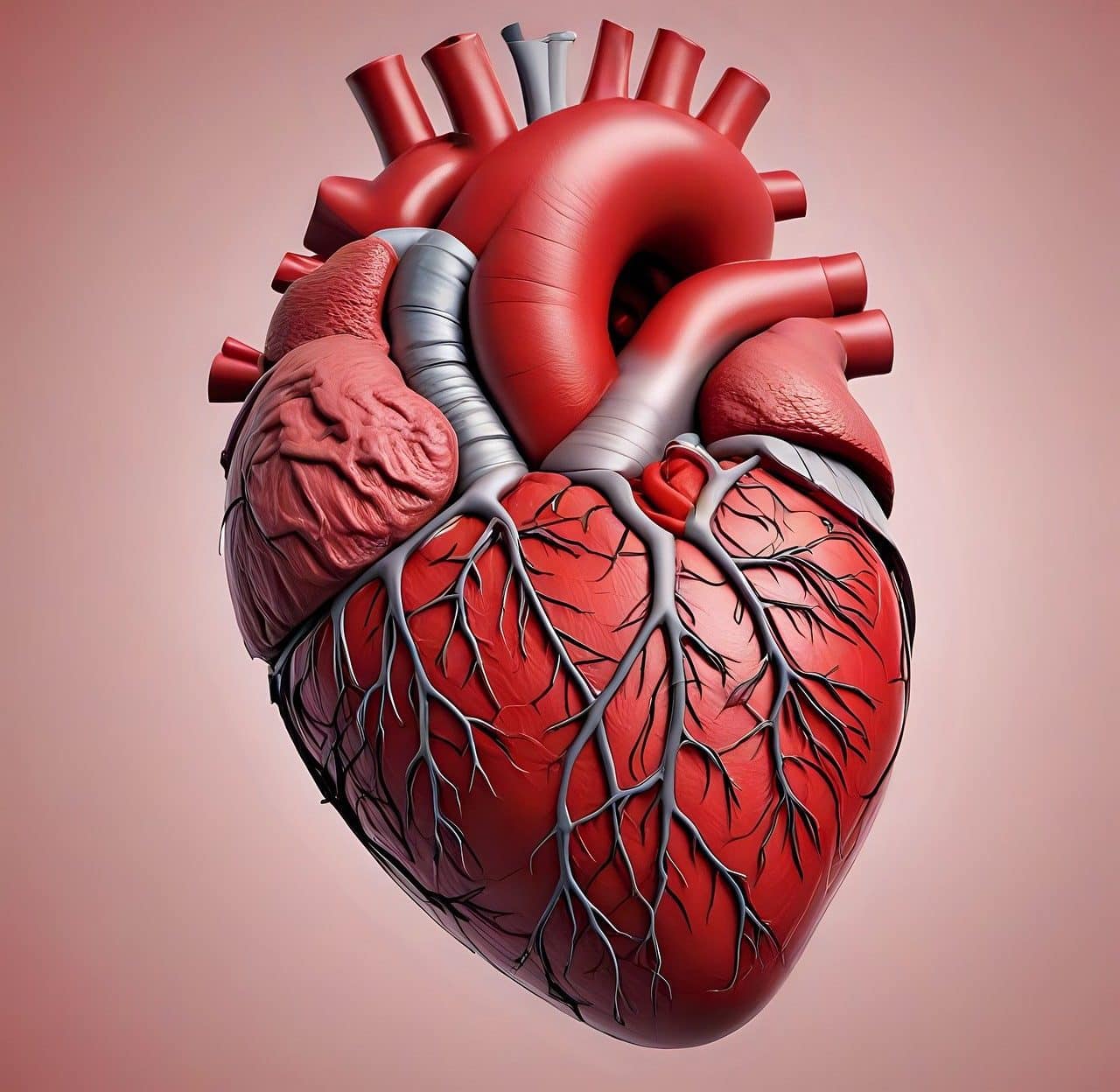
The anatomy of the heart is of interest to cardiology.
Anatomy is the analysis of the conformation, state and links of the different sectors of the body of the human being and other living beings. The term has its origin in the Latin anatomĭa which, in turn, comes from a Greek term that means "dissection" .
Anatomy, therefore, studies the characteristics, location and interrelationships of the organs that are part of a living organism. This discipline is responsible for developing a descriptive analysis of living beings.
history of anatomy
The first anatomical study dates back to 1600 BC. C. and is recorded in an Egyptian papyrus. Through it we can know that this ancient civilization had important knowledge regarding the viscera and human structure , although they knew little about how each organ worked.
The person who increased knowledge in this branch was Aristotle , in the 4th century BC. C. At that time, the first dissections of human corpses were carried out and, thanks to them, the functioning of the different parts of the organism was gradually known.
