The respiratory system is made up of the organs and muscles that make breathing possible.
System , from the Latin systema , is an ordered module of elements that are interrelated and interact with each other . The notion can refer to both real objects (material) and abstract concepts (symbolic) that are endowed with organization.
Respiratory , for its part, is that which serves for breathing or that facilitates this physiological process. It should be remembered that breathing consists of absorbing air , taking in some of its substances and expelling it modified. In aerobic living beings, respiration is essential for life. Humans, for example, take in oxygen when breathing in and then breathe out carbon dioxide .
What is the respiratory system
The set of organs and muscles that is responsible for capturing oxygen through inspiration and eliminating carbon dioxide through exhalation after the process of cellular metabolism is known as the respiratory system or respiratory system .
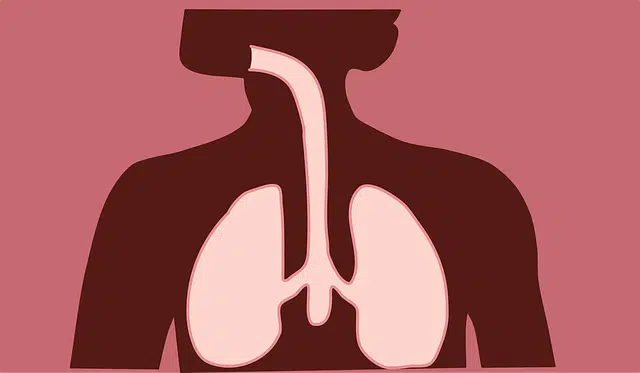
In the case of humans, the respiratory system includes components such as the nasal passages (which allow air to enter), the pharynx (helps air reach the lower airways), the larynx (filters inspired air) , the trachea (provides an open path for inhaled and exhaled air), the bronchi (conduct air from the trachea to the bronchioles), the bronchioles (carry air to the alveoli), the alveoli (which allow gas exchange), the lungs (they carry out gas exchange with the blood) and the diaphragm (a muscle that intervenes in breathing).
In the human respiratory system, a distinction can be made between the conduction system and the exchange system . The latter is known as the non-respiratory zone, since there is no gas exchange there.

Asthma is a disease that affects the respiratory system.
Frequent illnesses
Asthma
Asthma is known as a diffuse and obstructive lung disease that is characterized by the presence of cough, wheezing (a whistling sound produced when breathing) and difficulty breathing. It is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways found in the lungs; As the bronchi swell, their lumen becomes narrower, which generates greater mucus production and facilitates the contraction of its muscle fibers.
Inflammation of the bronchi makes them especially irritable and very sensitive to certain inhalant-type substances, as well as to certain situations, and these stimuli are called triggering agents . It is worth mentioning that the bronchi can narrow in a very short time.
Among the most common symptoms of asthma is cough (usually at night or in the early morning, but also while doing some type of physical exercise, crying or laughing), chest tightness (perceived as discomfort in the chest) and fatigue.
Bronchitis occurs when the bronchi suffer inflammation, which can occur as a result of a viral or bacterial infection , among other causes. It is possible to distinguish between acute and chronic bronchitis, of short and long duration respectively.
Some of the symptoms of bronchitis are coughing up mucus (sometimes with blood), blocked air sacs, wheezing, and difficulty breathing. Furthermore, this disease affects the mood and spirit of those who suffer from it, which is why they usually experience general discomfort.
It is an infectious disease that affects the respiratory system and is often confused with a normal cold, since they share certain symptoms, such as sore throat, congestion and cough. However, it differs mainly in the severity of the inflammation of the airways, greater in this case, and because it requires more extensive rest.
In addition to the aforementioned symptoms, a lack of energy, eye irritation, difficulty speaking, generalized body pain, and fever (during the first few days) are also usually noted.
