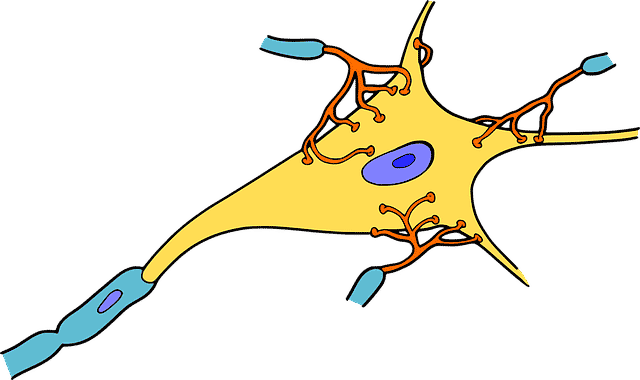
The composition of a neuron is called soma.
Soma is a concept that has multiple meanings. Derived from the Latin summa , the word can be used to identify a variety of coarse flour and bread made with this ingredient.
The notion also serves to refer to the total body structure of living organisms, with the exception of gametes.
Soma as a plant
From the perspective of botany, the notion is intended to identify a plant with psychotropic characteristics whose sap was used in Vedic religious rituals. This plant has not yet been identified, although it is mentioned in numerous ancient texts that refer to its energizing properties.
It should also be noted that the writer Aldous Huxley ( 1894 – 1963 ) named soma a substance consumed by the protagonists of his novel “Brave New World.” This drug, it is said, acts as an antidepressant since it causes people to forget their sorrows.
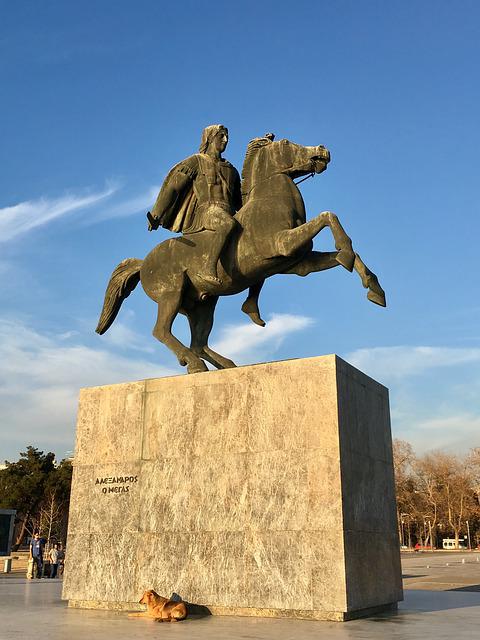

The mausoleum of Alexander the Great is often named soma.
A mausoleum, a puzzle and a therapy
The mausoleum that housed the remains of Alexander the Great has also been called soma. Archaeologists believe that it would be located in the Egyptian city of Alexandria .
The so-called Soma cube , meanwhile, is a geometric puzzle that challenges you to fit seven parts into a main structure. Piet Hein was the creator of this puzzle that was born in 1936 and that can be solved, according to some mathematicians, in 240 different ways. It should be noted that the Soma cube also allows you to create other geometric or figurative designs.
Soma or somatherapy , in other areas, is a therapy created by the Brazilian Roberto Freire that considers that neurotic conflicts arise from the power relations existing in society .
Soma according to neurology
Soma is also the name given to the composition of a neuron (encompassing its nucleus and nucleoli). That is, it represents the center of the cell that has the capacity to receive stimuli; Without it, the life of the neuron is not possible.
Regarding its size, it differs according to the neuron, it can range from 4 to 150 microns. It is made up of the nucleus , the cytoplasm (with all the parts of which it is composed: neurofilaments, endoplasmic reticulum, microtubules, etc.) and the extensions (formed by dendrites and axons).
Neurons are the structural units of the nervous system (present in all living beings belonging to the Animal Kingdom ) and, thanks to the fact that they are arranged in the organism through complex networks, they can fluidly communicate each region of the organism with the Nervous System. allowing one of the characteristics that differentiates living beings from other organisms, irritability (ability to respond to various stimuli from the external environment).
The functions of the soma within the neuron are three: to maintain the functional and anatomical efficiency of the neuron, to extend the extensions so that the surface area in which nerve impulses can be transmitted is increased, and to ensure the normal functioning of neurotransmitters through synthesis. of messenger type chemicals.
Neuron classification
Neurons can be classified taking into account various criteria.
From a morphological point of view they can be: unipolar (they have a single extension, called axon), bipolar (they have two extensions, called dendrite and axon) and multipolar (they have more than two extensions: two or more dendrites and one axon). ).
According to their functionality, they can be: sensory (they transfer impulses from a receptor to the nervous center), motor (they communicate the modulating centers with the effectors) and interneurons (they communicate the sensory pathways with the motor pathways within the nervous system) and motor neurons.
In turn, there is a third classification that takes into account the conduction speed, in this case the neurons can be unmyelinated (they lack myelin and conduct impulses slowly) or myelinated (the conduction speed is related to the thickness of the its myelin, the greater the thickness, the greater the speed).
It is worth mentioning that myelin is a substance with insulating characteristics that covers the axons of neurons, allowing the fluid conduction of stimuli from one region to another.