Later, the Romans and the Arabs advanced with research and, later, during the Renaissance, new studies emerged that became known as modern anatomy that was based, not on the writings of a few thousand years ago, but on the real observation that various scientists made. Among them was Andrés Vesalius ( 1514-1564 ), one of the key representatives of this science .
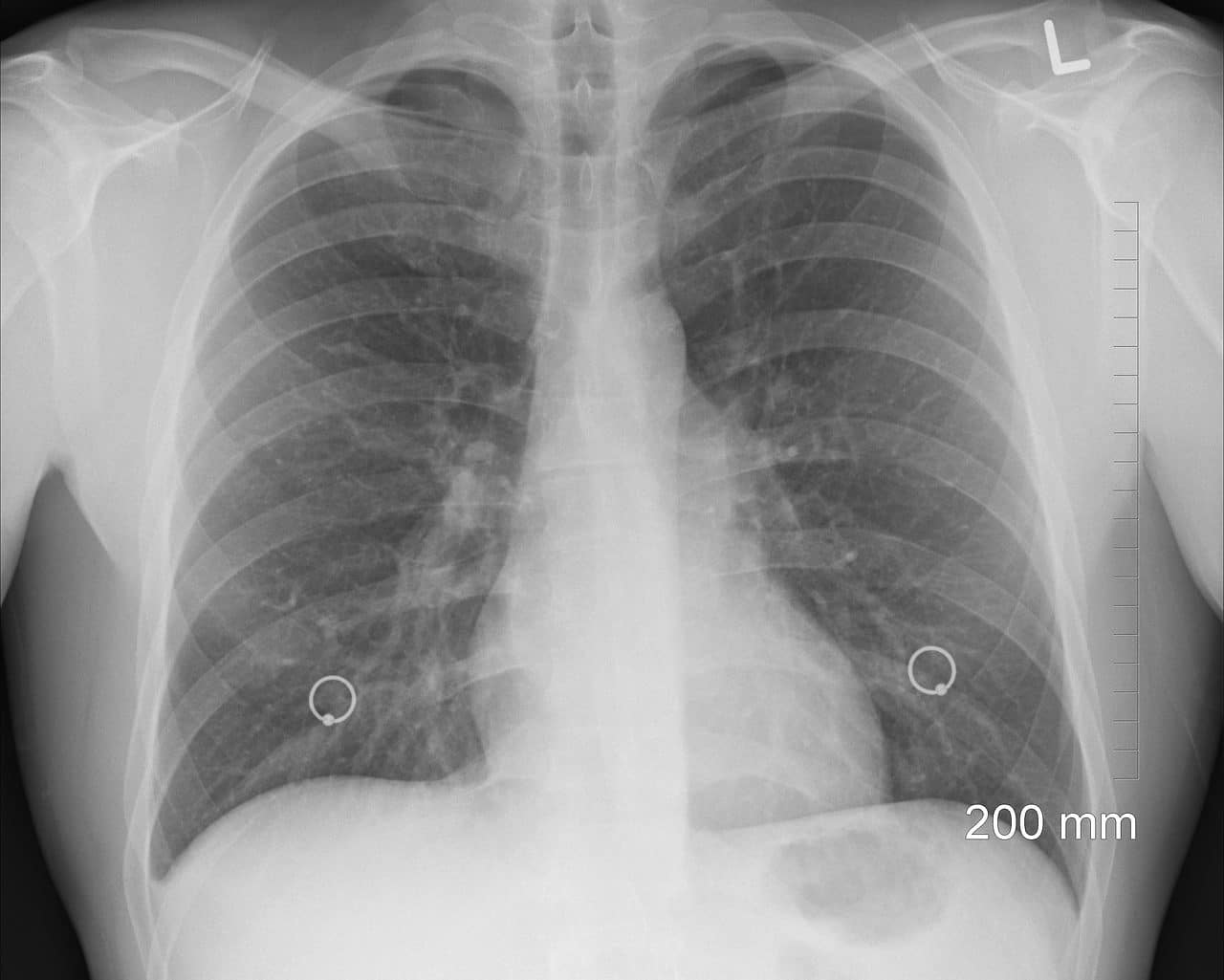
An x-ray, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and computed tomography (CT) are studies that allow us to see the internal anatomy.
The study of the human being
Human anatomy , as its name indicates, is dedicated to the study of the structures of the human body. In general, it is oriented towards knowledge about macroscopic structures, since other disciplines ( histology and cytology , among others) are responsible for minor elements, such as cells or tissues . The human body can be understood as an organization of structures at different levels: molecules that form cells, cells that make up tissues, tissues that establish organs, organs that are integrated into systems, etc.
It is worth mentioning that anatomy can also focus on the study of biological processes , as is the case of the development of life (through the study of embryos) or the pathologies that individuals of a species may suffer (by studying diseased organs to detect patterns of common diseases among living beings).
