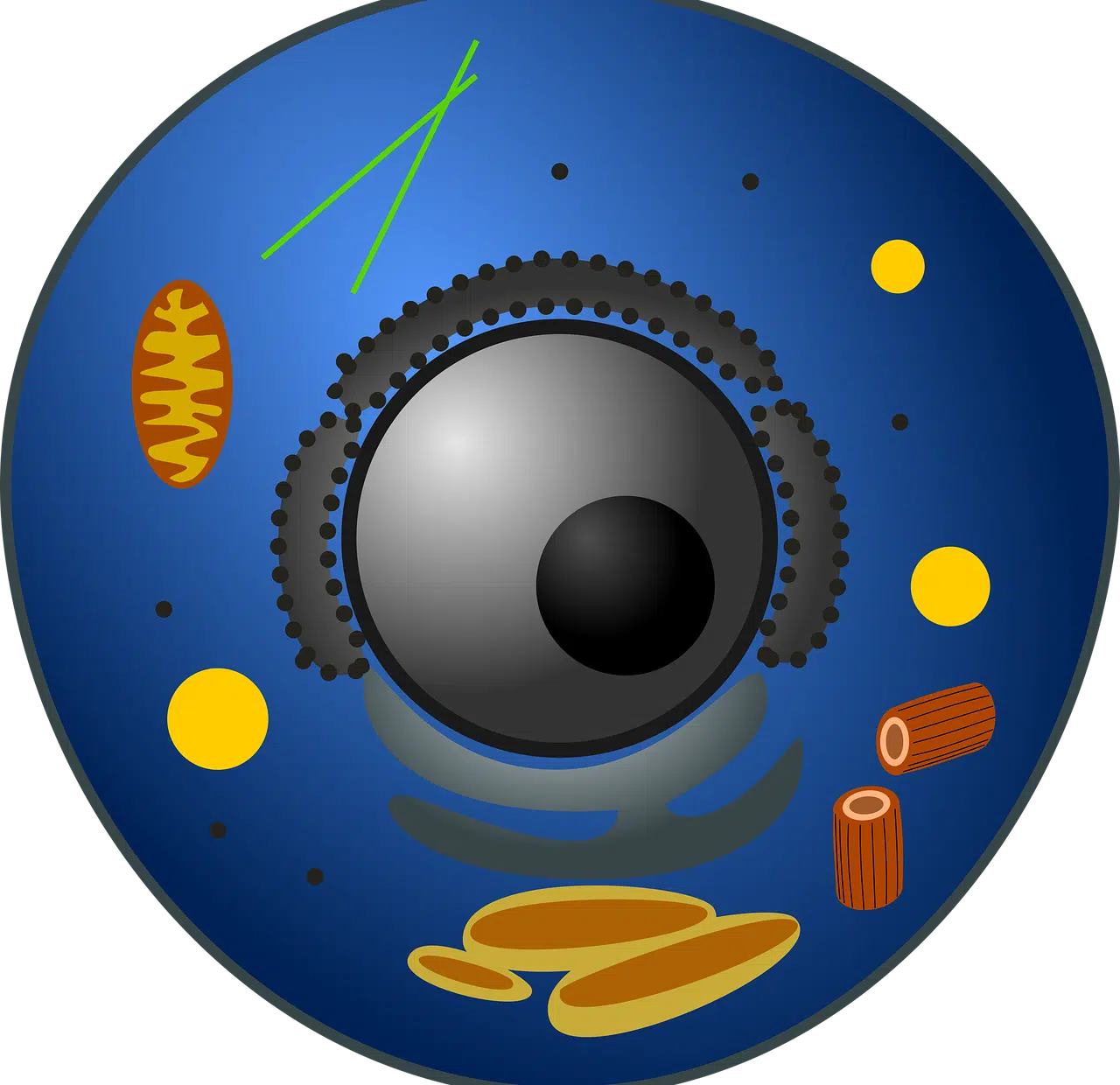
Eukaryotic cells are present in the animal, plant and fungal kingdoms.
Eukaryotic cells are those that have a cell nucleus defined by the nuclear envelope or membrane . This layer is composed of a double unit of lipid membrane: an inner and an outer membrane separated by the perinuclear space.
