Before getting to know the meaning of the term prokaryotic cell, it is necessary to know the etymological origin of the two words that give it shape:
-Cell is a word that derives from Latin, specifically from “cellula”, which can be translated as “small cell”. It is formed from the noun “cella”, which is synonymous with “cell”, and the diminutive “-ula”.
-Prokaryote, on the other hand, is a neologism formed from the following components of Greek roots: “pro-”, which can be translated as “before”; the word “karuon”, which is synonymous with “nut” and “tes” which is equivalent to “agent”.
The essential units of living beings, capable of reproducing independently, are called cells . These microscopic units have a region known as cytoplasm and a nucleus .
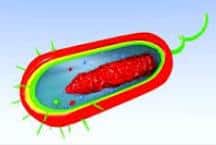 Prokaryotic cells are those whose nucleus is not delimited or defined . In this way they differ from eukaryotic cells , which do have a delimited cell nucleus separated from the cytoplasm.
Prokaryotic cells are those whose nucleus is not delimited or defined . In this way they differ from eukaryotic cells , which do have a delimited cell nucleus separated from the cytoplasm.
It is important to mention that, in the nucleus, the cell houses genetic information. In the case of prokaryotic or prokaryotic cells, since they do not have a defined nucleus, this material is distributed in a region of the cytoplasm known as the nucleoid .
In most prokaryotic cells it is possible to distinguish the cell wall , the plasma membrane , the cytoplasm (with the nucleoid ), the ribosomes and the so-called prokaryotic compartments .
In addition to all the above, we can establish that prokaryotic cells have two types of nutrition:
-Autotrophic feeding, which means that they can feed themselves. Specifically, they can do it using organic matter, making use of sunlight through what is known as photosynthesis or using inorganic matter.
-Heterotrophic feeding. This occurs when these prokaryotic cells need other organisms, which they parasitize, in order to obtain the nutrition they need to live. This type of parasitization can be of various types: symbiotic nutrition, which is when cells and organisms “come to an agreement” because both benefit; saprophytic nutrition, which takes place when there is a decomposition process of the organism; and parasitic nutrition, which is when it parasitizes the organism without causing death.
As for what reproduction is, it can also be of two types: parasexual or asexual.
Biologists link prokaryotic cells with the origin of life and maintain that the appearance of eukaryotic cells made the development of more complex organisms possible. The process that allowed the creation of eukaryotic cells is called eukaryogenesis .
There was, according to one hypothesis , a “last universal common ancestor” : LUCA , according to the acronym in English. This would be a prokaryotic single-celled organism from which the rest of living beings descend.
The vast majority of single-celled organisms, in fact, remain prokaryotes. Bacteria , for example, are prokaryotic organisms. They are made up of prokaryotic cells, with their genetic material dispersed in the cytoplasm area.
Archaea are other organisms with prokaryotic cells. Previously they were considered bacteria but later, when several differences with these organisms were discovered, this type of domain was “independent” in the domain Archaea .
