A rune is a character of a runic alphabet.
The etymology of rune takes us to the Norse term rūn , linked to mysteries and secrets. The concept is used with reference to the characters that the ancient Scandinavians used to write in Germanic languages.
The Germanic languages belong to the Indo-European family and are used primarily by the Germanic peoples, a group of peoples that emerged in the north of the European continent. Letters called runes were also used in the British Isles; On the other hand, throughout classical antiquity and the Middle Ages and even before and during the phenomenon known as Christianization (in which many Europeans were converted to the Christian religion), runic alphabets were also used in Eastern and Central Europe.
Runes as characters
In runic alphabets , therefore, each character was known as a rune. The different runes, in this way, allowed words to be formed. The variants of the Scandinavian alphabets that used runes are called futhark (young futhark, old futhark, etc.).
The word futhark, which is pronounced as if it were a serious word with a "z" instead of the "th", originated from the first six runes (which can be seen in the second image), whose transliteration is close to the following letters of our alphabet : F, U, Z (with the pronunciation typically used in Spain, which differentiates it from the "s"), A, R and K. Since these letters underwent changes between English ancient and modern, the variant Anglo-Saxon futhark is called futhorc .
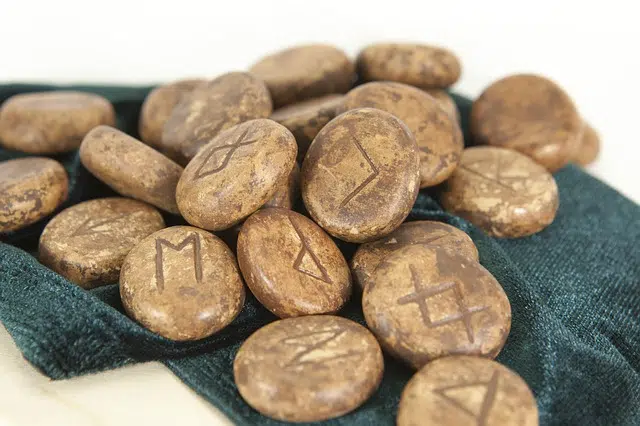

Divination with runes is an esoteric practice.
Inscriptions made with these alphabets
It is possible to find evidence of runic alphabets in the Noleby Stone (engraved around the year 600 ) and the Rök Stone ( 800 ), to name two examples . Both are found in Sweden and feature texts written with runes.
However, inscriptions of more remote origin may come from the year 150. In short, this alphabet was gradually replaced by the Latin one through conversion to Christianity, approximately in the 8th century in central Europe and, four centuries later in Scandinavia, when the Viking Age ended. Despite this phenomenon, Scandinavia continued to use runes until the early 1900s, mainly in rural Sweden for decorative purposes and in the development of runic calendars .
The runic calendar (also called runic staff ) is a writing that can be found carved on staffs made of various materials (such as wood, horn, stone or bone) or on scrolls and is considered a medieval Swedish creation. It is a perpetual calendar , that is, it gives the user the possibility of knowing which day of the week corresponds to any date, which is within a range of several centuries.
When the runic alphabet is encrypted through the replacement of the runes with other symbols , these characters are called cryptic runes or cipher runes .
Divination with runes
The ancient Scandinavians held that runes had a divine origin. For this reason, runes also have an esoteric connotation and are used for divination .
Elements that have runes engraved on their surface are called rune stones or simply runes. The diviner throws the runes onto a table, causing the stones to arrange themselves randomly. The person, in this way, reads the runes and can predict the future .
It is important to note that the reading of runes in an esoteric sense is not supported by science . It is a practice that appeals to mysticism and the supernatural to anticipate future events: there is no scientific or rational criterion that corroborates the possibility of knowing what will happen in the future by reading the runes.
