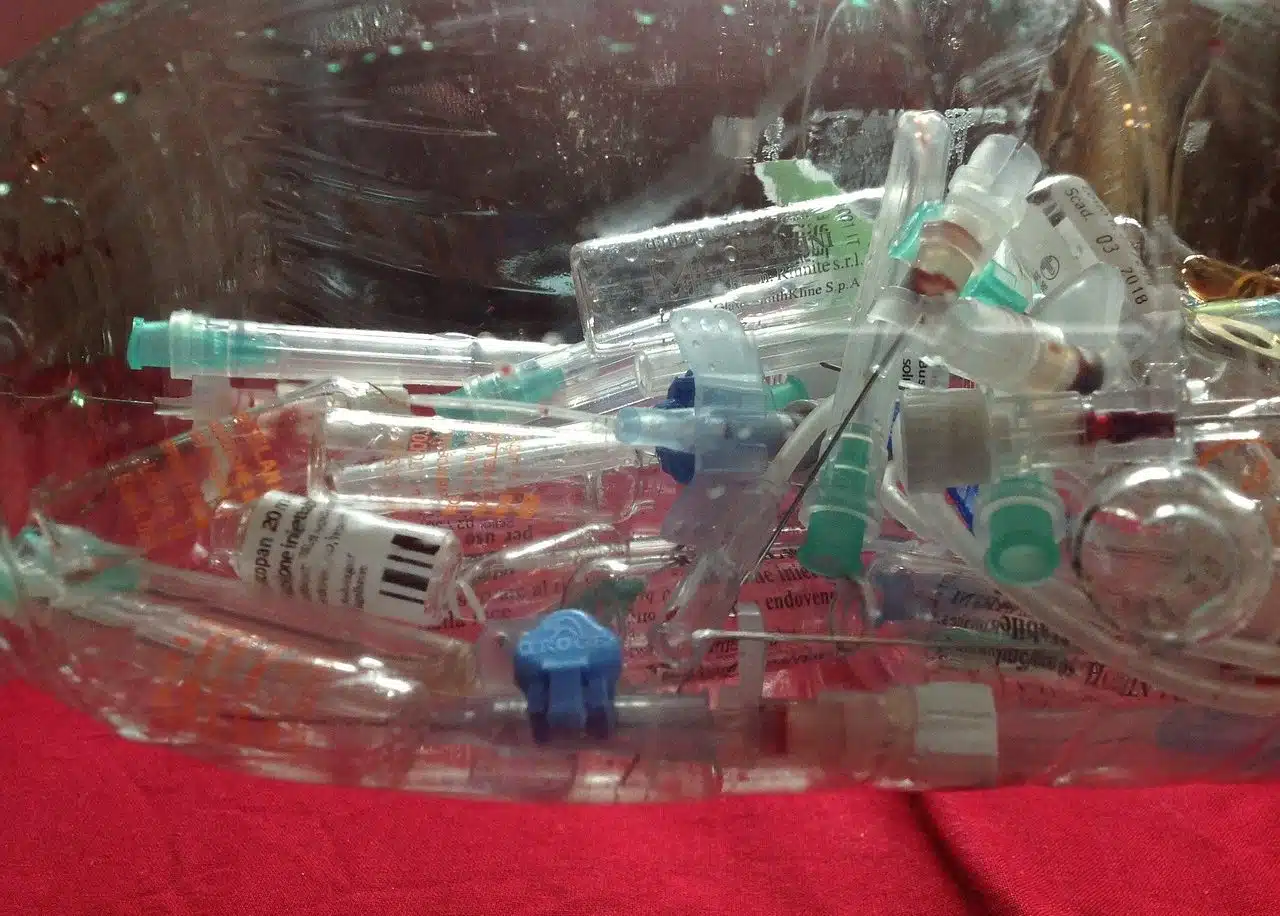
RPBI is the acronym that identifies hazardous infectious biological waste.
RPBI is the acronym for hazardous infectious biological waste . This is a classification that exists in Mexico to refer to a certain type of waste that, due to its characteristics, implies a risk to health and the environment .
RPBI are produced in laboratories, research establishments and health centers from the development of activities linked to the health of humans or animals. If we break down the acronym, we can indicate that it is "waste" since it is leftover elements and waste from other activities; "dangerous" because they can harbor microorganisms capable of damaging health; and "biological" and "infectious" for their microorganisms that can cause diseases.
This means that the microorganisms present in RPBI , if they are in a sufficient concentration and in an environment that allows their survival, can infect a certain host .
RPBI components
Cultures and strains of infectious agents used for research and diagnosis; the tissues or organs that are removed from a body; the blood; and disposable containers, utensils and instruments that are used in contact with these elements are part of the RPBI .
To avoid infections, RPBI must be disposed of in a particular way. This waste must be placed in specific bags , labeled with a symbol that allows you to know what is inside. They must also be stored in special places and transported in hermetically closed boxes to the site where their treatment will take place, which may be chemical, physical or of another type.
