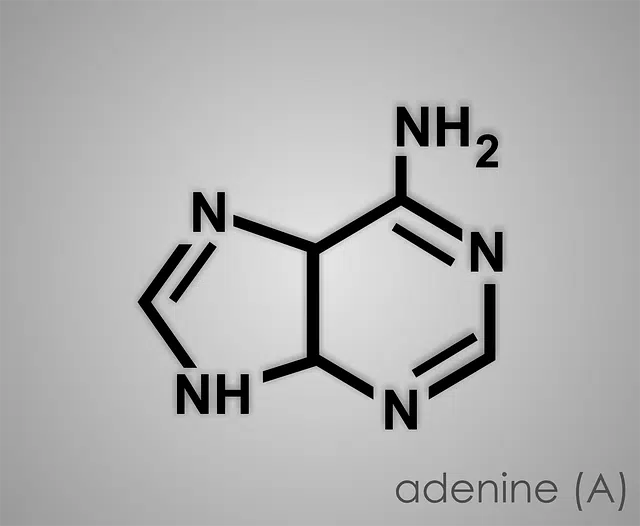
Adenine, an important purine in our body
The concept of purina comes from a German word, in turn derived from the Latin purus (which can be translated as “ pure” ). The term is used in the field of biochemistry to name a nitrogenous base that is formed with a pair of heterocyclic rings .
a chemical compound
It is important to keep in mind that nitrogenous bases are those nitrogenous chemical compounds (with nitrogen ) that make up nucleic acids (ribonucleic acid or RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid or DNA ). Heterocyclic rings, meanwhile, are cyclic structures that have at least one non-carbon atom.
Taking this into account, we can say that a purine is a chemical compound with nitrogen (a nitrogenous base) that has a ring -shaped structure with one or more non-carbon atoms (heterocyclic ring). Specifically, purine has two rings (one with five atoms and the other with six atoms) that are fused.
The German scientist Hermann Emil Fischer (1852-1919), winner of the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1902 , was the one who synthesized purine for the first time and was responsible for coining the concept . This expert started from uric acid to achieve the reactive sequence.
Metabolization and degradation
It is important to mention, in this sense, that the metabolization of purines within cells generates uric acid. If that uric acid is broken down by pancreatic enzymes in the small intestine, it is hydrolyzed into free bases and nucleosides. On the other hand, if for some reason it crystallizes within a joint, it can cause gout or other disorders; If it does so in the urinary tract or kidneys, it generates the so-called uric lithiasis .
At this point we need to refresh the definitions of some technical terms. Let's start with metabolism , which refers to any chemical and physical process in the body that serves to transform or use energy. Among the most common and easiest to perceive are breathing, muscle contraction, food digestion, blood circulation, and the disposal of certain substances through feces and urine.
Secondly we have uric acid , an organic compound consisting of carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen and oxygen. It is a weak acid that is produced in the liver, intestines, muscles, endothelium and kidneys, precisely as the last product of the metabolic process that degrades purines, more precisely adenine and guanine. This phase of metabolism is called catabolism , and it seeks to extract chemical energy that the cell can use.
Finally, we mention the disease known as gout , which occurs when crystals of the salt derived from uric acid accumulate. It can attack different parts of the body, although it particularly occurs in the kidneys, soft tissues and joints. The most common condition is the attack known as podagra , which generally begins at night and causes intense pain in the big toe.

Purina is also a major brand of animal food products.
The commercial brand
Purina , on the other hand, is a brand that belongs to Nestlé and that identifies pet foods produced by this company. Purina Cat Chow and Purina Dog Chow are some of their products.
The emergence of Purina took place in 1894, under the leadership of William H. Danforth , who began manufacturing feed for various species of farm animals. In 1902, the Ralston Purina Company emerged after a merger with another company. Almost a century later, in 2001, Purina was acquired by Nestlé, a major Swiss company dedicated to food products for both humans and pets .
