The periodic table is based on the chemical periodicity of the elements since it organizes them according to their periodic properties (characteristics that vary sequentially by periods and groups).
The periodic table is a scheme designed to organize and segment each chemical element, according to the properties and particularities it possesses. Full name periodic table of the elements , it is also known as the periodic system .
It is a fundamental tool for the study of chemistry since it allows us to know the similarities between different elements and understand what can result from their various unions.
Origin of the periodic table
As noted when researching the periodic table, the history of this structure is related to the discovery of the different chemical elements and the need to order them in some way.
Since the beginning of science, we have tried to understand the why and how of matter and the elements that make up our system. Thanks to the different experiences of scientists, it has been possible to decompose matter even further to analyze it inch by inch, finally finding out that it is much more complex than it appears at first glance.
Starting in the 19th century, scientists had the need to establish an order in the discovered elements. The way they decided to do it was starting from their atomic mass and grouping those that were similar; However, this task was not so simple because it was difficult to reflect the similarities and differences between them in an orderly table.
The contributions of Döbereiner, Chancourtois, Newlands and Meyer
The chemist Johann Wolfgang Döbereiner was the one who presented a report in 1817 that reflected the relationship that existed between the mass and the properties of the different elements. Thus, it formed groups of similar elements , such as triads, including those formed by chlorine, bromine and iodine, where the mass of one of them is located in the middle of the other two. Based on this research, in 1850 , around 20 triads were put together.
Later, Alexandre-Émile Béguyer de Chancourtois and John Alexander Reina Newlands discovered the law of octaves , which made it possible to improve not only the distribution of the elements in the table, but also the relationships reflected in it. This law observes that chemical properties are successively repeated every eight elements. However, some elements broke with it, so it was not enough to establish clear coherence in the table.
When in 1869 Julius Lothar Meyer verified that the atomic volume of the elements presented a certain periodicity, it was known that the elements had a volume similar to those elements that resemble them in composition.

The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) is the body that officially recognizes the chemical elements that make up the periodic table.
Mendeleev's periodic table
In 1869 , Dmitri Mendeleev finally presented the first version of the periodic table . It was composed of a column with 63 elements, grouped according to their common properties, and several blank spaces. The Russian chemist assumed that some were missing that had not been discovered, those corresponding to atomic masses that were not yet known and that allowed the table to have absolute numerical regularity. Although his theory was not accepted at the time, as it seemed inaccurate, years later when the missing elements were discovered , it was proven that Mendeleev was right.
Later, Mendeleev added the formulas corresponding to the oxides and hydrides of each section. At the end of the 19th century , the periodic table began to include group zero (with the so-called noble gases) , so called because of the absence of chemical activity (zero valence).
It is also necessary to recognize the importance of John Dalton ( 1766 – 1844 ) in the development of the concept of chemical atomism , when assuming about the possible combinations of the atoms of substances. Dalton chose the mass of a hydrogen atom as the reference unit and created a structure based on relative atomic masses.

When two or more elements that are part of the periodic table are chemically combined, a chemical compound is obtained.
The composition of matter
The composition of matter has always been a source of interest for human beings. Matter used to be defined as the substance that made up the elements and then the concept came to be associated with the entity that, by being present in space-time, makes the tension-energy tensor of its region different from zero.
The basic constituents of matter are called elementary particles . The proton , neutron , and electron are examples of these particles.
The smallest fragment of matter that has properties of a chemical element is the atom . These atoms , which join together to form molecules , have a nucleus that is linked to one or several electrons. The Bohr atomic model and the Rutherford atomic model were some of the proposals that emerged to explain the structure of atoms.
The atomic nucleus , in this framework, is made up of neutrons and protons that are bound together through a strong nuclear force. According to the number of protons in this nucleus, the atomic number is defined and the determination of the chemical element in question occurs.
It is interesting to mention that the atoms of an element can have different masses and different numbers of neutrons in the nucleus. In those cases, we speak of isotopes .
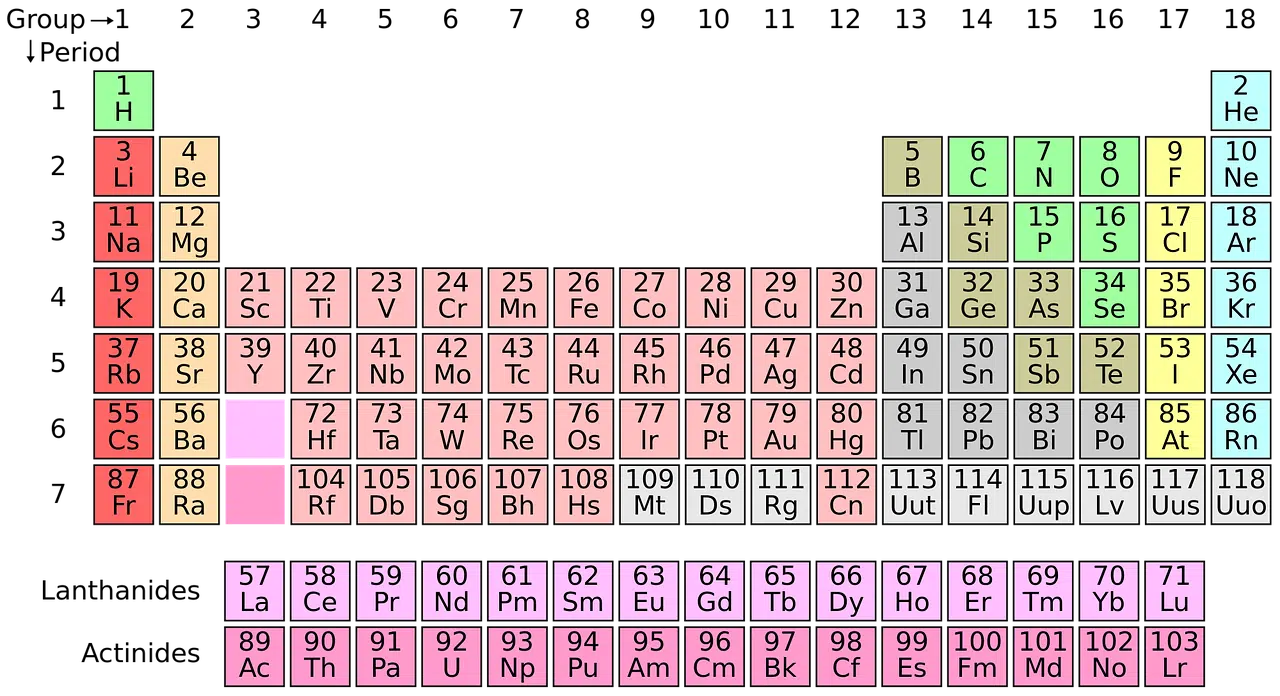
What the periodic table does is organize and gather the different chemical elements according to atomic number. It also considers the electronic configuration (how the electrons are arranged in the atom) and chemical properties .
The structure of the periodic table
The structure of the periodic table includes groups and periods . The elements, in this way, are organized in vertical columns (the groups, which can also be mentioned as families ) and in horizontal rows (the periods).
The order implies that the elements are located from left to right and from top to bottom in increasing order according to atomic number . As you move up and to the right, electronegativity , electron affinity and ionization increase; downward and to the left, while the ionic radius and the atomic radius increase.
Another possible division is done in blocks , depending on how the electron shells are completed. The name of the blocks obeys the atomic orbital in which the last electron is located.