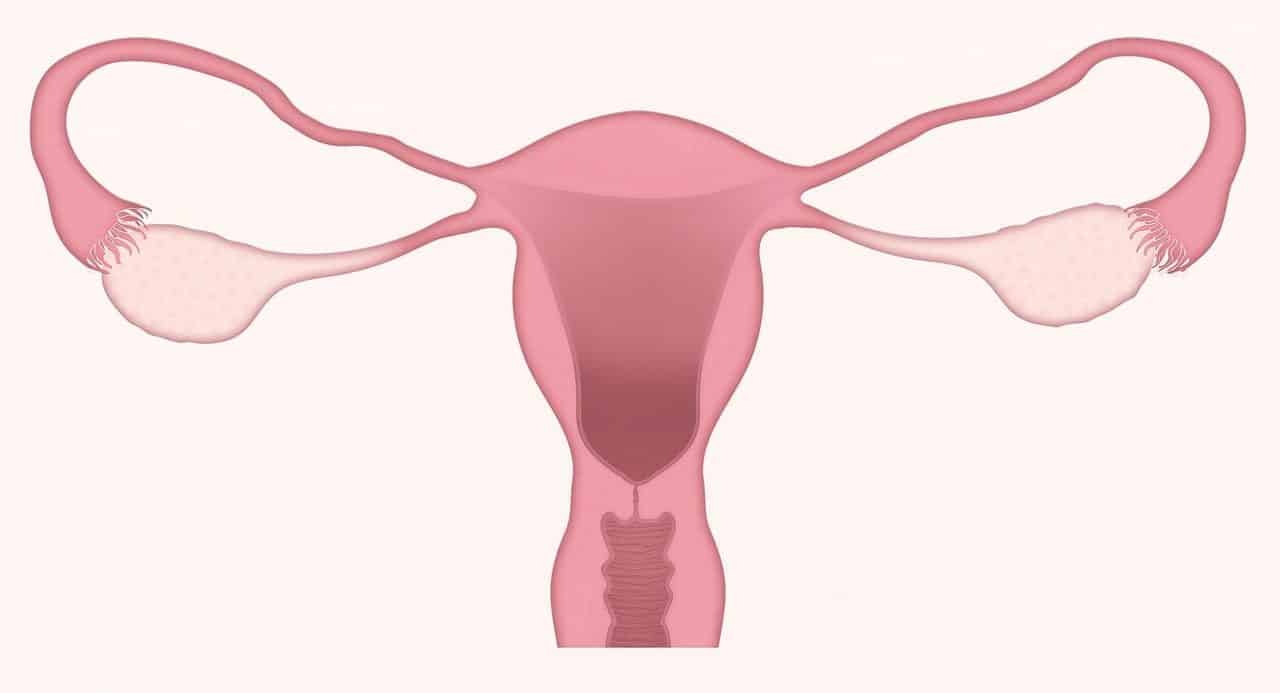
The anatomy of the reproductive system presents great differences according to sex.
Types of anatomy
According to its approach, it is possible to divide anatomy into clinical or applied anatomy (links a diagnosis to a treatment), descriptive or systematic anatomy (divides the organism into systems: circulatory system, digestive system, respiratory system, etc.), regional or topographic anatomy (appeals to spatial separations), physiological or functional anatomy (focuses on organic functions) or pathological anatomy (specialized in damage suffered by organs), among others.
In turn, according to the type of organisms that this science studies, it can be called plant anatomy or animal anatomy .
Plant anatomy, also known as plant anatomy , is a branch of botany that is responsible for studying the internal structure of species that belong to the kingdom Plantae . This science includes the study of organisms starting from the cellular level and covering both tissues and bone structure.
Animal anatomy, for its part, can be subdivided into human anatomy (already detailed above in this article) , animal anatomy and comparative anatomy . The first two are those that study each species (humans or other animals) according to the behavior of their cells and organs. Comparative anatomy is what complements the first two and allows us to establish similarities and differences between different types of living beings in the Animal kingdom .
Other uses of the notion
On the other hand, there are also surgical anatomy (it is responsible for studying the best ways to perform operations on the various organs) and artistic anatomy (it is responsible for anatomical issues linked to the representation of the human figure in art ), which They allow you to connect anatomy with other activities.
In turn, anatomy can be named taking into account the techniques used for its study, such as microanatomy or radiological anatomy .
Anatomy Examples
We can find examples of anatomy in the studies carried out on the different parts and structures of the body. Thus, anatomy allows us to examine the skeletal system with its bones ; the muscular system with the muscles ; the circulatory system with arteries , veins and capillaries ; the nervous system with neurons ; the respiratory system with the lungs and other organs; the digestive system that has the stomach as its main part; and the urinary system ( kidneys ), among other schemes.
The eyes , mouth , brain , spinal cord , joints , glands and blood , among many other elements and substances, are also studied by anatomy. The knowledge provided by its experts helps in the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of diseases, for example.
