Seismology is a science dedicated to the study of earthquakes or earthquakes.
Seismology is the science dedicated to studying earthquakes . An earthquake, for its part, is a sudden and abrupt movement of the ground that is produced by the action of forces within the globe.
Seismology - a term that comes from the Greek language - is considered to be part of geophysics , which is the discipline that analyzes the physical issues of our planet. The object of study of seismology, therefore, are the seismic waves that cause earthquakes.
Object of study of seismology
Seismology attempts to determine the origins of earthquakes and the mode of propagation of waves. Among its objectives is prevention to mitigate the destructive effects of earthquakes.
It is common for an earthquake to occur at the boundaries of lithospheric plates (also called tectonic plates ). When at least two of these plates interact, tension builds up at their boundaries and displacements then occur. To study these questions, experts use seismometers or seismographs .
These devices allow us to evaluate the tremors caused by the shifts of tectonic plates. Seismographs, thanks to their sensors, are able to record seismic waves and can study their propagation. The record made by these machines is called a seismogram .
Based on knowledge of seismology and the operation of seismographs, earthquakes began to be classified according to their magnitude . The Richter scale (considered according to the energy released) and the Mercalli scale (which studies the damage caused) are the popular ones.
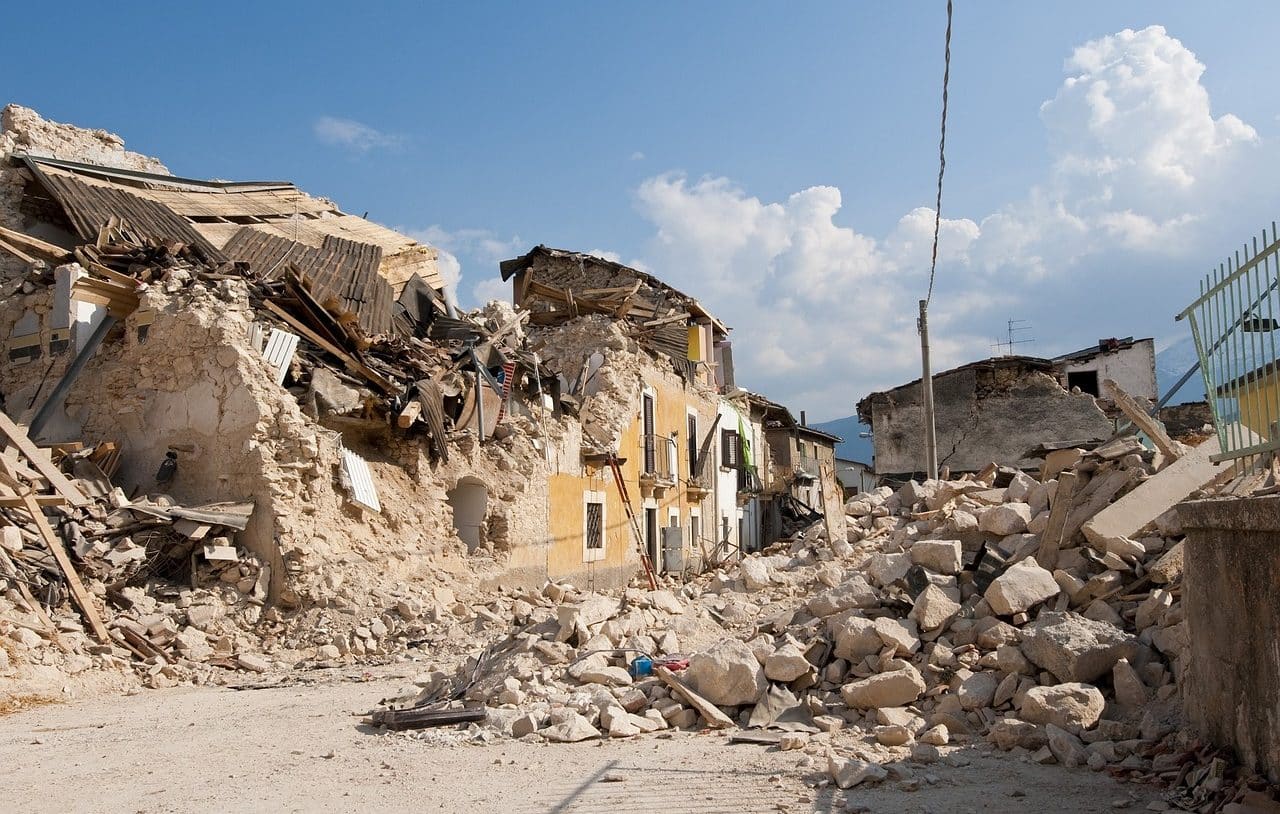

Seismology aims to prevent the destructive effects of earthquakes.
Research tasks
In many countries around the world there are centers, organizations and institutions focused on seismology, fundamentally dependent on the government, which what they do is record all the information related to earthquakes to analyze it, store it and, of course, find out if they are going to take place soon. more movements of that type.
In Spain , for example, there is the National Seismic Network and the Seismic Information Service , dependent on the National Geographic Institute . Through the web spaces of this service you can find out which earthquakes have taken place in recent times, as well as the existing statistics, including the seismic stations it has or what is known as the earthquake-resistant standard .
We can also mention that in Mexico there is the National Seismological Service , in Cuba there is the National Center for Seismological Research and in Colombia there is the National Seismological Network , to mention other institutions.
Seismology experts
Throughout history there have been numerous figures who have dedicated themselves to analyzing and studying different earthquakes in depth. This would be the case of the Frenchman Nicolás Lemery ( 1645 – 1715 ), the American John Mitchell ( 1711 – 1768 ) and the English seismologist Richard Dixon Oldham ( 1858 – 1936 ), who made great contributions to the study of wave types.
However, we must not overlook the role played in this discipline by the British Harold Jeffreys ( 1891 – 1989 ), whose analysis of seismic waves led to the discovery that the Earth 's core is liquid, and the Danish Inge Lehmann ( 1888 – 1993 ), who qualified the previous theory by exposing the combination of solid and liquid state in said nucleus .
