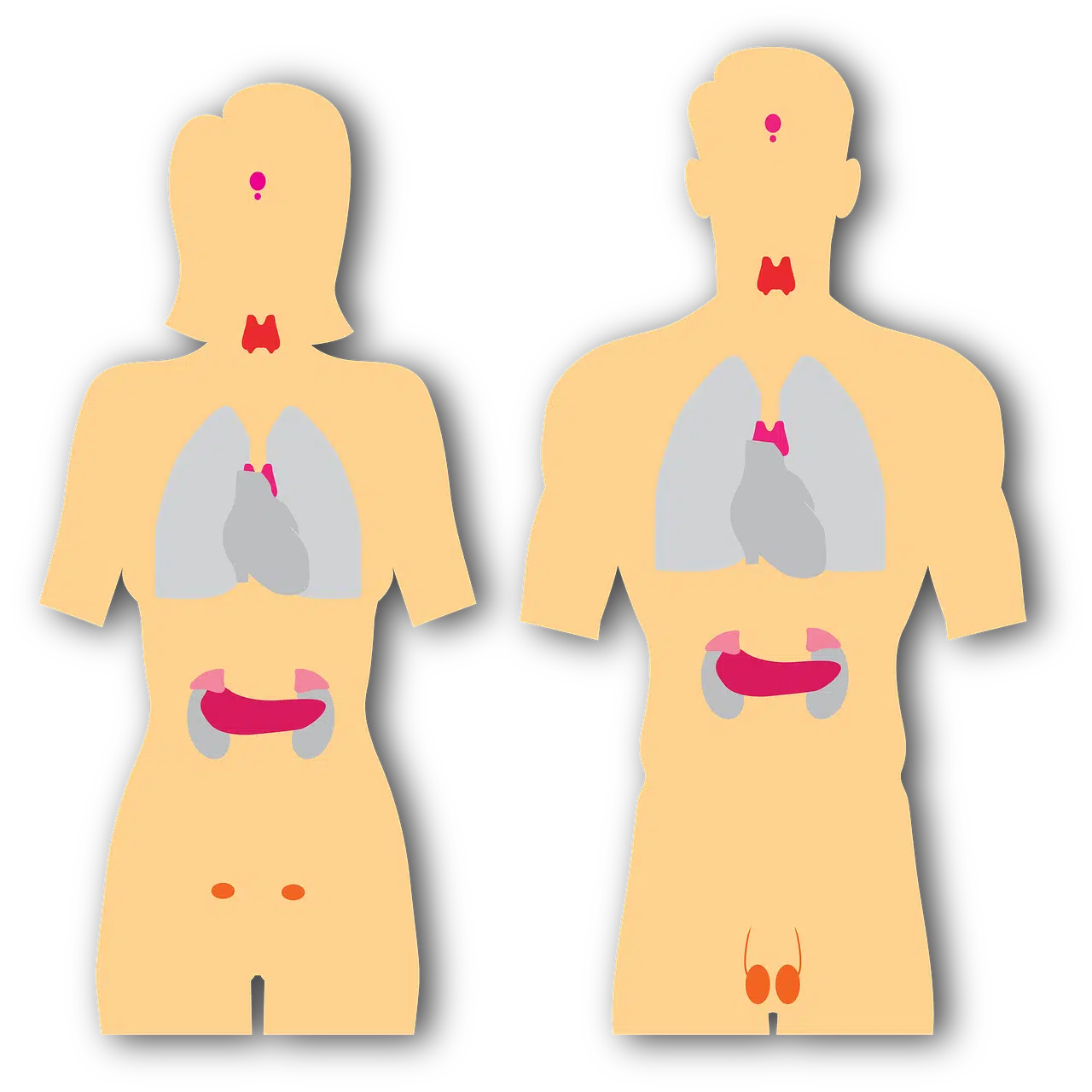
The endocrine system is made up of the internal secretion glands.
The endocrine system is made up of all the internal secretion glands . Its components are organs that secrete hormones, which are released into the bloodstream and are responsible for regulating the various functions of the body.
The ordered module of interrelated elements that interact with each other is known as a system . These elements can be real (physical) or conceptual (abstract). Endocrine , for its part, is an adjective that is used in biology to name that which belongs to or is related to hormones or internal secretions . Applied to a gland, the term refers to those that pour the products they secrete directly into the blood .
Glands of the endocrine system
Growth, metabolism, tissue functions, and mood, for example, are regulated by hormones. The endocrine system allows cellular communication that, when faced with stimuli , responds by releasing hormones and boosting the different metabolic functions of the body.
Among the glands that are part of the endocrine system, it is possible to highlight the thyroid , the pituitary and the adrenal . The thyroid gland is located in the front of the neck, above the windpipe. It is composed of two lobes joined by an isthmus, it produces proteins and regulates the body's sensitivity to other hormones.
The pituitary gland , also known as the pituitary gland, is located at the base of the skull and has the function of regulating homeostasis. The adrenal glands , for their part, are located above the kidneys and are responsible for regulating the response to stress through the synthesis of cathocolamines and corticosteroids.
Endocrinology is the medical specialty that studies the endocrine system.
Most common diseases
Two of the most well-known diseases of the endocrine system are described below:
Diabetes
The main characteristic of diabetes is the presence of very high levels of glucose in the blood. Insulin is the hormone responsible for ensuring that cells obtain the energy they need from the glucose that enters the body through the food we consume.
It is possible to speak of type 1 diabetes , when the body does not generate insulin, and type 2 diabetes (more common than the first) if insulin is not produced or used correctly by the body. Prediabetes , on the other hand, occurs when sugar levels are higher than normal, although not as high as in diabetes.
This disease of the endocrine system can have serious consequences on the body , including injuries to the kidneys, nerves and eyes, as well as heart disease, limb amputation and strokes.
To detect the presence of diabetes, it is possible to request a blood test, and to control it, it is advisable to stay in shape and follow a healthy and balanced diet , paying attention at all times to the level of glucose in the blood.
Obesity
Although many people do not consider obesity to be a disease, it is and can have serious repercussions on our health. In short, it is an excess of fat in the body, and should not be confused with overweight , a situation that can occur due to the combination of muscle mass, bone size, and water in the body, in addition to the fat. On the other hand, neither condition is healthy.
How do you become obese? Ingesting calories in quantities greater than those consumed by the body, although this proportion is different for each individual. Frequent physical activity and a diet free of saturated fats is a good start to avoid this disease of the endocrine system.
It is important to note that obesity increases the risk of stroke, certain types of cancer, heart disease, arthritis and diabetes.
