Parasympathetic is an adjective used to describe the sector of the autonomic nervous system whose centers are at the ends of the cerebrospinal axis and which functions as an antagonist of the sympathetic system . It is made up of nerves that arise from the spinal cord and brain.
Greek roots are what the term parasympathetic has. Thus, we can establish that it was formed from the prefix "para-", which means "against" or "beside"; of the particle "syn", which is equivalent to "together"; from the verb "pathein", which is synonymous with "feel", and the suffix "-ico". The latter is used to indicate "relative to."
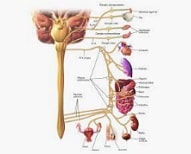 It is important to mention that the autonomic nervous system is responsible for controlling the involuntary functions of the body . This means that it regulates heartbeat, blood pressure, body temperature and digestion, for example. Two parts are recognized in the autonomic nervous system: the parasympathetic nervous system and the sympathetic nervous system .
It is important to mention that the autonomic nervous system is responsible for controlling the involuntary functions of the body . This means that it regulates heartbeat, blood pressure, body temperature and digestion, for example. Two parts are recognized in the autonomic nervous system: the parasympathetic nervous system and the sympathetic nervous system .
The tasks carried out by the parasympathetic nervous system are the opposite of those carried out by the sympathetic nervous system. While the parasympathetic system is responsible for decreasing the heart rate, the sympathetic system increases it, to mention one case. By working together and in a coordinated manner, both systems allow the body to respond to different situations and adapt to varied circumstances.
The parasympathetic remains active while the body rests and during the development of the digestive process. It is responsible for stimulating digestion, defecation and urination and reduces heart rate, respiratory rate and blood pressure . It also constricts the pupils .
In the same way, the parasympathetic nervous system is also responsible for allowing sexual arousal or stimulating saliva production, among other things.
At a general level, the parasympathetic system is dedicated to the stimulation of those processes that contribute to saving or storing energy . Its purpose is to guarantee well-being in the long term. The sympathetic system, on the other hand, aims to resolve incidents in the short term.
In addition to all of the above, it is important to know that the parasympathetic nervous system is made up of four different areas: the sacral, the hypothalamic, the mesencephalic and the rhombencephalic. The latter is the one that is made up of nerve fibers that run through various nerves of the brain.
Of course, we must not overlook that in the aforementioned system at hand there are two types of neurons specifically. Thus, on the one hand, there are the ganglion cells, which are short and are responsible for carrying out the release of acetylcholine. And, on the other hand, there are the so-called pre-ganglionic cells, which are long and are located very close to the cerebrospinal nucleus.
It is curious to note that people who have some type of alteration of the parasympathetic nervous system find a very therapeutic element in music. Yes, because different studies carried out by organizations such as Harvard University have determined that music helps them calm down.
