
A zoonosis is a disease that is transmitted from an animal to a person or vice versa.
Zoonosis is the infection or disease of the animal that is transmissible to humans under natural conditions or vice versa. The term derives from two Greek words: zoon ( "animal" ) and nósos ( "disease" ).
In a more specific sense, the disease that is transmitted from animal to man is anthropozoonosis , while that which is transmitted from person to animal is known as zooanthroponosis .
It is common that, in both cases, these are diseases that affect various vertebrates, including humans. Its treatment and prevention requires an interdisciplinary task that includes doctors, veterinarians and zoologists .
Types of zoonoses
Specifically, we can determine that there are several clearly defined groups of zoonoses:
- Viruses , including Japanese encephalitis, yellow fever, rabies...
- Fungal : ringworm or histoplasmosis can serve as a clear example.
- Prionic : in this case, the most significant is the infection or disease known by the colloquial name of "mad cow disease" .
- Bacterial . Under this name are pathologies such as cat scratch disease, tuberculosis, brucellosis or bubonic plague.
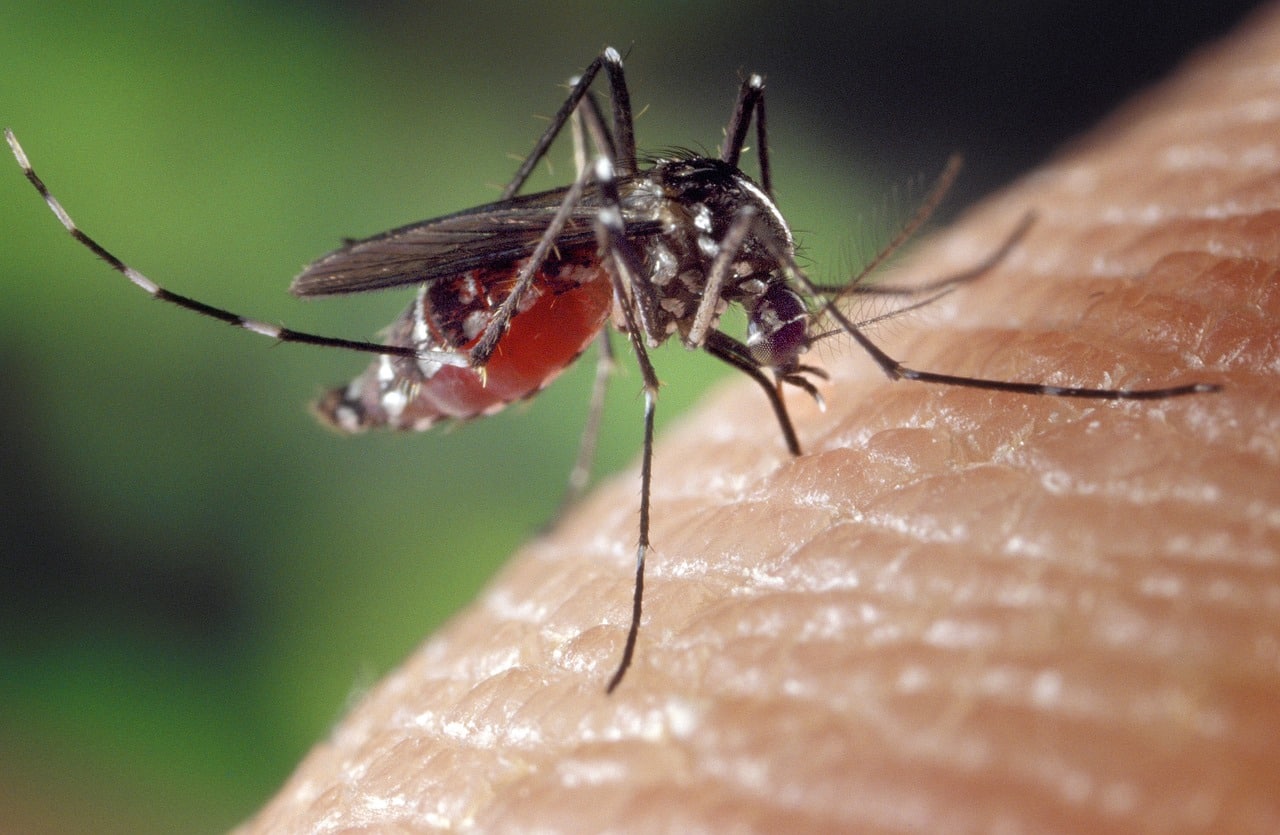
Dengue is a zoonosis transmitted by the Aedes Aegypti mosquito.
Some diseases
There are multiple diseases that are part of zoonosis. Yellow fever and dengue , for example, are transmitted to humans through the action of an insect that acts as a vector of the virus.
Avian influenza , also known as avian influenza , is an infectious viral disease that affects birds and can infect humans, pigs and cats, among other species. Rabies (with animal vectors such as dogs, raccoons and bats) and brucellosis (affecting cows, horses, sheep and pigs) are also examples of zoonoses.
Zoonoses prevention
Vital and fundamental is that they carry out the necessary hygienic-sanitary measures to prevent zoonosis from occurring. In this way, the current regulations established in this regard determine that two actions must be carried out in an irremediable manner:
- Programs for the prevention, control and eradication of different types of zoonoses in animals.
- Surveillance and notification system for possible cases of zoonoses.
More precisely, we can determine that both actions are carried out, for example, by Spain because the European Union imposes it so. However, we must not forget that the aforementioned country has its own microbiological information systems that are exclusively dedicated to investigating zoonoses, their causes, their treatments...
Specifically, those Spanish areas are especially focused on issues such as salmonellosis, tuberculosis or brucellosis. Of course, without forgetting the exhaustive analysis of zoonotic agents, trichinellosis or the cases that have been detected in the country due to one circumstance or another.
Food safety
The transmission of the disease from animals to humans occurs, in many cases, through the consumption of animal products. Food safety , therefore, is very important to avoid zoonosis.
In addition to consumer awareness (who must comply with certain habits such as cooking hamburgers well or boiling sausages for at least three minutes to avoid problems), authorities must control compliance with various measures in establishments that produce products intended for human consumption. .
