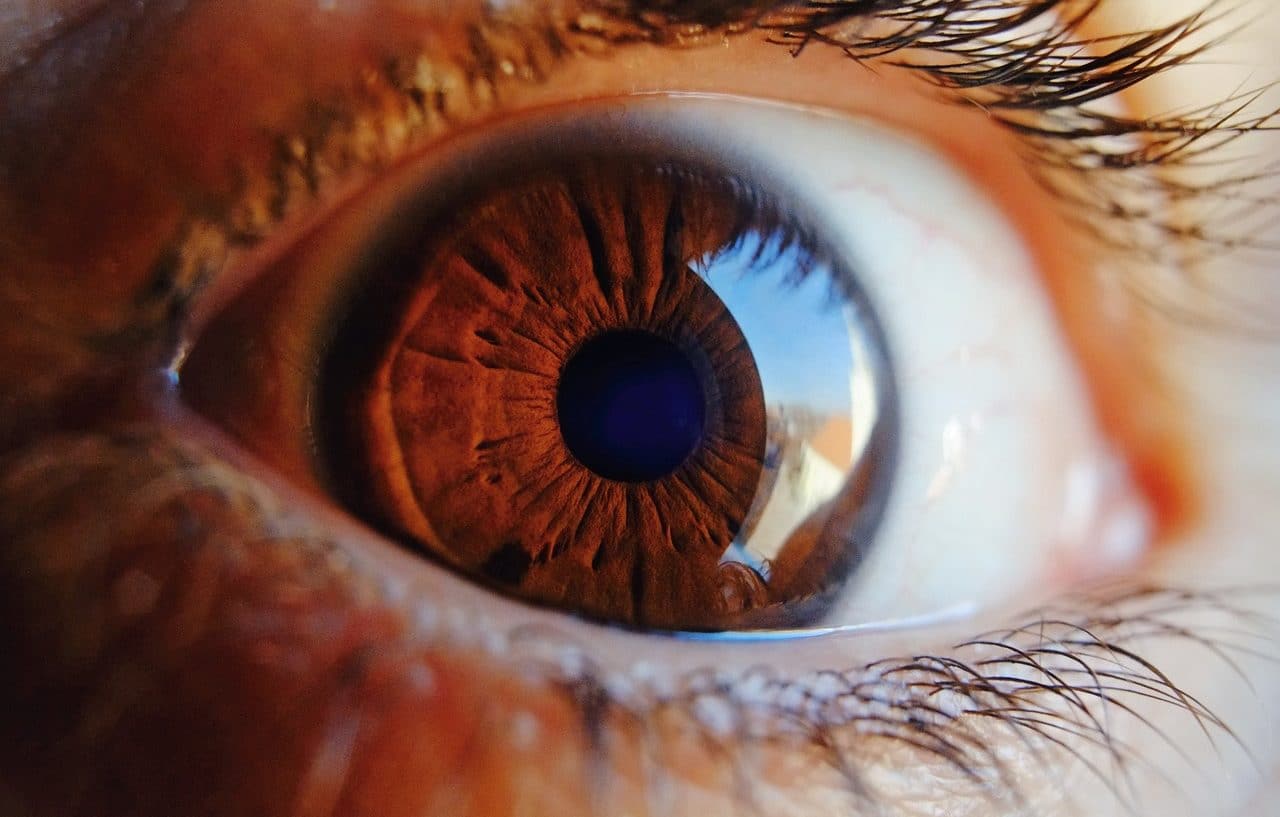
The retina is a membrane found in the eye.
The retina is a membrane located inside the eye that is responsible for receiving images and, through the optic nerve, sending them to the brain. Composed of different cellular layers, the retina is a type of tissue that is sensitive to luminosity and that generates various processes until reaching the transmission of a nervous impulse to the brain.
The photoreceptor cells (they are so named because they are sensitive to light ) are the rods and cones . It is estimated that, in humans, the retina houses more than 126 million of these cells, mostly rods. The latter, precisely, come into operation when there is low light and provide a black and white vision. The cones, on the other hand, act in good lighting conditions and allow color vision to develop.
The outer layer of the retina is called the pigment epithelium . Then other layers appear until we reach the so-called internal limiting layer , which divides the retina from the vitreous humor (liquid between the retina and the lens ).
Retinal disorders
The retina can be affected by various problems that reduce the ability to see. Hypertensive retinopathy causes a deformation of the retina due to high blood pressure, while diabetic retinopathy involves damage caused by diabetes to the blood vessels that are responsible for supplying the membrane.
Retinitis (an inflammation of the retina), age-related macular degeneration (a deterioration in the central layer of the retina, called the macula ), and retinal detachment (the separation of the membrane from the epithelium to which it should be attached) These are other disorders that the retina can suffer from.
Various disorders can affect the retina.
The detachment
Retinal detachment usually occurs when it suffers a perforation or tear , which causes fluid to leak from the eye . The appearance it usually has in this case, which is called posterior vitreous detachment , can be compared to that of an air bubble between a sheet of paper and a piece of adhesive tape. Other possible causes are very severe myopia or trauma , and the chances increase if there is a family history.
Regarding the symptoms of retinal detachment, we can point out the following: poorly defined vision ; spots on the image; flashes of light, mainly in peripheral vision; and inability to capture a complete image (partial blindness ).

A retinal exam can diagnose problems in the retina.
Diagnosis and treatments of retinal problems
Retinal diseases , as well as retinal dystrophies , can be diagnosed and treated in different ways. Retinal angiography , for example, is a procedure that allows the blood vessels of the retina to be analyzed.
A diagnostic test that is carried out with a retinograph is called retinography . It makes possible the identification of diabetic macular edema, retinitis pigmentosa, glaucoma and other disorders.
Optical coherence tomography is another non-invasive diagnostic method, which allows the ophthalmology expert to study the different layers of the retina.
Visual rehabilitation , meanwhile, can be carried out in different ways. A retinal surgery is laser photocoagulation , which eliminates or shrinks abnormal structures in the retina. There are also other innovative retinal treatments that involve the use of retinal stem cells .
The ophthalmologist, depending on the pathology, is responsible for determining the appropriate way to reverse blurred vision and other problems and recover, whenever feasible according to the condition, visual acuity .
A type of screen
The name Retina Display (or "Retina Display" ) refers to a trademark belonging to the North American company Apple , used to identify a series of screens that are characterized by having an especially high pixel density .
According to Apple , thanks to this technology , a greater number of pixels is achieved than the retina of the human eye is capable of perceiving, although many specialists have opposed this statement, considering it a mere marketing instrument.
Companies responsible for the development and manufacturing of retina displays include Sharp, Samsung, Japan Display and LG . The technology on which they are based is In-plan switching (with its acronym IPS ), created by Hitachi in 1996 to improve viewing angles and color quality in Twisted Nematic ( TN ) monitors, which, on the other hand, Part, they offer an optimal response time.
The pixel density of the retina display is 326 per inch , and Apple relied on this number to maintain that it exceeded the capacity of our retina, pointing out that it does not reach 320 ; In other words, in a monitor with these characteristics, we are not able to distinguish one pixel from another, so the sharpness is theoretically unsurpassable (or excessive).
