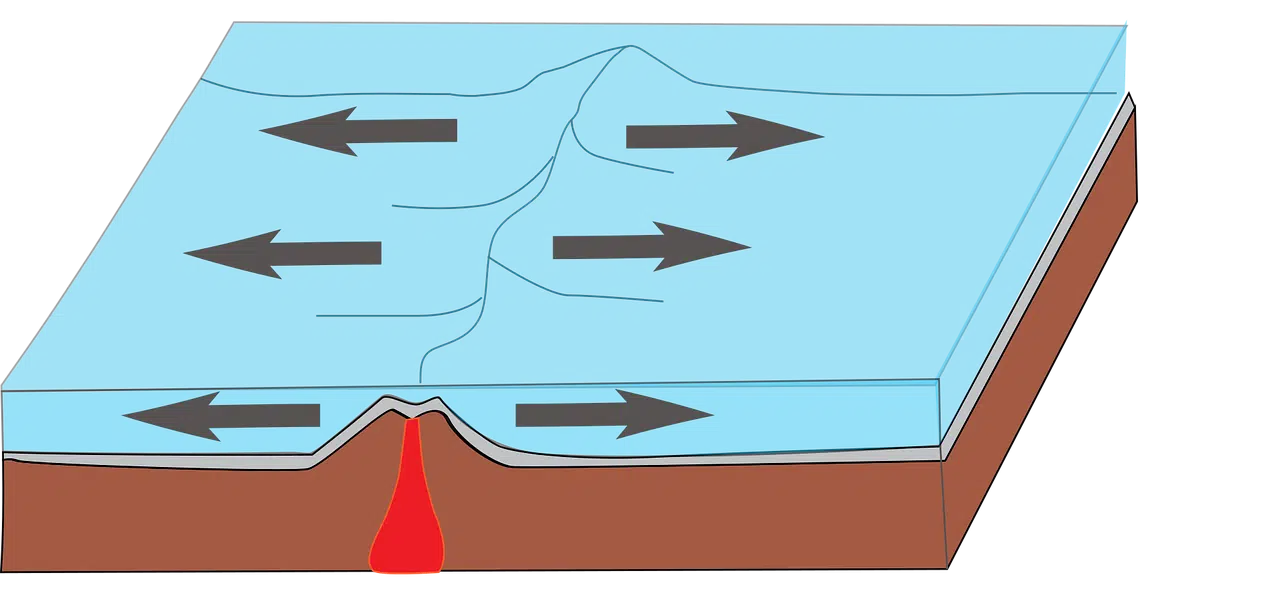
The idea of folding is used in geology.
Folding is a notion used in geology to name what happens in the planetary crust when horizontal pressure affects the rocks . This causes compression that creates waves in the rocks, without breaking them. When rocks break, we do not speak of folding, but of failure .
Lateral pressure is typically exerted over millions of years on the edge of a tectonic plate. The crust thus rises in certain regions and, in turn, sinks in others. Folding becomes a failure when the elasticity of the rocks cannot withstand the pressure and, therefore, the material breaks.
Parts of a fold
It is also important to know that every fold has clearly differentiated parts such as the following: the crest , the flanks , the axial plane , the fold axis , the valley , the pitch , the core , the direction and the hinge . The latter we can say is the area in which there is the most curvature of the entire fold.
The characteristics of folding or the eventual appearance of a fault, in this way, will be determined by the elasticity of the rocks and their ability to adopt a new shape according to the magnitude of the force exerted. Folding is responsible for the creation of the mountain ranges that exist on our planet.
Folding allows a protein to develop its three-dimensional structure.
Classification according to type
It is possible to recognize different types of folding within the framework of a folding. Monoclines exhibit a horizontal branch and another inclined branch; Anticlines , on the other hand, have two descending branches towards sinuses with contiguity; synclines are those with a bowl shape; and, finally, periclinal folds can have external or internal inclination.
However, although this is a general classification, we have to say that there are many other more specific classifications of the various types of folding:
- If symmetry is taken into account, they can be divided into two groups: symmetrical and asymmetrical .
- Based on their shape, they can be antiform , when the fold is convex upward, or synform , when it is convex downward or concave upward.
- Starting from the thickness of its layers, we find anisopaque folding , when the thickness of the layers is not uniform, or isopachous , when it is.
- If we start from what the angle formed by the flanks is, we would have to talk about three types: soft , isoclinal or tight .
The folds of a fold can be measured according to the height or the length of the wave . While some are almost imperceptible, others are many kilometers long.
Folding in biology
We cannot forget that within the biological field the term folding is also used.
In this case, we talk about what is known as protein folding, which defines the entire process through which a protein acquires its three-dimensional structure, key to being able to perform the function entrusted to it. When the opposite phase takes place, it is called protein denaturation.
