 The notion of palatine has different uses depending on its etymological root. When it comes from the Latin palātum , it refers to that linked to the palate .
The notion of palatine has different uses depending on its etymological root. When it comes from the Latin palātum , it refers to that linked to the palate .
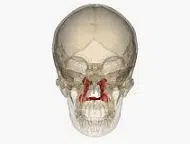
The palate is the upper and inner sector of the mouth in vertebrate animals. The palatine bone , in this framework, is the one that allows the formation of the vault of the palate (also called, precisely, palatine vault ). It is a short, irregularly shaped bone that has a vertical and a horizontal portion, each with a pair of faces.
The palatine tonsils , meanwhile, are those that are found between the pillars of the soft palate, on both sides of the pharynx, in the deepest part of the mouth cavity. It is important to mention that the organ that develops from the union of lymph nodes is called the tonsil .
The limits of the palatine tonsils, which are located on both sides of the oropharynx, are the following:
* the posterior pillar of the muscle known as the palatopharyngeus ;
* the anterior pillar of the palatoglossus , another muscle;
* the superior constrictor muscle, which limits them laterally.
Another name by which the palatine tonsils are known is tonsils , and it is a pair of accumulations of lymphatic (or lymphoid ) tissue , which is made up of reticular fibers of type III collagen that form a network and have a particular type. of fibroblasts at their intersections that are called reticular cells.
It is worth mentioning that the palatine tonsils are found in Waldeyer's ring , a group of lymphatic tissue structures located in the pharynx that, despite having a diffuse presence, form more than one main conglomerate that are named under the name of tonsils , of which there are four types: the palatal (located in the oropharynx), the lingual (in the lower part of the tongue), the pharyngeal (which are also known as adenoids and are in the rhinopharynx) and the tubal (they are smaller and They are located next to the opening of the Eustachian tube).
Regarding the function carried out by the palatine tonsil, we can say that it is defensive, since it is responsible for protecting the respiratory and digestive mucosa from any attack by pathogenic microbes that enter the body.
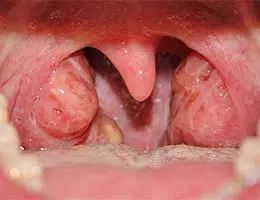 Typically, the size of the palatine tonsil is largest during childhood, and begins to shrink from about 10 years of age. This process of decrease in size is called physiological involution . The nerve branches it receives originate from the lesser palatine and glossopharyngeal nerves. Blood comes to it from several arteries, among which are the following: tonsillar, lingual, ascending palatine, ascending pharyngeal and internal maxilla. Through the lingual and pharyngeal veins, which converge into the internal jugular vein, venous return is carried out.
Typically, the size of the palatine tonsil is largest during childhood, and begins to shrink from about 10 years of age. This process of decrease in size is called physiological involution . The nerve branches it receives originate from the lesser palatine and glossopharyngeal nerves. Blood comes to it from several arteries, among which are the following: tonsillar, lingual, ascending palatine, ascending pharyngeal and internal maxilla. Through the lingual and pharyngeal veins, which converge into the internal jugular vein, venous return is carried out.
The idea of palatine may also come from palatīnus , another word from the Latin language. In this case, the term refers to what is related to a palace : the home of a king, a nobleman or another great personage.
According to the dictionary of the Royal Spanish Academy ( RAE ), palatine can describe the individual who had his office in a palace or mention a high dignitary .
The palatine guard , on the other hand, was known as a military unit created in 1850 by Pius IX . Its mission was to defend Vatican City and the Papal States . In 1970 , Pope Paul VI ordered the dissolution of this body.
The chapel of a palace, finally, is called the palatine chapel . Naples and Palermo , for example, have palatine chapels.
