
Sidereal space is the area of the universe that is beyond the Earth's atmosphere.
The adjective sidereal , which has its etymological origin in the Latin word siderālis , is used to describe that which is linked to the stars or stars . The concept, in this way, appears in various notions of astronomy (the science that studies the stars).
Delving a little deeper into the etymology of the word sidereal, we find that another of the Latin terms that gave rise to it is sidus , which can be translated as planet, celestial body , constellation or star, depending on the context.
sidereal space
Sidereal space , also known as outer space or sidereal space , refers to the sector of the universe that is located outside the atmosphere of our planet .
Because the density of the atmosphere gradually reduces as altitude increases, there is no exact limit that marks the end of the atmosphere and the beginning of sidereal space. It is usually considered that sidereal space begins at 80, 100 or 120 kilometers away from the Earth's surface.
The concept in astrology
The sidereal or eastern zodiac is called the one that recognizes the twelve constellations of traditional astrology , although it takes a gradual, slow and continuous movement of the constellations that can be observed from our planet, and the latter distinguishes it from the tropical zodiac.
One of the currents that belong to the sidereal zodiac accepted in 2011 the inclusion of a new constellation, which is located in thirteenth place, and they named it Ophiuchus.
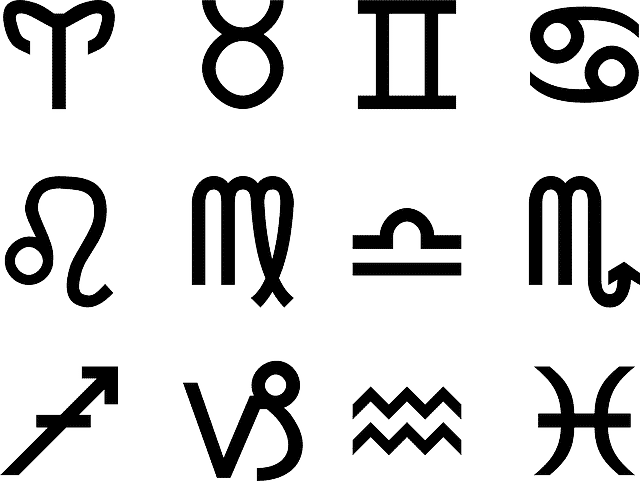
The sidereal zodiac recognizes the usual constellations of astrology, but considering a slow, gradual and continuous movement of the constellations visible from Earth.
Differences between the sidereal and tropical zodiac
To understand another difference between the sidereal and tropical zodiac, it is necessary to define a couple of complementary concepts:
* the ecliptic : it is the curved line through which our planet passes in its constant translation around the Sun ;
* the vernal point : also known as the Aries point , it is located on the ecliptic and from there the Sun can pass from the southern celestial hemisphere to the northern one, which takes place at the spring equinox.
Taking this vernal point as a reference, the ecliptic is divided into 30° portions, so that the 12 signs that we are used to seeing in Western societies and that many associate with personality traits are obtained. However, a phenomenon called precession of the equinoxes , which consists of a slow and gradual alteration of the orientation of the planet's axis, establishes a difference of 24° between the sidereal and tropical zodiacs.
It is curious to note that according to the bases of the sidereal zodiac, almost 90% of people have a different sign , the one that directly precedes the one that assigns them the tropical one. For example, the vast majority of Capricorn individuals according to the tropical zodiac belong to Sagittarius for the sidereal.
A temporary period
One of the concepts that this term includes is the sidereal year , the time period that develops between two consecutive passages of the planet Earth through a certain point in its orbit with respect to the location of the stars . The sidereal year, therefore, is equivalent to little more than a "conventional" year (since, to the 365 days, six hours, nine minutes and twenty-four seconds must be added).
The tropical or tropic year is the time necessary for the average longitude of the Sun in the ecliptic to increase by 360°, and lasts 365 days, 5 hours, 48 minutes and 45.1 seconds. To understand its difference with the sidereal year, the concept of precession of the equinoxes, mentioned above, must be included in the equation.
Sidereal as far away
In colloquial language, the notion of sidereal is used to refer to something very distant or unattainable .
For example: "The discovered star is at a sidereal distance from the Earth" , "European clubs pay sidereal amounts that are inaccessible to us" .