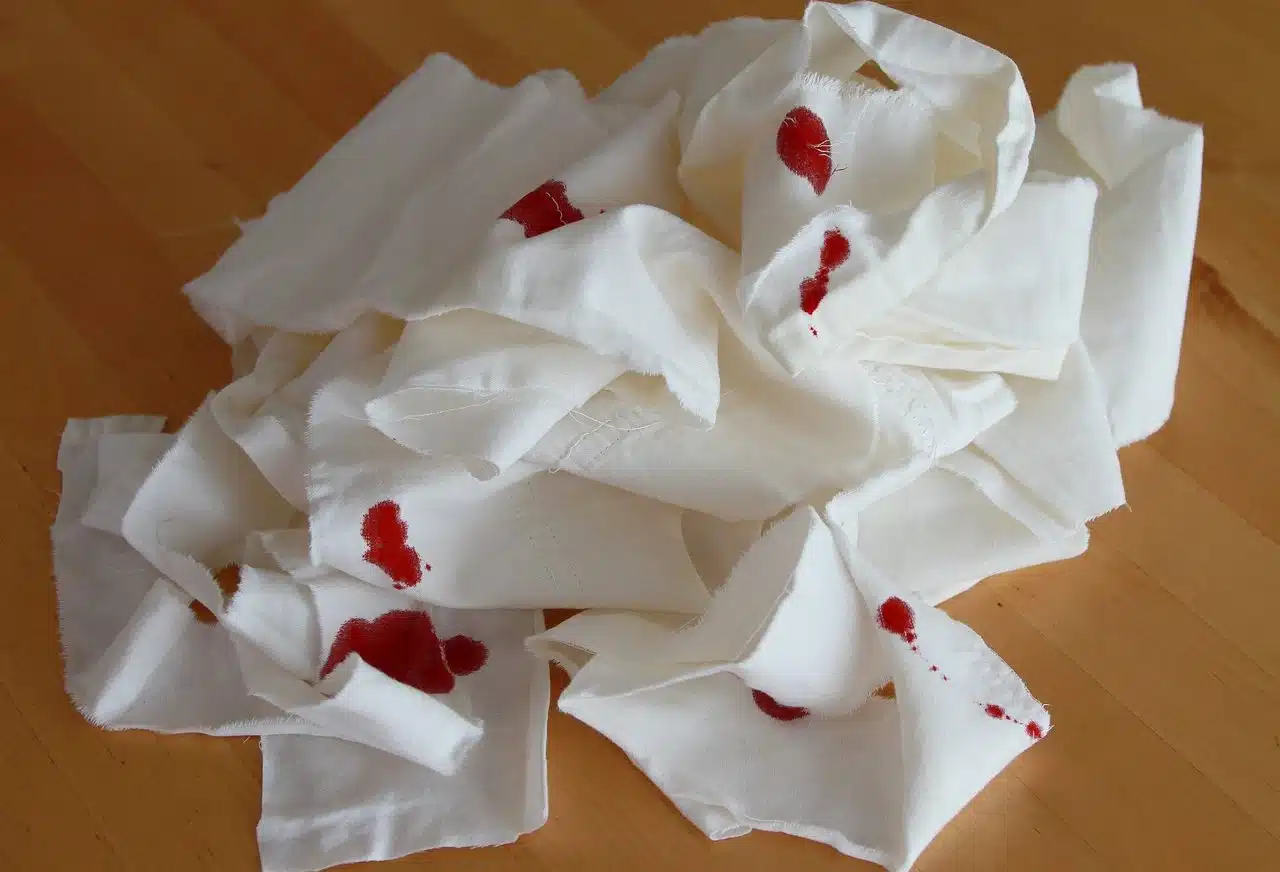

RPBIs must be managed carefully to avoid health problems.
Its management
The management of RPBI includes 5 fundamental steps, which are explained below:
- Identification of RPBI : as soon as the procedure in which the waste is generated has been completed, it must be properly identified by the responsible persons who generated it and at the same site. The primary objective of this step is to prevent waste from being reclassified , since this reduces the risks associated with its subsequent collection . Among the types that are recognized during this first phase are sharp objects (syringe needles, scalpels, lancets and catheter stylets), non-anatomical ones (such as gauze soaked in blood or various secretions), pathological ones (such as placentas ) and used disposable utensils .
- RPBI packaging : having passed its identification, it is time to package the waste, taking into account its type and physical state to choose the appropriate container, according to official standards in each case. For example: sharp objects must go in rigid containers made of polypropylene; non-anatomical waste and remains of human tissue or body parts that are not in formalin, in plastic bags; and liquid blood and samples for analysis (excluding feces and urine), in airtight containers.
- Temporary storage of RPBI : it is necessary to previously establish a site in which RPBI can be stored temporarily, to prevent it from being confused with the rest of the garbage. It is important to highlight that they must remain covered, without exceptions. Furthermore, they should not be located near other waste, even if all of it is properly classified.
- Collection and external transportation of RPBI : the personnel in charge of this task must have undergone a training process that has prepared them to understand the risks of handling this waste . On the other hand, you should also be aware of all the types of garbage that the establishment you work for generates, so that you do not mix them. The route for transportation must always be the same, to prevent workers from other sectors from passing through it.
- Treatment : The cleanest and most economical method for final treatment of RPBI is to use an autoclave , a hermetically sealed device used for steam sterilization (this does not apply to sharps or body parts). When the waste has been properly sterilized, it can be thrown away with the rest of the garbage.
