A numbering system is the set of guidelines and symbols that make it possible to generate valid numbers.
System is a term that has its etymological origin in the late Latin systēma , in turn derived from the Greek sýstēma . The notion refers to a set of elements that are linked together in an orderly or rational manner.
Numeration , meanwhile, comes from the Latin numeratio . It can refer to the act and result of numbering (indicating a quantity with numbers, counting) or to the method that allows the expression of all numbers with a limited number of figures , characters or words.
The idea of a numbering system , in this way, refers to the set of rules and symbols that make it possible to generate the numbers that are considered valid . It is important to consider that the guidelines for creation and the characters used vary according to each system.
Numbering system concept
It can be said that a number system contains those signs that can be used, following a certain method, to assign symbols to numbers. This number of signs is finite: not just any character can be used, but only those that are supported by the system in question.
It is possible to distinguish between positional or weighted number systems and non-positional number systems . In the first case, the value of the numbers is defined by the symbols and by the relative position occupied by these symbols; In non-positional systems, however, only the value is considered and the position does not matter.
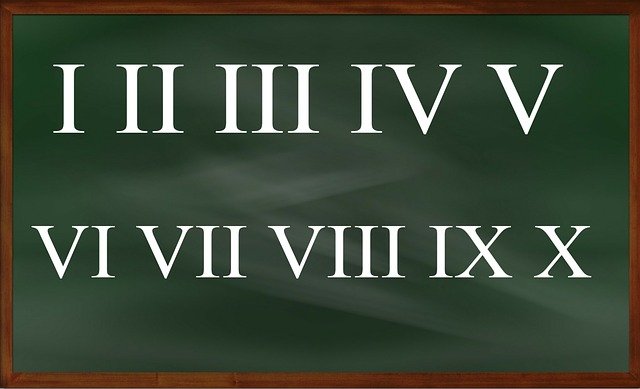
The Roman numeral system is non-positional.
positional notation
Positional numbering systems use so-called positional notation . This means that the value of the digits, as we already indicated, is associated with the relative position of the symbols. This position , in turn, is established according to the base .
The base idea is used to name all the available symbols and also specifically the number that sets the order of magnitude in which each successive figure increases. If we focus on the decimal number system , the base is 10 : ten digits are used ( 0 , 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 and 9 ) and it is increased in that proportion.
Let's think about number 3 . This digit ( 3 ) takes on different values in 3 , 30 , 300 , 3000 and 30000 , among other numbers.
Continuing with the decimal system, it is possible to affirm that they reach ten digits to write any kind of value, regardless of the “size” (very small or very large). The 0 , which has a null value, is key for this operation .
The Roman numeral system
In the group of non-positional systems, one of the best known is the Roman numeral system . Created in Ancient Rome from Etruscan numbering , it is classified as additive and subtractive : the value of the signs has nothing to do with the relative position, but is added or subtracted from the previous sign.
Among the Roman numerals, we have I ( 1 ), V ( 5 ) and X ( 10 ), for example . The 8 , in this framework, is written VIII ( V+I+I+I , equivalent to 5+1+1+1 ). 9 , likewise, is IX ( I is subtracted from X ; that is, 1 is subtracted from 10 to obtain 9 ).
