The magnetic poles are not coincident with the geographic poles.
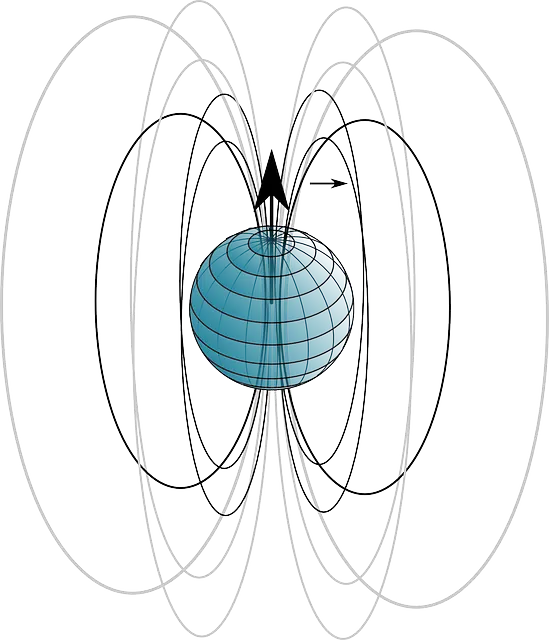
The set of points on the globe that is located in the polar areas and that, due to the Earth 's magnetic field , exerts attraction on the magnetized elements is known as the magnetic pole . Compasses , for example, have needles that, due to magnetization, always point to the magnetic south pole.
The magnetic poles do not coincide with the geographic poles : the location of each magnetic pole, in fact, shows a displacement against the geographic axis of the planet . The angle created between said axis and the magnetic axis is represented by the letter delta (from the Greek alphabet) and is known as declination .
The Earth's magnetism is due to the materials in its core: nickel and iron . This composition makes the Earth itself act like an immense magnet , which explains how compasses work. Because different poles are attracted and identical poles repel, the compass points to the geographic north pole, which is almost equivalent to the magnetic south pole.
The reversal of the magnetic poles
For a long time it was speculated that the reversal of the Earth's magnetic poles could cause great changes in the planet, even leading to its destruction. Astronomers, however, explain that such reversal is normal and takes place every certain (long) period of time .
This inversion is linked to the weakening of the Earth's magnetic field, which protects our planet from dangerous projectiles of charged particles and radiation that come from the Sun and space. This phenomenon , which puts our planet at risk, was evident in 1980, thanks to the work of some scientific missions.
Our most remote ancestors experienced a reversal of the magnetic poles, although for them it did not mean the chaos that it could represent in the present, given that all the technologies on which modern life is based would be compromised, from mobile phones to the Internet . passing through global positioning systems (GPS). A complete reversal took place 780,000 years ago, and some theorists wonder, ironically enough, whether such a disruption could take us back to the Stone Age.

Compasses indicate the south magnetic pole.
The Swarm Mission
Although it takes thousands of years for the poles to reverse, our satellites and Earth's power supply can be affected in the process, which is why experts got to work in late 2013. The European Space Agency ( ESA) put three satellites into orbit to monitor our planet's magnetic field for four years, in a mission that was named Swarm (which can be translated as Swarm ).
The Swarm mission has the objective of collecting as much information as possible about the Earth's magnetic poles to study the operation of the magnetic shield and prepare a strategy for the catastrophe that would mean being completely exposed to solar radiation and particles.
Magnetic poles as ends of magnets
It should be noted, on the other hand, that the ends of the magnets are also known as magnetic poles. At these poles , the attraction exerted by the magnets is more powerful than in the rest of your body.
A magnet has two poles: north and south . Since one pole cannot exist in isolation from the other, breaking a magnet in two produces two magnets, that is, two bodies consisting of a north and a south pole each. However, if such a fracture occurs, the attractive force of each part is less than that of the original magnet. The force resulting from the attraction between two poles forms closed lines , which go from one to the other in an uninterrupted manner.
