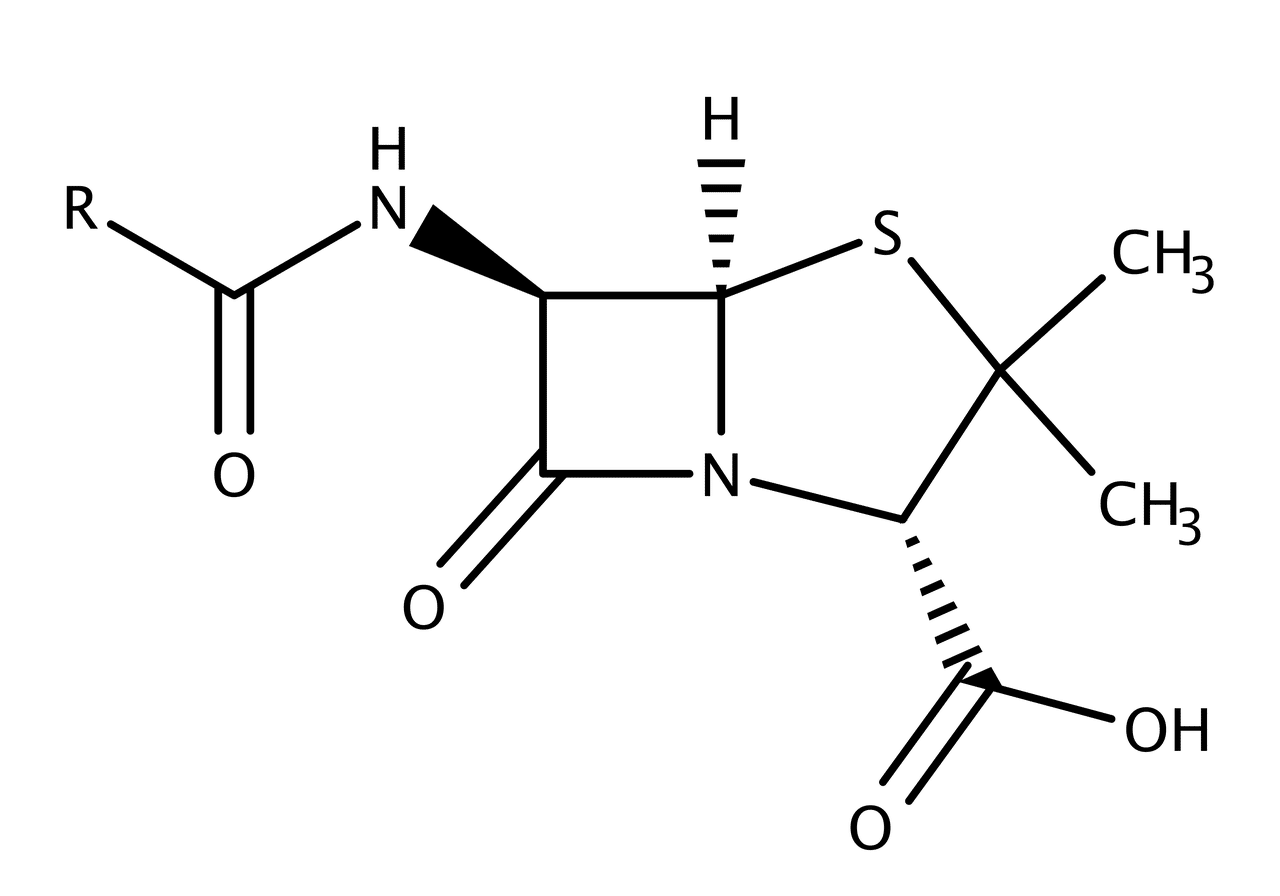
Penicillin is an antibiotic that is usually derived from 6-aminopenicillanic acid.
Penicillin is an antibiotic substance used to combat diseases caused by different microorganisms. The term comes from the English penicillin , which in turn derives from the Latin Penicilliumnotatum . This Latin concept names the mold from whose crops the substance in question is extracted.
Penicillins are usually derived from 6-aminopenicillanic acid and differ from each other according to the substitution made in the side chain of the amino group. In general, penicillins are antibiotics that belong to the beta-lactam group.
The first antibiotic that was widely used in medicine was penicillin G , also known as bencipenicillin . This antibiotic was discovered by Alexander Fleming in 1928 , who, together with Ernst Boris Chain and Howard Walter Florey , was responsible for mass producing it.
Types of penicillin
The different types of penicillins fulfill different functions. Benzylpenicillin helps fight bacteria such as streptococci , staphylococci , meningococci and gonococci . This antibiotic is administered parenterally since it is sensitive to stomach acid.
Ampicillin , on the other hand, can be given orally to act against bacteria such as salmonella , shigella and haemophilus .
Penicillin should not be administered together with certain antibiotics, such as neomycin and chloramphenicol , since this reduces its effectiveness. On the other hand, penicillin reduces the effects of birth control pills .
There are different ways of administering penicillin.
Possible adverse effects
Penicillins are considered the least toxic antibiotics , although they can cause allergies . Therefore, before applying penicillin, the doctor should always consult the patient if he or she suffers from any allergies.
Among the most common side effects that the aforementioned penicillin can produce in patients are headaches , diarrhea, vaginal discharge as well as pain in the mouth and tongue that may also be accompanied by the appearance of a series of white spots. in said oral organ.
However, there is the possibility that when penicillin is applied to a patient, he or she may have another series of adverse effects that, although they are not as frequent, can also occur. These would include fever , joint pain, skin rashes, breathing faster than usual, inflammation in the facial area or the skin becoming more reddish and beginning to flake.
In the same way, there are another series of consequences or reactions to penicillin that are absolutely rare and infrequent but that have also appeared in some cases. Among those we should highlight, for example, seizures, vomiting, yellowing of the skin and eyes, anxiety , depression , bleeding, seeing or hearing elements that do not exist and even confusion .
The usual thing is that in the face of the aforementioned types of adverse effects that penicillin has, it is not necessary for the doctor to act since these will disappear by themselves as the patient's body adapts to said medication. However, if they are very annoying or continue to be evident, it is vital that the healthcare professional takes measures to eliminate them.
