establishes the evolutionary closeness between species.
To know the phylogeny of an organism, its DNA , anatomy and morphology must be studied, among many other characteristics. The results of this type of study allow us to know the similarities and differences between species and thus establish their evolutionary relationships.
A clade is a group made up of an ancestor and all of its descendants. Also called a monophyletic group , it consists of the common ancestor (a kingdom , a species, or a population) and all the organisms that descend from it. If any descendants are excluded from this group, it is called a paraphyletic group . Meanwhile, groups composed of species that descend from more than one ancestor are known as polyphyletic .
In the same way, we cannot ignore the importance of what is known as human phylogeny. Specifically, this discipline has among its main objectives to know and understand the bases of evolution, discover the origin of Darwin's theory and, of course, establish the connections between humans, relatives and ancestors.
In what is the phylogenetic tree of the human being we find the modern prosimians, the New World monkeys, the Old World monkeys, the gibbon, the orangutan, the gorilla, the chimpanzee and man.
Precisely starting from that, the timeline in the evolution of the human being is made up of the following figures that determine how we reached the current man: pliopithecus, proconsul, dryopithecus, oreopithecus, ramapithecus, autralopithecus, paranthropus, advanced australopithecus, homo erectus, early homo sapiens, solo man, rhodesian man, neanderthal, gro-magnon man and modern homo sapiens.
