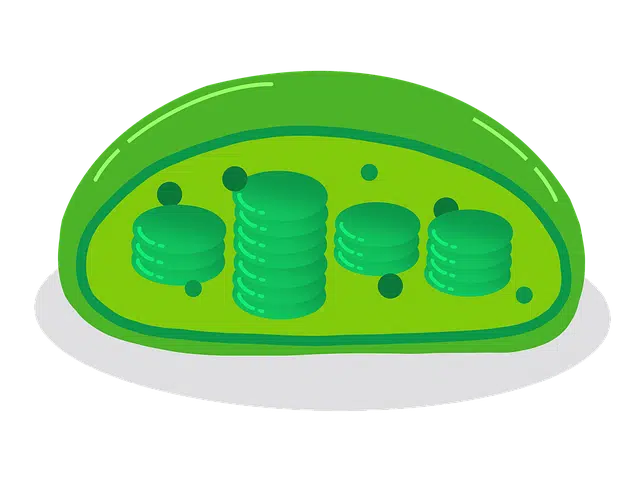
Plant cells are the fundamental units of plants.
A cell is the fundamental unit of a living organism that has the capacity for independent reproduction. There are two main types of cells: eukaryotes (which house genetic information in a cell nucleus) and prokaryotes (whose DNA is dispersed in the cytoplasm since they do not have a differentiated cell nucleus).
A vegetable , on the other hand, is an organic being that grows and lives without changing its location by voluntary impulse. Plants have the ability to synthesize their own food through the process of photosynthesis .
The plant cell , therefore, is the one that forms this type of organisms. These are eukaryotic cells, whose nucleus is delimited by a membrane. The cell wall is cellulose and has the necessary rigidity to prevent changes in position and shape.
Types of plant cells
There are many types of existing plant cells. However, among the most significant we could highlight the following:
Sclereids are identified because they make up very hard tissues such as the peels of certain fruits.
Meristematics . Under this name are the plant cells that are responsible for ensuring that any plant can grow and develop both in length and width.
Colenchymatic are those that are known primarily for their supporting function.
Parenchymatic . In this case, this term is used to refer to all those plant cells that participate in photosynthesis and in the storage of all those substances that are used as a reserve.
It is possible to differentiate between different types of plant cells.
Its components
Plant cells contain a central vacuole (which stores and transports water, nutrients, and waste) and plastids (structures that synthesize food). The presence of chloroplasts, on the other hand, turns plants into autotrophic beings that produce their own food through photosynthesis.
The existence of plasmodesmata (cytoplasmic bridges) allows communications between plant cells. These bridges, which are usually located in areas of the cell where the wall is thinnest, facilitate the circulation of solutes and water.
However, we must not forget another important series of parts that give shape to every plant cell. Among them we would have to highlight the chromatin , the mitochondria, the tonoplast, the dictionsome, the vacuole, the nucleolus, the peroxisome or the thylakoid.
Differences between plant cells and animal cells
Among the main differences between plant cells and animal cells, the cellulose wall, chloroplasts and the existence of a single vacula in the case of plants stand out.
The cell wall or cellulose is a fundamental element in all types of plant cells and is basically made up of two types: the primary wall and the secondary wall. The first is characterized by being thin, flexible and found especially in cells that are young or that are in the process of development and growth.
The secondary wall, for its part, is the one that appears on the primary wall once it has stopped its growth phase.
The vacuole, on the other hand, is what functions as a storage or reservoir for water as well as another important series of chemical substances.
