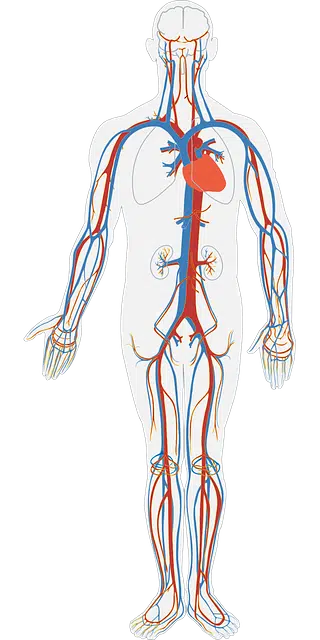
Veins are blood vessels.
A vein is a conduit or blood vessel that is responsible for carrying blood from the blood capillaries to the heart . It generally carries waste from organisms and CO2, although some veins carry oxygenated blood (such as the pulmonary vein ).
Veins are made up of three layers: an external layer (also called adventitia ), a middle layer ( muscular ), and an internal layer ( endothelial ).
Differences between veins and arteries
Unlike arteries , the precise location of veins varies greatly from individual to individual.
Veins, on the other hand, are located at a more superficial level than arteries (that is, closer to the skin ). Another difference between veins and arteries is that the former have a thinner wall.
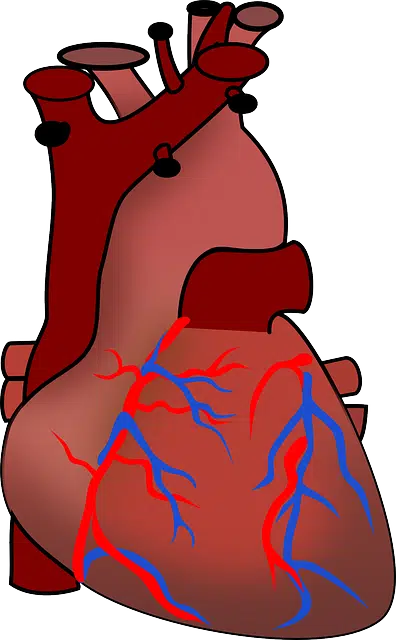
Veins carry blood to the heart.
Most important conduits
In addition to the pulmonary veins (which transport oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart), other important veins in the human body are the vena cava (which divides into the upper -receiving blood from the upper half of the body- and the lower -taking the blood from the organs located below the diaphragm), the portal vein (whose trunk is inside the liver), the jugular vein and the femoral vein .
Specifically, we can make a great classification where the veins are organized depending on the system in which they act. Thus, first of all, we find those that are part of the so-called general system, which are those through which the blood that has less oxygen circulates and does so from the capillaries to the right side of the heart . These stand out because they have a series of semilunar valves responsible for ensuring that said blood does not return to the aforementioned capillaries.
Secondly, there are the veins of the pulmonary system in which, as their name suggests, the corresponding blood with oxygen travels from the lungs to what is the left motor part of the body, the heart.
And finally, in third place we would have to talk about the veins of the portal system. These are in which blood circulates from one capillary to another. It is important to highlight the fact that there are two types of systems of this typology: the hepatic portal system and the pituitary portal system.
Vein diseases
Among the most common diseases of the veins are varicose veins (which are dilations that are characterized by preventing the normal return of blood to the heart) and thrombosis (which is noticed by the appearance of a clot inside the blood duct).
Phlebitis (swelling of the walls of the veins) is another of the many disorders that can affect people.
More uses of the term
In addition to everything stated above, we can determine that the term in question has other meanings and meanings.
Thus, it is also used to determine the mood or mood changes of a person. An example would be the following: "Manuel is defined because he has a negative streak that causes everything around him to be seen by him with pessimism and sadness."
