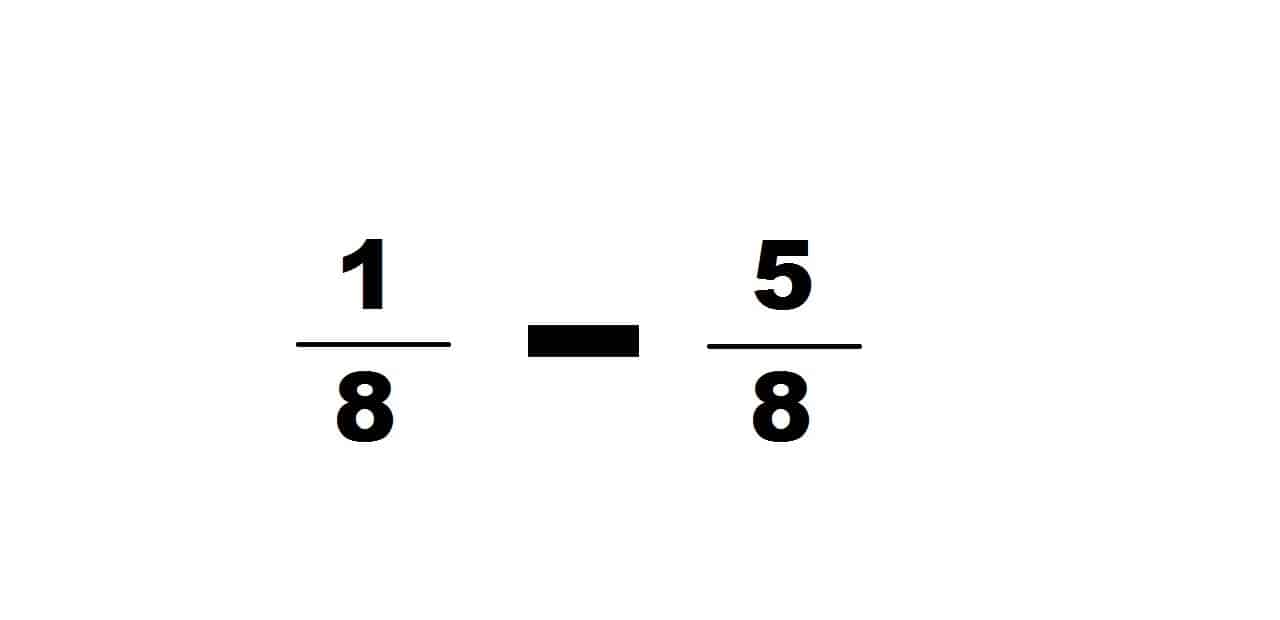
Subtracting fractions is a mathematical operation.
A subtraction of fractions is a mathematical operation . To understand the concept, it is necessary to first focus on several terms .
The term subtraction usually refers to the operation that consists of subtracting . This verb, for its part, refers to reducing, shrinking or separating a part from a whole . If we focus on mathematics, subtraction consists of finding the difference that exists between two expressions or quantities.
In this way we can talk about different types of subtraction, such as algebraic subtraction , subtraction of polynomials , subtraction of vectors and subtraction of matrices . In this case, as we already indicated, we are going to focus on the subtraction of fractions.
Development of subtraction of fractions
To understand this operation, we must know that, in mathematics, a fraction is an expression that reveals a division . It is, in other words, a quantity that is divided by another quantity.
A fraction is made up of two numbers : the upper one is called the numerator , while the lower one is known as the denominator . The way to develop a subtraction of fractions will depend on whether both fractions have the same denominator or not.
When the fractions have the same denominator , we must simply subtract the numerators as in any algebraic subtraction and keep the denominator. For example:
7/2 – 4/2 = (7 – 4)/2 = 3/2
If the denominators are different, we must first equal them , finding the common denominator . To do this we can multiply each fraction by the denominator of the other:
9/7 – 2/3
(9 x 3) / (7 x 3) – (2 x 7) / (3 x 7)
27/21 – 14/21
Once we find a common denominator, we proceed to subtract as explained in the previous example:
(27 – 14)/21 = 13/21
The subtraction of fractions can have different complexities.
The learning
Students in the childhood stage, before entering secondary school, are when they begin to learn to add and subtract fractions , since these mathematical operations are basic and fundamental when it comes to expanding their knowledge in this subject.
Specifically, they begin by doing problems with two fractions and then, to consolidate what they have learned, they proceed to perform the same operation but with three or more. In that case, the procedure is similar. Thus, in the event that they share a denominator, everything is much simpler because they will only have to proceed to subtract the numerators.
If what happens is that they have a different denominator, then we will have to follow the previously mentioned process of finding what the least common multiple is and from this, once it has been achieved, develop what would be the subtraction with the numerators.
Other operations beyond subtraction of fractions
Addition and subtraction are the simplest operations to undertake with the aforementioned fractions. However, it should not be overlooked that you can also choose to perform multiplication and division . In the first case, what you have to do is multiply the numerators on the one hand and the denominators on the other. Example: 3/2 x 5/4= (3 x 5) / (2 x 4) = 15/8
In the second case, when dividing two fractions, what you have to do is multiply the numerator of one fraction by the denominator of the other to obtain the final numerator and multiply the denominator of the first fraction by the numerator of the second to obtain the final denominator. Example: 3/2 : 5/4 = (3 x 4) : (2 x 5) = 12/10 .