It should be noted that the adjective eukaryotic is synonymous with eukaryote : a qualifier used with respect to cells that have a differentiated nucleus , which is covered by a membrane .
The nucleus of eukaryotic or eukaryotic cells contains genetic information . Molecules can enter and leave this cell nucleus through the pores in the nuclear membrane.
Etymology of the concept
Before moving forward with the definition of the concept, it is important to know the etymological origin of the two words that give it shape:
- Cell is a noun derived from the Latin cellula , which can be translated as "small cell" . It is the result of the addition of cella – which is synonymous with “cell” – and the suffix diminituvo -ula .
- Eukaryote , on the other hand, is a neologism formed by the sum of several components of Greek origin: the component eu , which means "good" ; the noun karyon , which is equivalent to "nut" ; and the -tes element, which is used to indicate "agent" .
Types of eukaryotic cells
It is important to establish, in addition to everything stated above, that when talking about eukaryotic cells, reference is made to several clearly differentiated types:
- Plant cells , which are made up of a vacuole , cell wall, plastids and plasmodesmata.
- Animal cells , which have vacuoles, centrioles, cell walls and chloroplasts.
- Fungal cells , which are very similar to plant cells but have less definition.
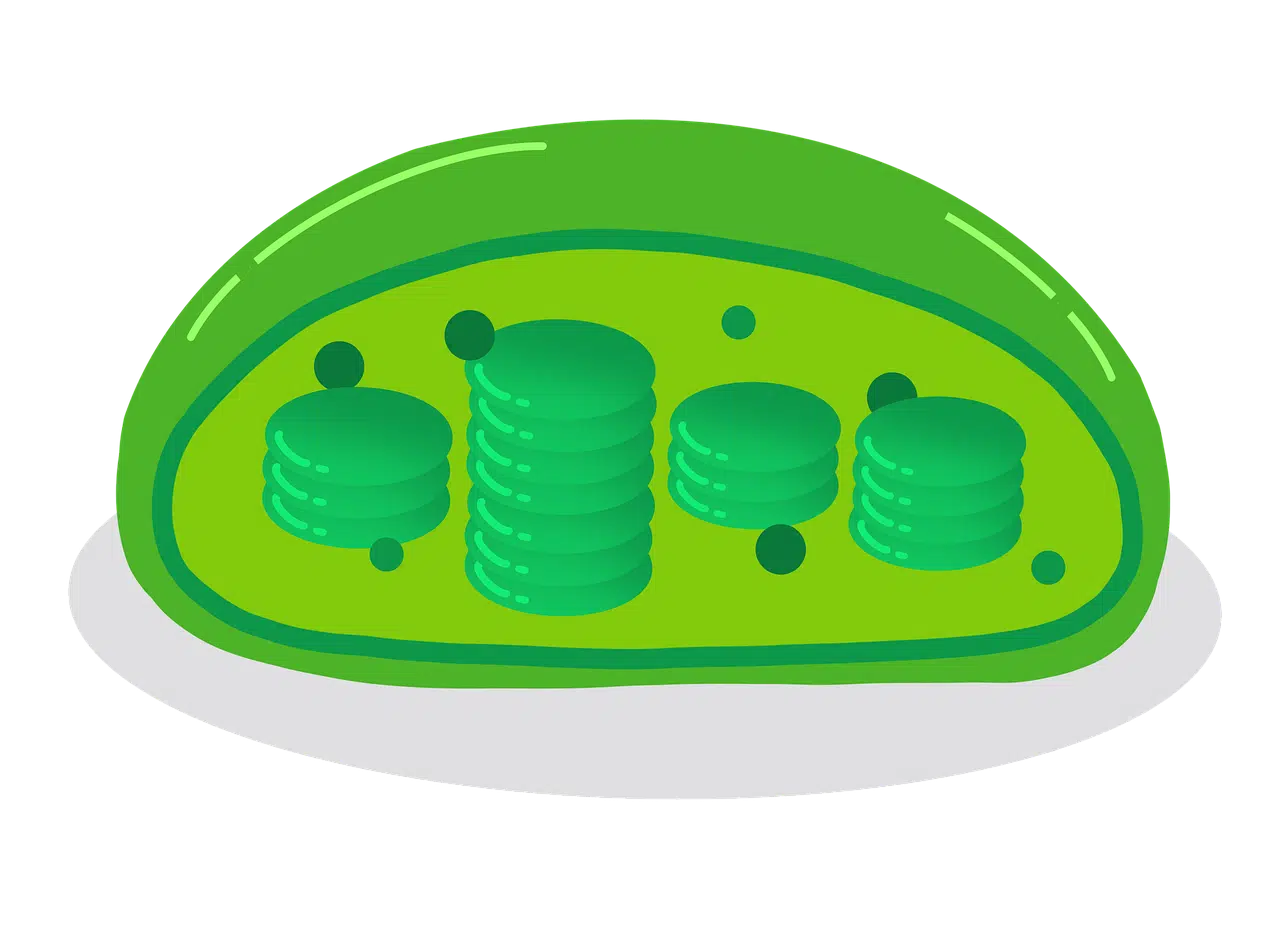
In plants, eukaryotic cells have chloroplasts to carry out photosynthesis.
