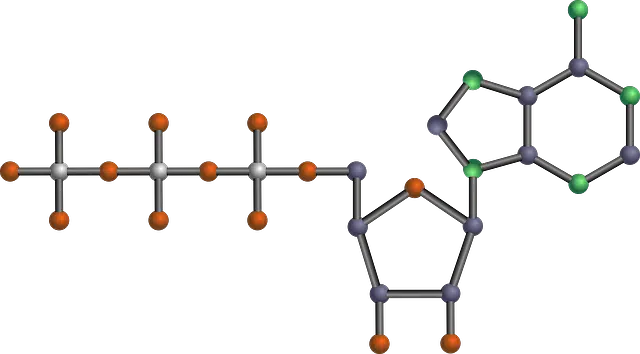
An aldopentose present in some nucleic acids is called ribose.
The dictionary of the Royal Spanish Academy ( RAE ) explains that ribose is an aldopentose found in certain classes of nucleic acids called ribonucleic acids . It is evident that, to understand this definition, we must know what the mentioned terms refer to.
An aldopentose is a monosaccharide that has five carbon atoms and an aldehyde functional group. Monosaccharides, for their part, are polyalcohols (organic elements that have different alcoholic groups) with an additional ketone or aldehydic group.
As for ribonucleic acids or RNA , it can be said that they are biopolymers that have ribonucleotides as a unit . Ribonucleotides, meanwhile, are nucleotides with ribose as a constituent sugar.
What is ribose
In short, ribose is a polyalcohol, monosaccharide, and aldopentose that is present in biopolymers called ribonucleic acids . This last name, in fact, is linked to ribose itself (that is, ribonucleic acids receive that name due to the presence of ribose).
Ribose, being present in RNA, is part of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and is essential for the development of the metabolism process that allows the production of adenosine triphosphate or ATP , a vital energy source for cells .
Ribose is found in RNA.
A supplement
It should be noted that ribose, in some cases, is prescribed as a supplement . People with heart problems may have a low ATP level: therefore, consuming ribose in capsules, powder or liquid helps to improve this level and recover cardiac function. Excessive consumption of ribose supplements, however, can have certain side effects, such as stomach upset.
Some ribose formulas are especially indicated for people who play sports regularly, as it provides them with the energy necessary to make a difference in the most decisive moments. It is recommended to consume products indicated by a professional, and always prioritize those that contain pure ribose and no excipient (an inert substance that gives shape, consistency or flavor to a medication, among other properties that make its use and dosage easier).
The ribose distributed in this way must dissolve in water and its flavor is very pleasant. Since it is a widely consumed supplement in the field of athletics , there are various products that adjust to the needs and activity level of each person.
ribose-5-phosphate
Ribose-5-phosphate is known as one of the products of the so-called pentose phosphate pathway , as well as an intermediate of the same. This metabolic pathway is also called the pentose phosphate shuttle and is closely linked to glycolysis , a metabolic pathway in which glucose is oxidized to generate ribose, which participates in the biosynthesis of nucleic acids and nucleotides .
One of the phases of this pathway is called oxidative , and begins when NADPH is obtained from glucose-6-phosphate, through the phosphorylation of free glucose. Throughout this phase, the enzyme called pentose-5-phosphate isomerase appears, which acts by isomerizing ribulose-5-phosphate through an endiol intermediate, and transforms it into ribose-5-phosphate (this is possible because converting the ketose group into aldose). From this reaction , a component used for the biosynthesis of nucleotide cofactors, DNA and RNA, arises, and the transition to the next phase, the non-oxidative phase, also begins.
The non-oxidative phase of the pentose phosphate shuttle only begins if the cell requires NADPH in greater quantities than ribose-5-phosphate, and here a highly complex sequence of reactions takes place, consisting of the change of sugars in the pentose phosphate shuttle. C3 to C7 of pentoses with the aim of producing fructose-6-phosphate and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate, which can continue glycolysis.
