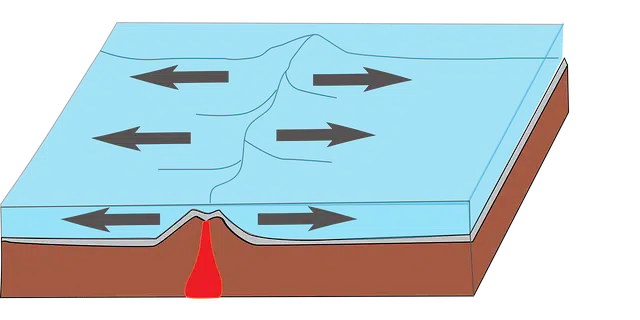
A geological fault is a fracture in the Earth's crust.
Failure is a term with multiple meanings. When it comes from Vulgar Latin, it derives from a word that can be translated as "defect" .
The adjective geological , meanwhile, refers to that linked to geology : the science dedicated to the analysis of the history of the Earth . Geology studies, among other issues, the emergence, development, characteristics and current state of those materials that make up our planet.
From these definitions, we can focus on the idea of a geological fault . This is the name given to a fracture that occurs in the Earth 's crust, associated with the displacement of one of the edges.
What is a geological fault
Faults are flat fractures of the terrain that are generated by the sliding of blocks. Its origin may be due to different types of tectonic stresses. The appearance of mountains, for example, has to do with the formation of faults.
The surface on which the rupture is recorded is known as a fault plane or zone . If the fracture is wide, like the associated deformation, it is referred to as a failure band .
It is important to note that tectonic plates have edges that are related to these faults. These faults can be several thousand kilometers long .
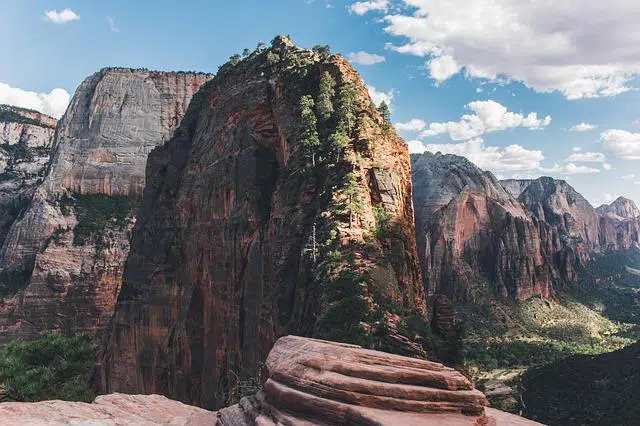

The development of mountain ranges is linked to the formation of geological faults.
tectonic plates
The surface layer of the planet is called the lithosphere . In the lithosphere it is possible to recognize fragments with movement on the asthenosphere (the layer below the lithosphere): these fragments are the tectonic plates .
It can be said, therefore, that the lithosphere is divided into tectonic plates. The edges of these plates concentrate the geological processes that enabled the emergence of basins and mountains .
A geological fault, then, is a fracture of the Earth 's crust . Throughout it the movement of those blocks that the invoice itself separated develops.
It should be noted that, in the absence of lubrication, the tectonic plates do not move smoothly. The protrusions of the blocks cause resistance to movement, which causes energy to accumulate. When this pressure is no longer supported, the rupture occurs, a violent slide of the block takes place and that energy that was accumulated ends up being released as seismic waves that cause earthquakes .
Types of geological faults
According to their characteristics , it is possible to differentiate between several types of geological faults. When a block that is above the fault plane descends relative to another block due to a distension of the tectonic plates, it is a normal fault .
If the movement, on the other hand, is generated parallel to the direction of the failure surface, with a lateral slip of the blocks, it is called a displacement fault . Finally, if the block located above the fault plane rises compared to the one located below the plane, the fault is classified as reverse .
It is essential to know the location and characteristics of the faults when carrying out construction. When a building is erected in a fault zone, the risks of damage are very great. Therefore, the investigations carried out by geologists with the aim of recognizing and locating faults are key to architecture , engineering and other sciences .
