Pneumonia is caused by a bacteria known as pneumococcus.
Pneumonia is the name given to a disease that affects the lungs or certain sectors of them. The condition is generally caused by the action of pneumococcus , a bacteria that can cause different kinds of infections in the body. Due to the name of this microorganism, pneumonia is also often called pneumonia .
The development of pneumonia involves inflammation of the lung tissue, causing pain and cough . Other symptoms of the disease are the appearance of fever, muscle pain , headache, chills, difficulty breathing, slowness in overcoming a simple cold or flu, and nausea.
Types of pneumonia
There are different types of pneumonia, depending on its degree of incidence or its origin. One can speak, in this way, of:
- Interstitial pneumonia : This is a group of lung disorders characterized by inflammation and damage to deep lung tissues . The name derives from interstitium , tissue that surrounds the air sacs called alveoli, which absorb oxygen and swell during breathing. The disease in question prevents the correct expansion of the alveoli since the interstitium hardens. The consequence is a decrease in the amount of oxygen that enters the body.
- Lobar pneumonia : This type of pneumonia is also known as lobar or segmental pneumonia and is characterized by the presence of lesions in a large part of the lung or in an entire lobe. The normal thing is that it compromises or affects all the structures in the affected area. In addition to the dull sound (dry, dull) that is perceived during percussion, auscultation returns what is called a tubal murmur , a sound similar to that produced while blowing on the spout of an empty container.
- Bronchopneumonia : it is an inflammatory and usually infectious process that compromises the bronchi and lungs. It is also known as bronchopneumonia . It usually occurs as a continuation of a previous bronchiolitis or bronchitis and appears very frequently, especially during breastfeeding (since the person has fewer means to defend themselves against pathogenic microorganisms, of high or low virulence) and old age (very often when they suffer from of a serious illness).
- Community-acquired pneumonia : Since the most common name for this disorder has the word pneumonia instead of pneumonia, the acronym by which it is known is CAP . It is an infectious disease that appears specifically in people who have not been admitted to a hospital recently . Age is not a determining factor, nor is the country of residence. It is important to note that it is among the most prominent causes of mortality. The way in which someone can acquire this disease is by breathing in or inhaling fungi, bacteria, parasites or viruses, among other pathogenic microorganisms.
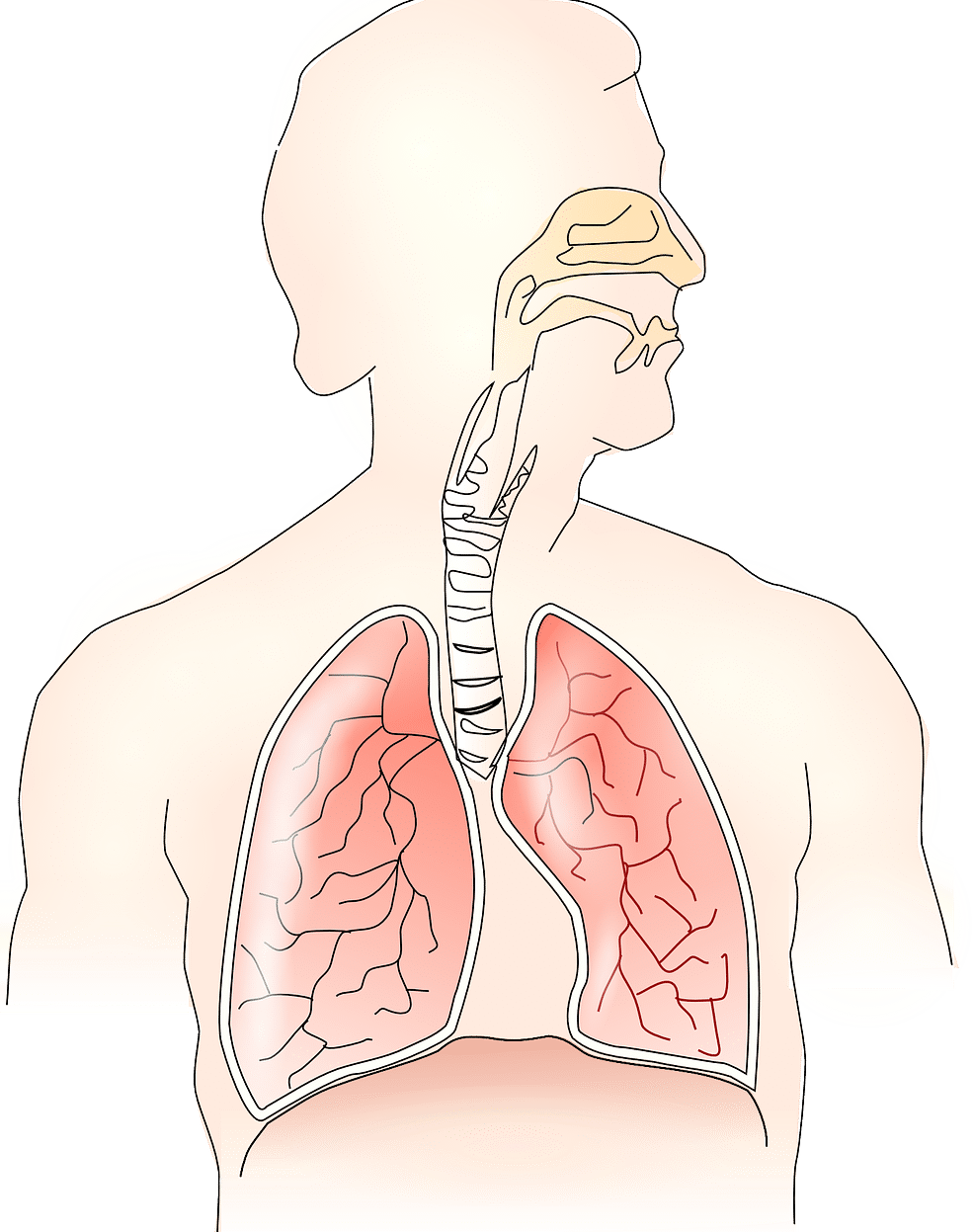
Pneumonia affects the lungs.
Diagnosis and treatment
Chest x-ray is the most common method for diagnosing pneumonia. The doctor may also order a blood test to confirm the infection and identify its cause.
It is important to note that pneumonia always requires medical attention . It is even a potentially fatal disease, especially in the elderly and in individuals who suffer from immunological depression. The coughing and sneezing of those infected makes pneumonia easily spread.
Pneumonia can usually be treated without hospitalization. The doctor will be in charge of prescribing certain antibiotics (such as erythromycin or amoxicillin) and ordering the patient to rest . When the person is elderly or has breathing problems, it is likely that they will be admitted to a hospital so that their care is intensive and thus avoid possible complications.
