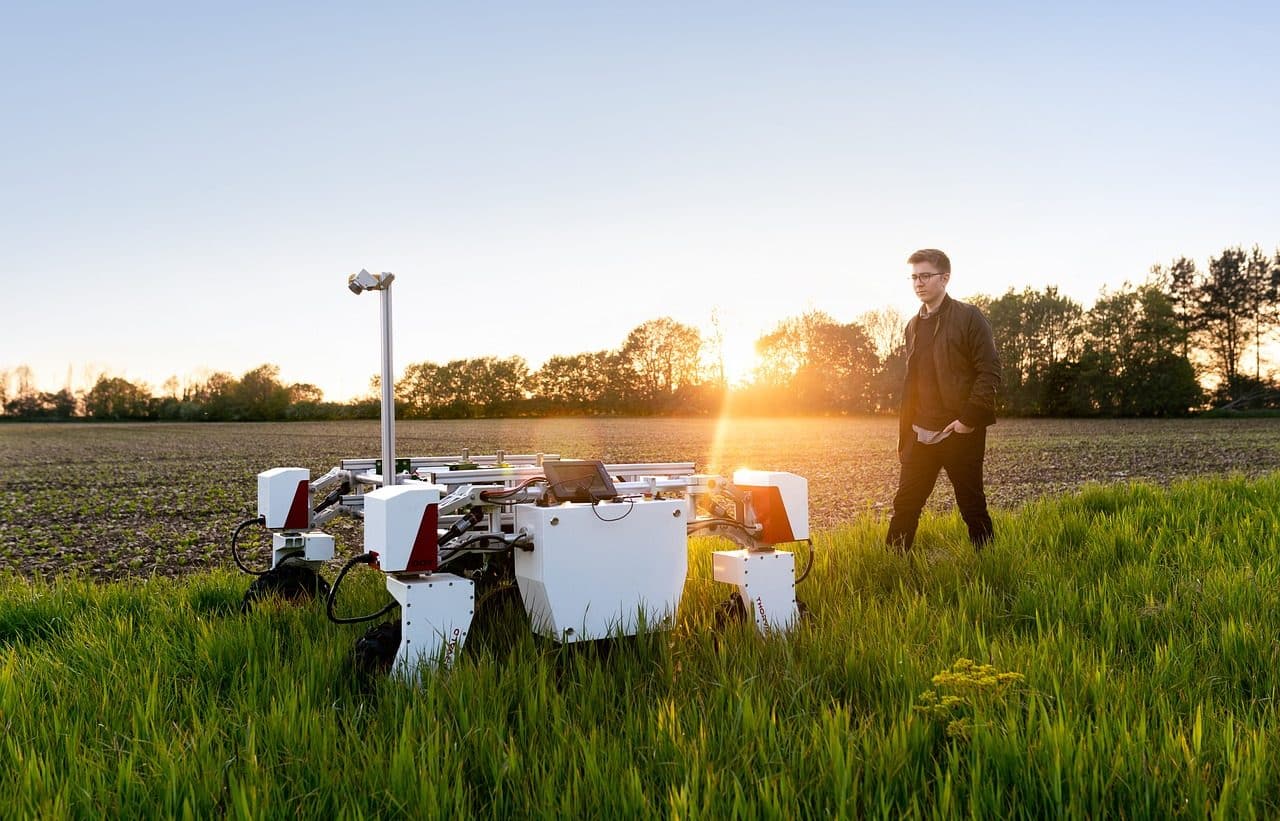

Precision agriculture can use agricultural robotics, autonomous machines and remote sensors.
Precision agriculture is a type of agricultural activity that is based on the use of various techniques and technologies to optimize production . Through different processes and actions, the aim is to obtain and analyze information to manage multiple variables with greater efficiency.
Precision agriculture can be understood as a management strategy . By collecting and comparing data, it contributes to decision making considering the estimated variability.
History of precision agriculture
The history of precision agriculture begins in the early 1980s in the United States. The concept was coined in that country, although the application of technological resources for crop planning already existed.
USA,Australia y Canada están consideradas como las naciones pioneras en agricultura de precisión. La utilización del GPS (sistema de posicionamiento global), drones, espectrorradiómetros, estaciones meteorológicas automatizadas, imágenes satelitales, aspersores inteligentes, robots de cosecha, sensores de nutrientes del suelo y tecnología de seguimiento y trazabilidad caracterizan a estas prácticas.
The use of the Internet of Things ( IoT ) in agriculture was decisive for the advancement of this modality in recent years. With machines connected to agricultural data management systems, large amounts of information can be generated and processed, giving rise to the so-called agriculture 4.0 (which involves the digitalization of processes).
The use of big data in agriculture , in this framework, is another of the drivers that drive this strategy , which in Latin America is in full growth, especially in Argentina and Brazil .
