Relative position refers to the location of a place with respect to another or others.
The Latin word positio came into Spanish as a position . The term can refer to how or where something or someone is located . Relative , on the other hand, is an adjective that refers to that which is related to another element .
The idea of relative position is usually used in the field of geography to name the location of a site with respect to another or others . This position, therefore, is determined by the link between the place in question and other places. The absolute position , on the other hand, is defined by its geographical coordinates on the Earth 's surface.
Relative position example
Take the case of Paraguay . The relative position of this nation indicates that it is located in the center of South America , more precisely north of Argentina , south of Bolivia and west of Brazil .
This means that, knowing the location of Argentina , Bolivia and Brazil on a map, it is possible to point out where Paraguay is. The absolute position, on the other hand, places the country between latitudes 19°18' and 27°30' S and between longitudes 54°19' and 62°38' W.
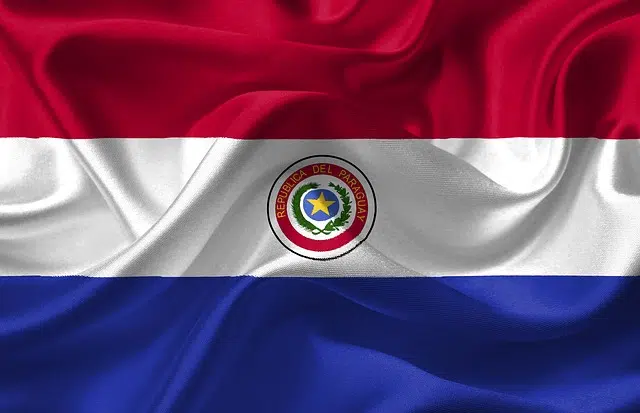

The relative position of Paraguay indicates that this country is located west of Brazil, south of Bolivia and north of Argentina.
The notion in geometry
The notion of relative position also appears in geometry . To discover the relative position of two lines , it is necessary to pay attention to their direction vectors : those that orient it and give it direction.
By observing the direction vectors, you can know the relative position of the lines . When the direction vectors of two lines are proportional to each other, they are parallel. If these lines with parallel direction vectors have no points in common, they are also parallel , while if they have a point in common, they are coincident lines . In the event that the direction vectors of the two lines are not parallel, they are secant lines .
Relative position in computing
In the field of computing we can also find this concept or those of relative path or address , and their absolute counterparts, to refer to the location of a file or data on a storage medium or in memory, among others. odds. Although this degree of accuracy may seem capricious, we must not forget that in science one cannot proceed with assumptions but that a tiny change in a value can produce an error or a result considerably different than expected.
If we think about the design of a website, for example, developers must create complex trees of directories and files, in which they house the different parts of the site to access them when they need it. Among the most common directories, the one for images stands out, where many more can also be created to group them by date or size: it is common for at least two versions of each image to be hosted on the server, one of them smaller to use in the view prior.
Now, within this system we have several code documents, and they contain the lines that refer to images and other documents to present the content dynamically. At this point we can choose two paths: use the relative position of each element, to call it from "where we are standing", or the absolute one, so that the line of code can be executed from any point (as long as the server grants us the appropriate permission).
Let's look at this in a practical example: if on a web page we specify the loading of an image that is located "one directory up, and then in the so-called "image"", this will only work as long as the structure is not altered; If one day we changed the name or location of the "image" directory, we would get an error since its relative position would not be the same.
