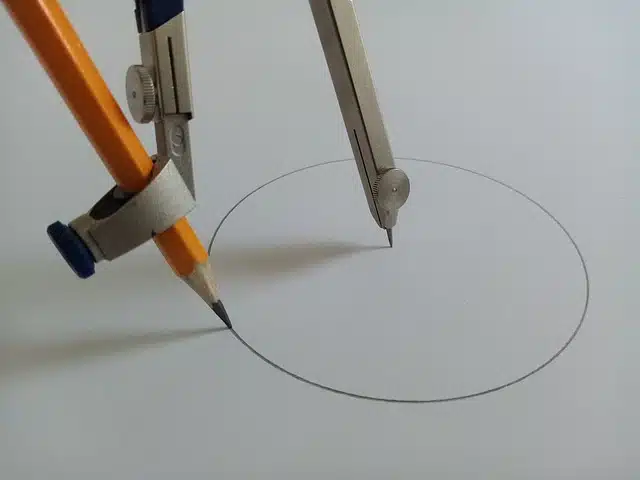
A compass is an instrument that helps draw circles.
A compass is an instrument that has a pair of articulated arms, which are linked together by an axis or a hinge in its upper sector. With a compass it is possible to record distances and draw arcs or circles .
Typically, the compass features a point at the end of one arm and a pencil at the end of the other arm. In this way, the user sticks the tip into the paper and then separates both arms according to the radius of the circumference he intends to draw. Finally, with one movement, he makes the pencil move over the paper to draw the circle with the desired characteristics.
The flat compass
The flat compass is a device in which four geometric instruments are merged into one: the ruler, the square, the protractor and the compass described in the previous paragraph. Thanks to its versatility, it is not necessary to go from one to the other when we want to draw geometric figures on a sheet or a blackboard.
Its invention is attributed to a teacher from Mexico named Carlos Ricardo Hernández Ortiz , who presented it in 2007 to make up for the lack of materials in some schools in his country.
The concept in music
The notion of beat is also used in the field of music to refer to the cadence or rhythm of a composition. The compass can be understood as an entity made up of various figures that are distributed in sets, contrasting the unstressed parts and the accented parts.
The sign that establishes the value links between sounds , or that sets the rhythm of the composition, is called compass. The same thing happens with the movement made with the hand to precisely mark each measure. The term, on the other hand, refers to the space on the staff delimited with vertical lines where the various notes of a measure are written.
According to the number of beats , it is possible to differentiate between binary measures , ternary measures and quaternary measures . Furthermore, according to other subdivisions that are usually established, one can speak of simple measures or compound measures .

A compass together with a square and a letter G make up the symbol of Freemasonry.
The compass as a symbol
The compass is also one of the symbols of Freemasonry , along with the letter G and the square.
Masonic symbology is the study of Freemasonic symbols to find their meanings and understand the messages they represent, which are based mainly on the instruments used by ancient French masons. It is believed that the expressions of Freemasonry can only be fully understood by the Freemasons themselves, and their symbols can be decoded using two systems, which increases their complexity.
The pantometer
The compass of proportions , also called pantometer , is an instrument that is used for calculating or solving various problems in an indirect way. It is an analog calculator that relies on proportionality between segments.
It appeared for the first time in 1555 in France, according to a patent in the name of Abel Foullon , who called it a "holometer." However, it became popular thanks to the Italian philosopher Galileo Galilei .
The compass as a navigation instrument
Compass is also the common name given to the navigation instrument that allows determining the direction of a ship (in other words, it is a compass ). The reference point is always north, and in this way it is possible to calculate the angle of deviation with respect to this cardinal point and thus deduce the position on a map, combining this data with others.
Given the technological advances since the appearance of the first compass, there are currently several types, such as magnetic , gyroscopic and electronic , each of which performs calculations differently, in addition to offering advantages and disadvantages with respect to to the others.
