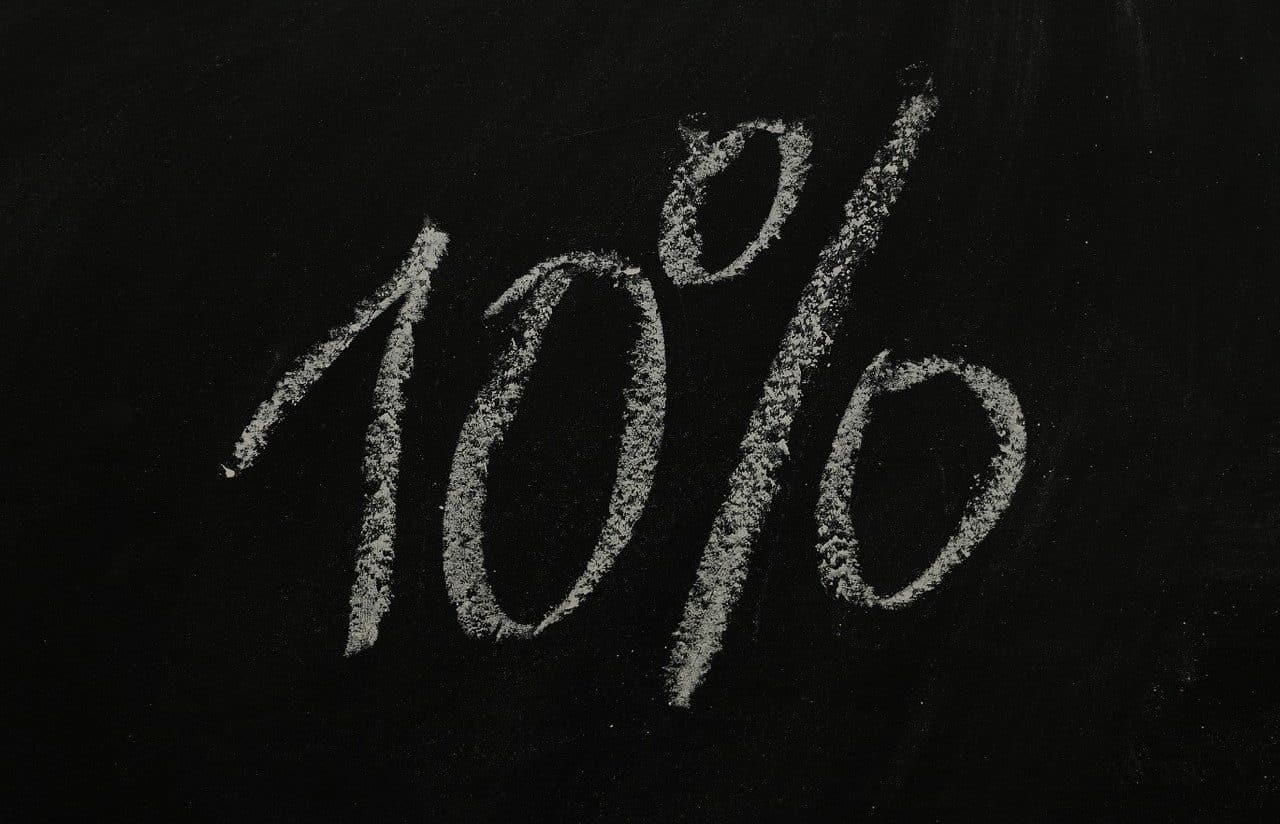
The resulting price is the one paid after the application of discounts or surcharges.
Resulting is the adjective that qualifies that which results . It should be noted that the verb result, for its part, refers to demonstrating, verifying or having a result .
For example: “After the merger of both companies, the resulting service is really terrible” , “25% unemployment is the figure resulting from the policies applied by this government” , “If you mix these substances, the resulting effect can be very dangerous" .
Let's take the fictional case of two animal protection associations that decide to merge: Let's Fight for Animals and Happy Animals . The organization resulting from this decision is a new entity, which they decide to name Let's Fight for Happy Animals .
Resulting price
The resulting price , on the other hand, is the value that is finally paid for a product after different discounts or surcharges. Suppose a person takes advantage of a credit card promotion and pays 200 pesos for a pair of pants knowing that, days later, they will return 10% of what they paid. Thus, once you receive the refund, the resulting price of the pants is 180 pesos (the original 200 pesos minus 10% ).
In times of sales is where the most work is done with resulting prices, since buyers go to stores knowing that they will be able to take home different clothes at a much cheaper value than what they had before, since they have experienced discounts. . These discounts will appear duly indicated on the label so that you can calculate the final price of the item in question.
In physics, the geometric sum of vectors is known as a resultant.
Uses of the term in mathematics
In the field of mathematics, the resulting term that concerns us now is also used. Specifically, it is used to refer to the product of the differences of the roots of two monic polynomials on a field .
However, it should not be overlooked that the resultant results are also commonly used within algebraic geometry . Specifically, in this case they take center stage when it comes to undertaking the calculation of intersections.
resultant force
In the field of physics , the geometric sum of different vectors is known as a resultant . Forces (actions that, when applied to a body, change its speed through acceleration) can be considered vectors or vector magnitudes. In this way, when these vectors are added, we obtain what is known as the resultant force (which is equivalent to the sum of all the forces that act).
Likewise, it is also important to keep in mind that, sometimes, when reference is made to the resultant force, it is always associated with what is called equilibrating force . This is identified as a force that has both the same direction and the same module as the previous one, but its direction is the opposite. Hence it is considered that it acts as a balance of the system.
An interesting fact regarding both types of force is that it is established within physics that by adding, in a vector manner, what the two are, resultant and equilibrating, the figure of zero is obtained.