Its parts
It is possible to recognize different parts in a eukaryotic cell. This type of cell is surrounded by a cell membrane (composed of proteins, phospholipids and other elements) that gives it its shape. Outside this membrane, in the case of cells of the Plant kingdom and the Fungi kingdom, is the cell wall .
The central organelle, as we have already indicated, is the nucleus that houses DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) , organized in chromosomes . Likewise, in the cell nucleus is the nucleolus , where the transcription of ribosomal RNA (ribonucleic acid) takes place, which then constitutes ribosomes .
It should be noted that eukaryotic cells have cytoplasm , an aqueous medium formed by the cytosol and multiple organelles or organelles ( mitochondria , lysosomes , vacuoles , cilia , chloroplasts , centrioles , leukoplasts , Golgi apparatus and cytoskeleton , among others depending on the type of cell) . The smooth endoplasmic reticulum and the rough endoplasmic reticulum are also located in the cytoplasm.
Eukaryotic cells participate in the body's immune response.
Functions performed by a eukaryotic cell
Eukaryotic cells fulfill various functions. Metabolic reactions take place in them that provide them with the energy necessary for their development, such as protein synthesis and cellular respiration. These cells also absorb nutrients.
Mitosis and meiosis are the processes that allow it to reproduce. DNA replication and gene expression are also part of the functions of the eukaryotic cell.
Playback methods
Regarding reproduction, it is important to establish that eukaryotic cells can carry it out by three methods:
- Budding occurs when a protuberance appears on the cell and it develops progressively until it leads to the formation of another cell.
- Bipartition , which, as its name indicates, consists of one cell dividing into two, giving rise to a pair of identical cells.
- Sporulation that occurs when the cell divides its nucleus into several replicas and also the cytoplasm into new cells.
From prokaryotic cells to eukaryotic cells
While eukaryotic cells have a defined nucleus, prokaryotic cells (or prokaryotic cells ) are those whose cell nucleus is not defined. Therefore, in prokaryotic cells, genetic information is dispersed in an area of the cytoplasm known as the nucleoid .
Biologists claim that the evolution of prokaryotic to eukaryotic cells allowed for greater complexity of life forms. Eukaryotic cells enabled the development of multicellular beings such as animals and plants and favored, in the long term, the creation of multiple species.
The process that led to the creation of eukaryotic cells is known as eukaryogenesis . Prokaryotic organisms are linked to the very origin of life; That is why eukaryotic organisms are derived from them. The specific moment that led to the emergence of the first eukaryotic cell, however, is not clear, and there are various theories in this regard.
cancer
There are multiple disorders that can affect eukaryotic cells and lead to different types of problems for the body. One of them is cancer .
This disease is linked to changes in the specific DNA sequence, which generates uncontrolled cell division . This can be associated with oncogenes (which cause cancer when they are more active) or tumor suppressor genes (which usually block the disease but, when eliminated or altered, can promote it).
