
Ergometry requires the development of intense physical exercise.
In a first approach to the concept of ergometry, it is interesting to analyze how the word is formed. In its composition we find the Greek word érgon (which can be translated as “work” ) and the suffix -metry (which refers to a measurement ).
The notion of ergometry is used in the field of medicine to refer to a study that allows measuring the effort made by the body or carried out by certain muscles in a given situation . It is a test that makes it possible to make diagnoses based on the results obtained and that is used to evaluate an already diagnosed coronary heart disease .
What is ergometry?
Also mentioned as a stress test , ergometry requires the patient to perform physical exercise on a stationary bicycle or treadmill while the effort is progressively increased based on a protocol. Before starting the exercise, two electrocardiograms are performed (one standing and the other lying down) and then, with the test already underway, the electrocardiographic evolution is monitored continuously . Finally, cardiac function is also recorded during the recovery period using different methods.
Monitoring requires the attachment of electrodes to the individual's chest. These electrodes, in turn, are connected to a machine.
The ergometry can last between six and twelve minutes. Recovery time, meanwhile, is estimated between three and five minutes.
Medical observations
The health professional who is in charge of ergometry should pay attention especially when the instance of maximum effort arrives to see if the individual runs out of breath or shows angina . It is important to mention that the test can reveal cardiovascular disorders that do not appear when the subject is at rest.
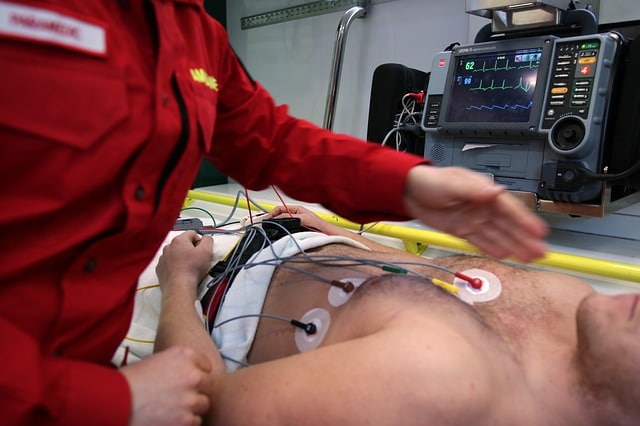
Before the start of ergometry, the patient undergoes resting electrocardiograms.
A patient may suffer from coronary heart disease that does not prevent normal blood flow at rest, but causes problems with physical exertion. This is because the effort increases the work done by the heart, which requires a greater blood supply at that particular moment. Blockage of an artery , in this setting, can cause angina and other conditions.
Ergometry is considered positive if alterations are detected in cardiac monitoring or if the person suffers chest pain while exercising. There are cases of false positives (when the exercise test seems to indicate problems that are later ruled out with subsequent studies) and false negatives (if the test is normal but then the existence of a heart disease that could not be detected previously is revealed).
Patient preparation and contraindications for ergometry
The patient must go to the place where the ergometry will be performed without having consumed alcoholic or caffeinated beverages and without having eaten a large meal in the previous three hours. Additionally, you do not have to have done intense physical exercise in the preceding twelve hours.
It is also recommended to wear comfortable clothing and shoes. The doctor, on the other hand, may indicate the suspension of certain medications the day before the exercise test. Of course, in each particular case, you must consult a specialist and follow their instructions .
Ergometry is contraindicated if the person suffered multiple angina pectoris or a heart attack in the previous four days or if they have inflammation or an infection . In addition, some neurological diseases, bone problems and lung disorders can make the development of this test impossible.
