
The piggy bank (or piggy bank) has a slot to allow coins or bills to pass through.
Surface to insert something
Typically, the concept is used in reference to the channel that is created in a surface to allow the insertion of a part . Depending on the context, the slots have different characteristics.
It is common that the slots allow the assembly of different elements. When you insert something into the slot, it attaches to the sector in question. In any case, there are slots whose function is to allow ventilation or the introduction of relatively thin objects, such as a bill, a coin, etc.
Many devices, for example, have slots for air passage. Thus, when its operation causes heating, the heat escapes through the slots and damage to the equipment is avoided. We can find this in desktop and laptop computers, in the most modern video game consoles, in televisions and in sound system receivers, among others.
Since the function of these slots is to allow hot air to flow out of the appliance, it is extremely important to always keep them clean , free of dust and other objects that may represent an obstruction. Similarly, it is recommended to have these devices in smoke-free environments, since smoke can easily enter and settle on the most delicate parts.
To deposit money
Vending machines , on the other hand, have slots for the user to deposit money and pay for what they intend to buy. Similarly, automated teller machines ( ATMs ) have slots for inserting and withdrawing bills.
A person, in this framework, can put a bill in the slot of a candy vending machine to get a chocolate, to mention one possibility. Or withdraw a thousand pesos from a savings account by placing your card in an ATM slot and obtaining the money from another slot.
Expansion slots
Computers , meanwhile, have expansion slots on their motherboard, also known as motherboard, motherboard, mainboard or motherboard . Thanks to the slots (which are also known by their English name, slots ), it is possible to connect multiple components.
There are different types of expansion slots, PCI-Express being one of the most used today. They can connect video cards , audio cards and other elements that are key to the performance of the computer. Another name by which this slot is known is simply PCIe , and should not be confused with PCIX or PCI-X , a more modern version of the also known PCI .
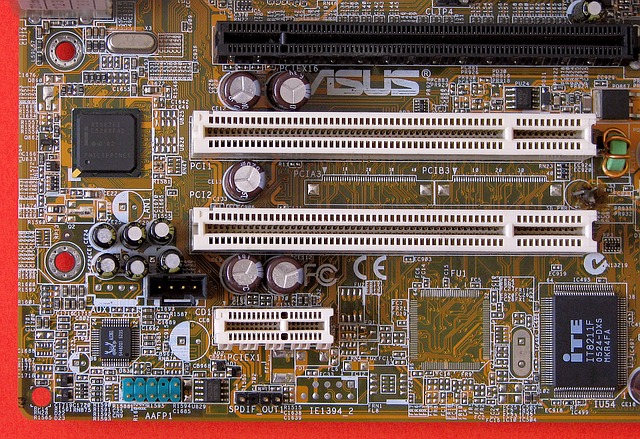
A motherboard with several expansion slots
The PCIe bus has a structure of point-to-point links that work in series . Speaking of versions 1.1, 2.0 and 3.0, we started from a speed of 250 MB per second on each link and reached 1 TB per second in the last one, since it was doubled in each generation. In each of these expansion slots there can be between one and thirty-two data links between the cards we connect and the motherboard (the quantity must be a multiple of 2 and is written with an "x" in front: x2 , x8 , etc.) .
Going back to PCI for a moment, it's important to note that a single PCIe link achieves almost twice the speed of the previous one; If the expansion slot has four links, its bandwidth can be compared to the faster PCI-X 1.0. We can also mention another expansion slot, the so-called AGP , developed in 1996 by Intel and used to connect the video card and memory directly; PCIe with eight links achieves similar bandwidth to the fastest AGP.
