
Color theory explains the formation of various shades.
Theory is a concept that comes from the Greek word theōría . The notion refers to a hypothesis with effects that can be applied to an entire scientific discipline or to a sector of it; to a series of laws that relate certain phenomena; or to speculative knowledge.
The idea of color , meanwhile, refers to a sensation that is generated when light rays reach the eyes. The impression caused by these rays varies depending on the length of the wave, giving rise to different colors.
What is color theory
Color theory is called, in this framework, a set of guidelines that indicate how colors should be combined to achieve the desired result . This is a guide that is often followed in design, photography , painting and other areas.
It is important to indicate that color theory is made up of multiple postulates and principles . In a broad sense, we can distinguish between the theory of additive synthesis and the theory of subtractive synthesis , which refer to different ways of obtaining colors.
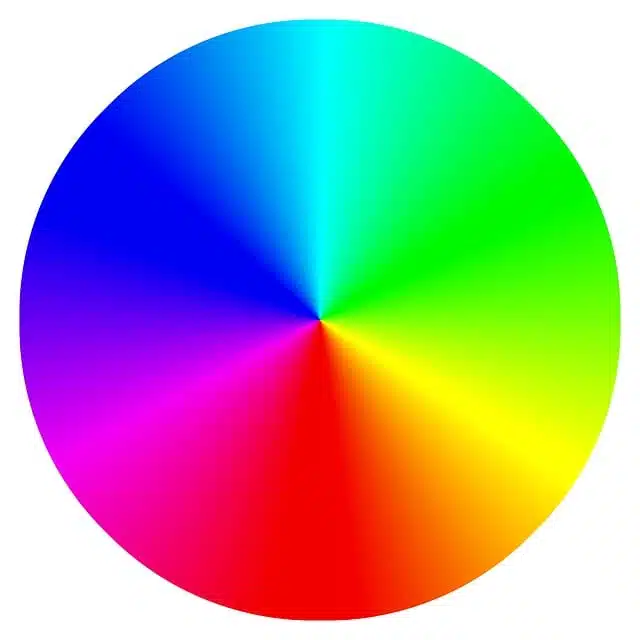
Color theory indicates that the color wheel makes it possible to represent shades.
The additive synthesis
The model that promotes the generation of a specific color through the addition of different chromatic components is called additive synthesis . In general, blue, green and red are used for the production of the other colors.
This means that, when these primary colors are combined with others, the various colors of the spectrum are made. The result depends on the intensity used.
Color theory and subtractive synthesis
The subtractive synthesis model, on the other hand, is based on the absorption of certain wavelengths and the reflection of others. Thus, depending on how the colors are mixed, new ones are produced.
What this model of color theory indicates is that the color attributed to a body is the result of the sector of the electromagnetic spectrum that it reflects. It can also be understood that color derives from the area of the spectrum that the body cannot absorb.
The color wheel
The color wheel , also mentioned as a color wheel , is a scheme that allows colors to be represented based on their tone or hue. Its use is compatible with both types of synthesis (additive and subtractive).
Generally, cool colors are positioned on the left side of the wheel, while warm colors are positioned on the right side. The conventional model places red as opposite to green; to blue on the opposite side to orange; and yellow as opposed to violet, for example .
The characteristics of tones according to color theory
Color theory explains that all colors have three essential attributes. It's about saturation , lightness and hue .
Saturation is associated with purity , which comes from the gray level : the higher the gray concentration, the less saturation (that is, the less purity). Luminosity , for its part, is linked to light intensity , given by the distance or proximity to black or white.
The nuance , finally, is the color itself. It can also be mentioned as tonality or tone .
