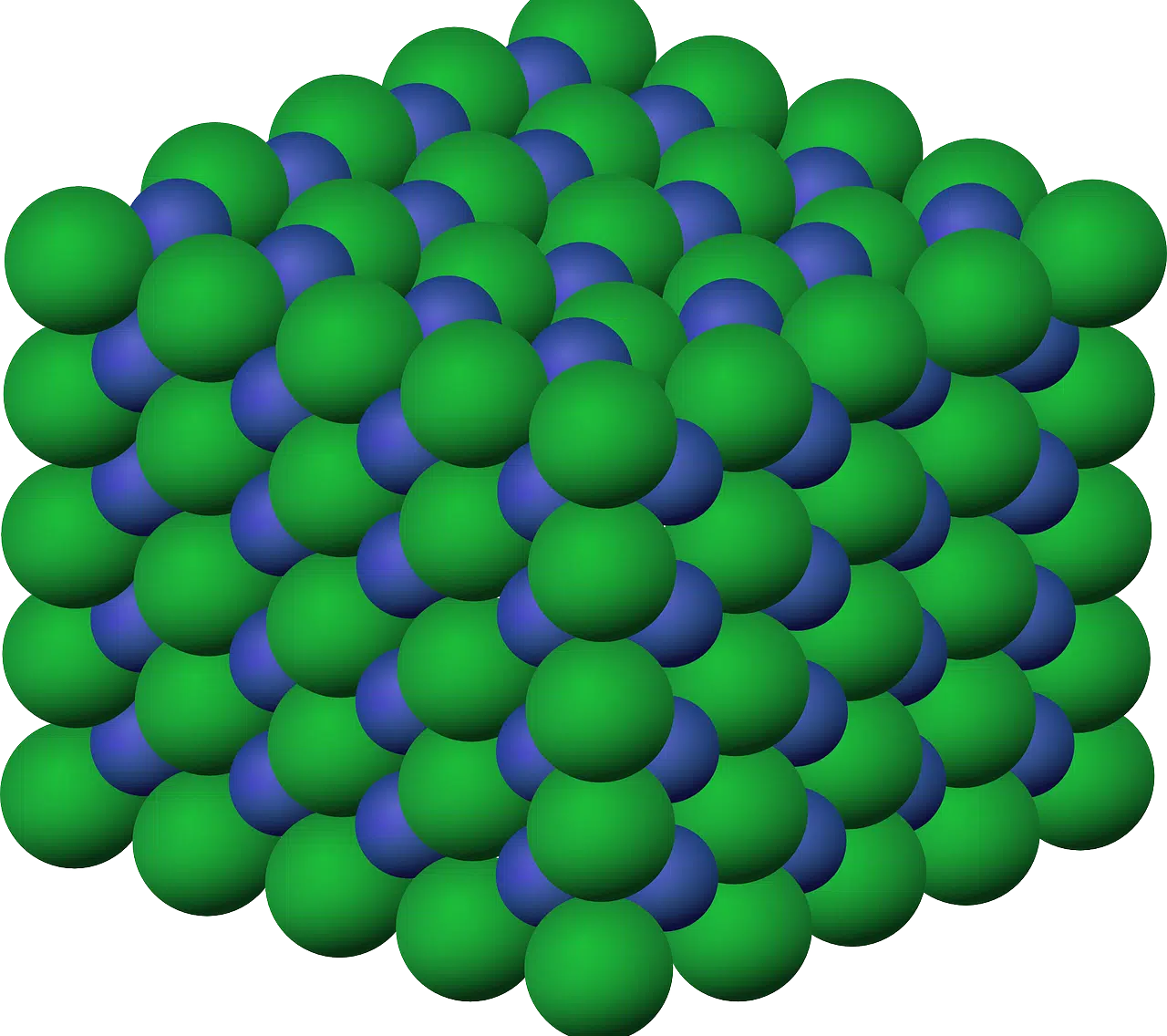
The ionic radius is understood from the atomic radius.
Ionic radius is a concept that can be understood from the atomic radius . The atomic radius is the average distance between the nuclei of two atoms linked through a covalent bond. In the case of the ionic radius, it is the radius that exists after the atom has gained or given up electrons. That is why this radius is associated with ions .
Before moving forward, it is important to record the etymological origin of the two words that give it shape:
- Radius derives from the Latin radius , which is equivalent to “ray of light” or “rod” .
- Ionic emanates from Greek and can be translated as “relative to groups of atoms that are electrically charged.” Specifically, this term is the result of the sum of two main elements: ion , which is synonymous with "he who walks" , and the suffix -ico , which is used to indicate "relative to" .
What is ionic radius
Radio is a concept with multiple meanings. Today we are interested in taking the term as half the diameter of a circle . Ionic , for its part, is an adjective that refers to what is linked to the ion (an atom or set of atoms that gains electrical charge from gaining or losing electrons).
An ion, therefore, has a charge, which can be negative or positive. Its origin is found in the tendency of chemical elements to resemble the noble gas that is closest. Positively charged substances are known as cations , while negatively charged substances are anions .
When talking about the ionic radius, two specific circumstances can occur: that the element in question proceeds to lose electrons or, on the contrary, it gains them. That species that lost an electron has a smaller ionic radius compared to the atomic radius, since the electrons experience a greater attraction towards the nucleus. On the other hand, the species that added an electron has a larger ionic radius compared to the atomic radius (the added electron is not very attracted to the nucleus).
The ionic radius depends on the gain or loss of electrons.
Some considerations
While the ionic radius grows along with the decrease of a group , it is difficult to establish a trend with respect to the periods , because these depend on the ions and there are elements with several possible ions.
In addition to all of the above, it is necessary to make known that the ionic radius does not have the particularity of presenting a clear tendency to growth at a specific and determined moment because this depends on the ion in question.
Likewise, regarding this circumstance, it must be stated that it is marked by very important factors such as the effective nuclear charge , atomic mass and atomic number .
