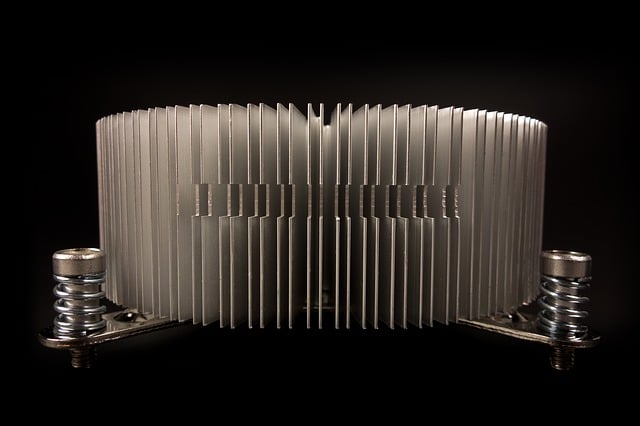
A computer radiator
A radiator is a heat exchanger . It is an element that allows heat to be dissipated from something , either to prevent it from overheating or to use it to heat a place.
Radiation and convection
Radiators can work by radiation and convection . What these devices do is receive or give up heat, depending on their function and the temperature difference between the exchange media.
In combustion engines used in automobiles and other machines, the radiator is used to remove heat from the coolant , giving it to the air . Their operation is very important since, while they are on, these motors produce a lot of heat that must be dissipated.
The radiator, in this framework, is part of the vehicle's liquid cooling circuit . In order to enhance the effect of convection, a fan with a thermostat and equipped with a small motor promotes air circulation through the device.
On electronic devices
Computers ( computers ), on the other hand, have radiators coupled to fans to dissipate the heat generated in the circuits, thus preventing damage to the electronic components. These radiators, known as heatsinks , enable the cooling of microprocessors, especially the CPU and GPU.
Today, this also occurs on other devices, beyond computers. For example, in video game consoles. Basically, any device that requires at least a microprocessor for its operation and that, for reasons related to its design and application, generates too much heat to be dissipated in any other way, requires the installation of a radiator.
Interestingly, today's most popular devices, mobile phones, do not take advantage of this technique to dissipate heat, as they are too narrow. How do manufacturers of phones, tablets and other ultra-thin devices prevent their processors from burning out? They generally take advantage of the metal casing itself to act for this purpose. In fact, one of the reasons why they do not generate as much heat as a desktop computer is that they use a much smaller amount of electrical energy.
Appliance
As a heating device, finally, the radiator is a device that contemplates the circulation of a hot liquid inside to radiate heat to the environment . It may have tubes, fins or panels to emit said heat. Generally, this resource is used in the development of a centralized heating system .
In this context we speak of heat transfer fluid , the liquid that transports heat from one point to another, passing through different conduits. The process is relatively simple, although it must be repeated many times throughout operation: the fluid is heated at one point and then moved to release it at another. There are different types of radiators, such as steel tubes , which are usually arranged vertically and welded to two collectors, one above and one below.
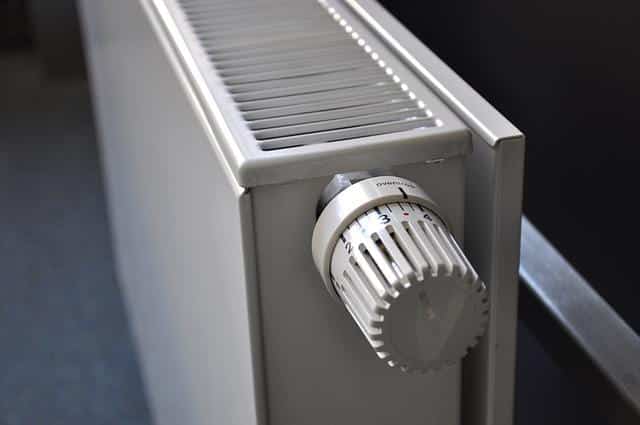

A radiator used for space heating
Steel tube radiators effectively resist pressure and are used in industrial environments, at high altitudes and where there is steam in the environment. We also have tubular radiators with fins , which have a larger emission surface. These fins are placed on the tubes and thanks to this design it is possible to manufacture smaller radiators, although cleaning becomes more difficult, given that it has more recesses than the previous one.
Another common type of radiator is the flat panel radiator, which consists of two sheets of steel with a maximum thickness of 4 millimeters, smooth or channel-shaped. It is the cheapest on the market.