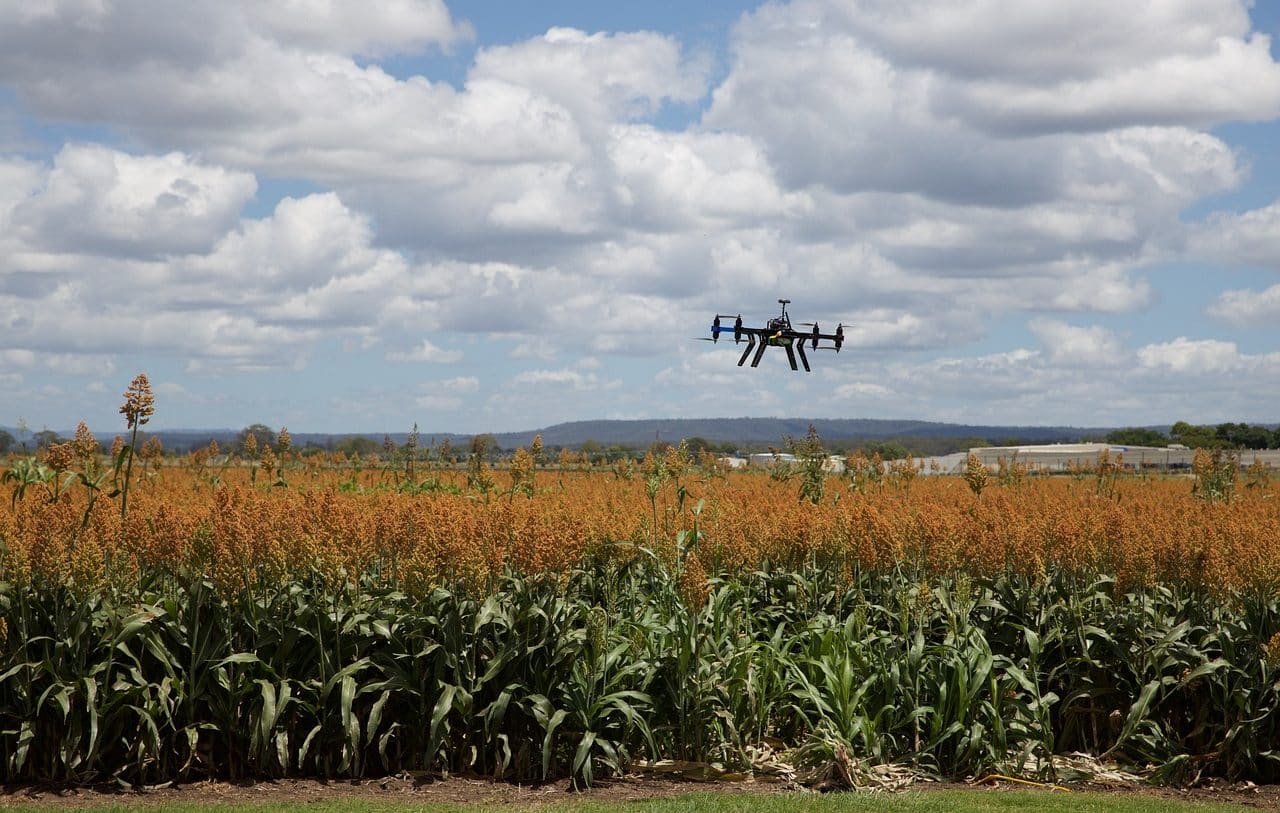

Precision agriculture software is key to processing information collected with the use of GPS in tractors and drones, for example.
Your applications
The applications of precision agriculture occur in each step or stage of agricultural activity . From surveying to harvesting, through leveling and land preparation, sowing and fertilization, each phase can be carried out efficiently thanks to these resources.
Precision agriculture allows you to analyze the state of the soil and meteorological and climatic factors before, during and after planting. This precision contributes to an optimization of production and contributes to sustainability.
Specifically, precision agriculture with sensors, drones, satellites and other devices is applied to monitor crops and yields , early detection of pests and diseases, and predict harvests, to name a few possibilities.
Adequate data analysis in precision agriculture is essential for decision making.
Benefits of precision agriculture
The benefits of precision agriculture are greater efficiency and sustainability , as we already mentioned. It also enhances competitiveness , which has a social effect: there is a direct link between precision agriculture and agricultural employment since, with more competitive crops, there is more work and the migration of the rural population to the cities is reduced.
In a broad sense, it is often said that precision agriculture means making the best possible decisions at the right times and in the right places . This means, for example, that pesticides are not used massively and indiscriminately over the entire surface of the field, but rather that they are only applied in the appropriate place and when necessary.
Another advantage of precision agriculture is that its products have greater traceability . Therefore, consumers can access data that allows them to define their purchase according to sustainability or proximity of production .
It should be considered that precision agriculture requires, in the first instance, a higher investment than other types of agricultural projects. In any case, increasing productivity and improving competitiveness make it possible to overcome this issue.
The importance of drones
Among the multiple technological advances that are applied for agricultural development, precision agriculture with drones is one of the most widespread practices globally. It must be remembered that a drone is an unmanned flying vehicle .
Each drone can be equipped with numerous devices. Multispectral cameras , to mention one of these devices, simultaneously capture images at different wavelengths, which allows a comparison between the different temperatures in the crops.
Drones can also have software to measure the intensity of radiation reflected by plants, a key piece of information to estimate quality and level of development. The application of exact doses of pesticides and fertilizers, millimeter mapping for irrigation calibration and monitoring of large areas of land are other contributions of these aircraft to precision agriculture.
Precision agriculture and technological integration
According to specialists, one of the current challenges of agriculture is the integration of different technologies so that precision agriculture is combined and enhanced with other production and management modalities.
Artificial intelligence , the Internet of Things , robotics and other resources, when fully integrated, will favor a general improvement of all operations. For example, while the Internet of Things already used in precision agriculture simplifies obtaining information, artificial intelligence and machine learning can facilitate the interpretation of data to transform it into knowledge that can be applied in practice.
Through the use of algorithms and artificial intelligence, more and better predictive analyzes and faster and more effective identification of possible anomalies are also expected. This way you can work on prevention , but also on immediate correction .
